Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Connect and Visualize Live AlloyDB Data in Databricks Lakehouse Federation with CData Connect Cloud
Use CData Connect Cloud to integrate live AlloyDB data into the Databricks platform and create visualization dashboards with real-time AlloyDB data.
Databricks Lakehouse Federation enables organizations to query and integrate data from multiple sources without requiring data movement. It allows federated queries across databases, data warehouses, and lakehouses, providing a unified interface for data analysis and management within Databricks. When combined with CData Connect Cloud, it enables seamless access to AlloyDB data for data virtualization, while also supporting data lineage and fine-grained access control.
This article explains how to use CData Connect Cloud to establish a live connection to AlloyDB and how to access live AlloyDB data from the Databricks platform.
CData Connect Cloud offers a seamless SQL Server, cloud-to-cloud interface for AlloyDB, enabling you to effortlessly create dashboards and visualizations using live AlloyDB data in Databricks. While building visualizations, Databricks requires SQL queries to retrieve the necessary data. With built-in optimized data processing, CData Connect Cloud pushes all supported SQL operations (such as filters and JOINs) directly to AlloyDB, utilizing server-side processing for fast and efficient data retrieval of AlloyDB data.
Configure AlloyDB connectivity for Databricks in CData Connect Cloud
To work with AlloyDB data in Databricks - Lakehouse Federation, you need to connect to AlloyDB from Connect Cloud and provide user access to the connection.
- Log into Connect Cloud, click Connections and click Add Connection.
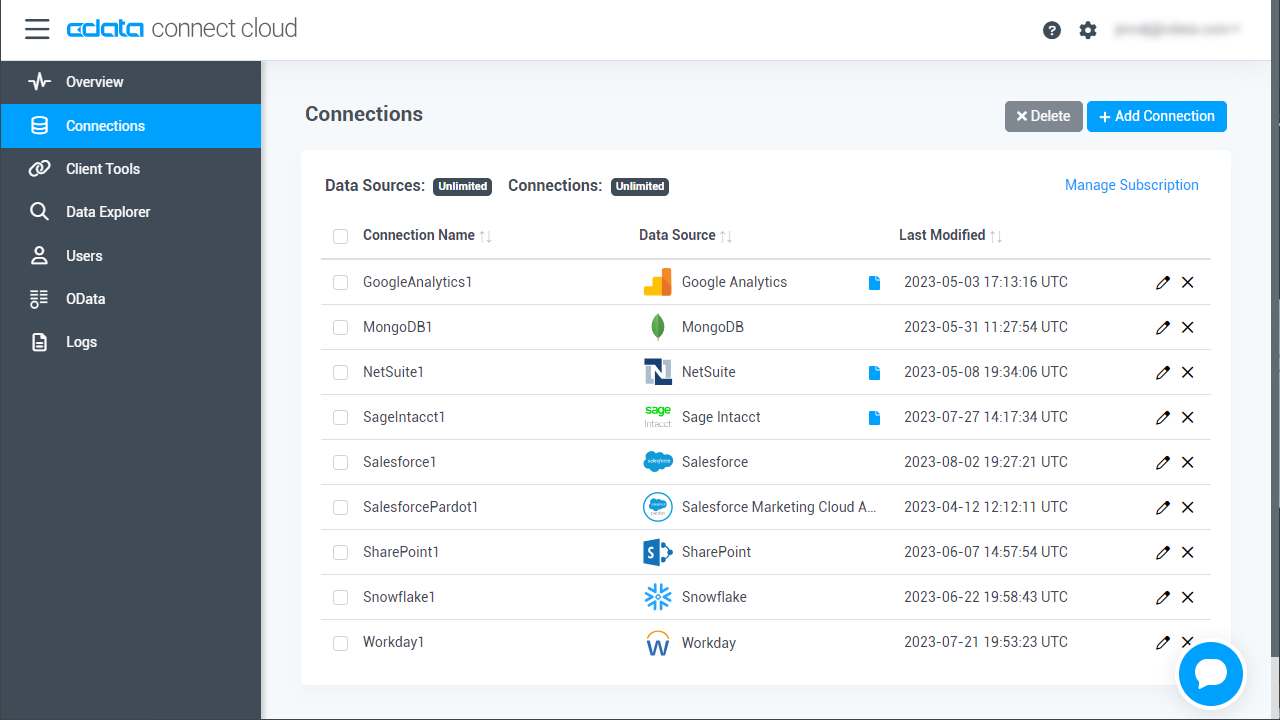
- Select "AlloyDB" from the Add Connection panel.
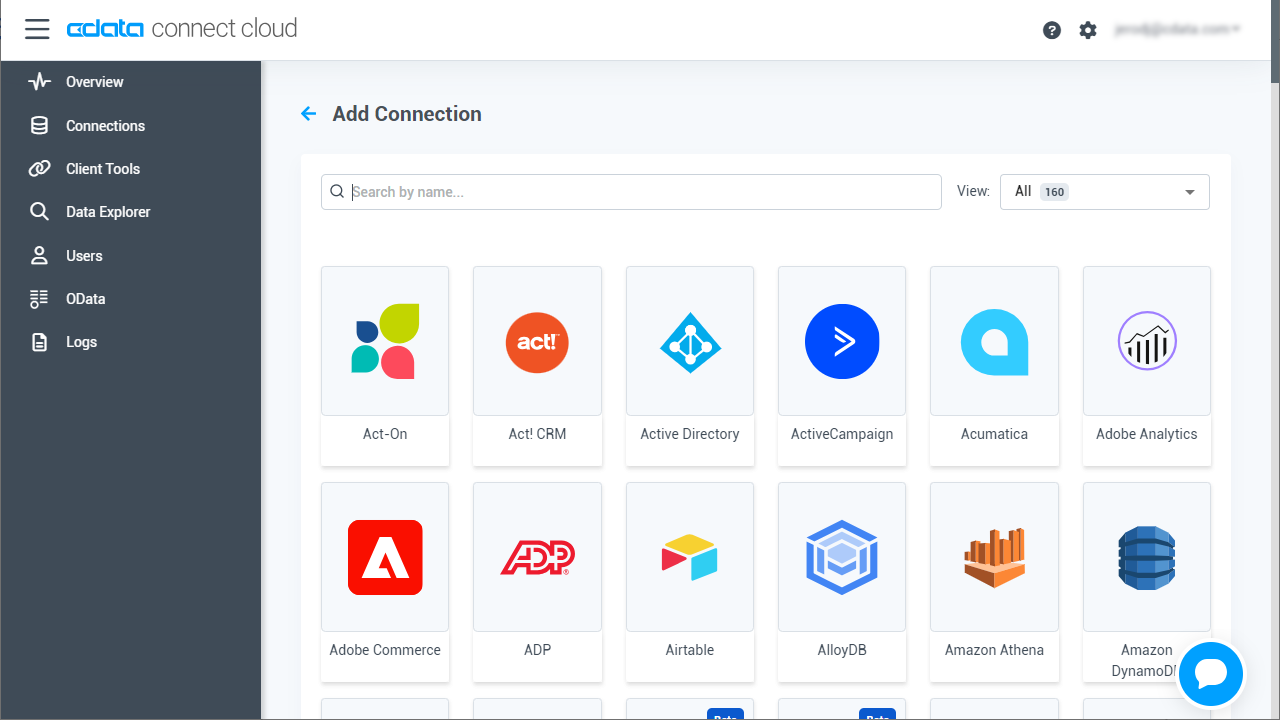
-
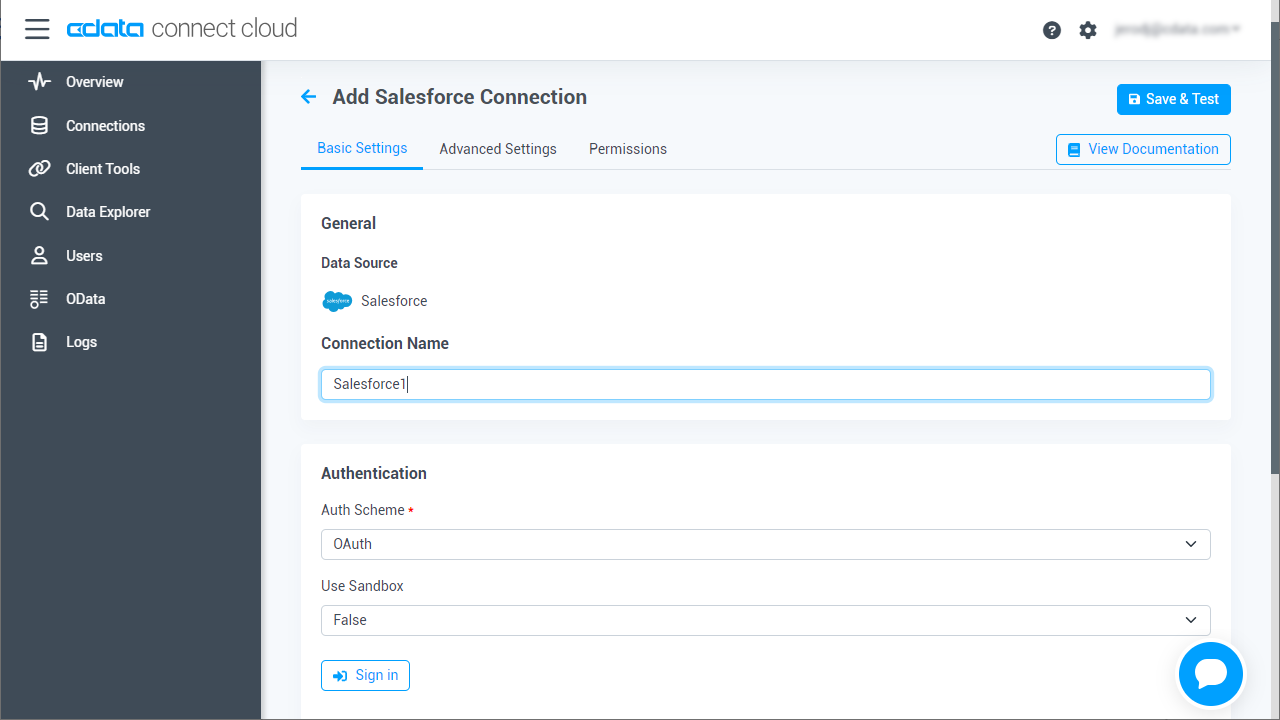
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to AlloyDB.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
- Click Create & Test.
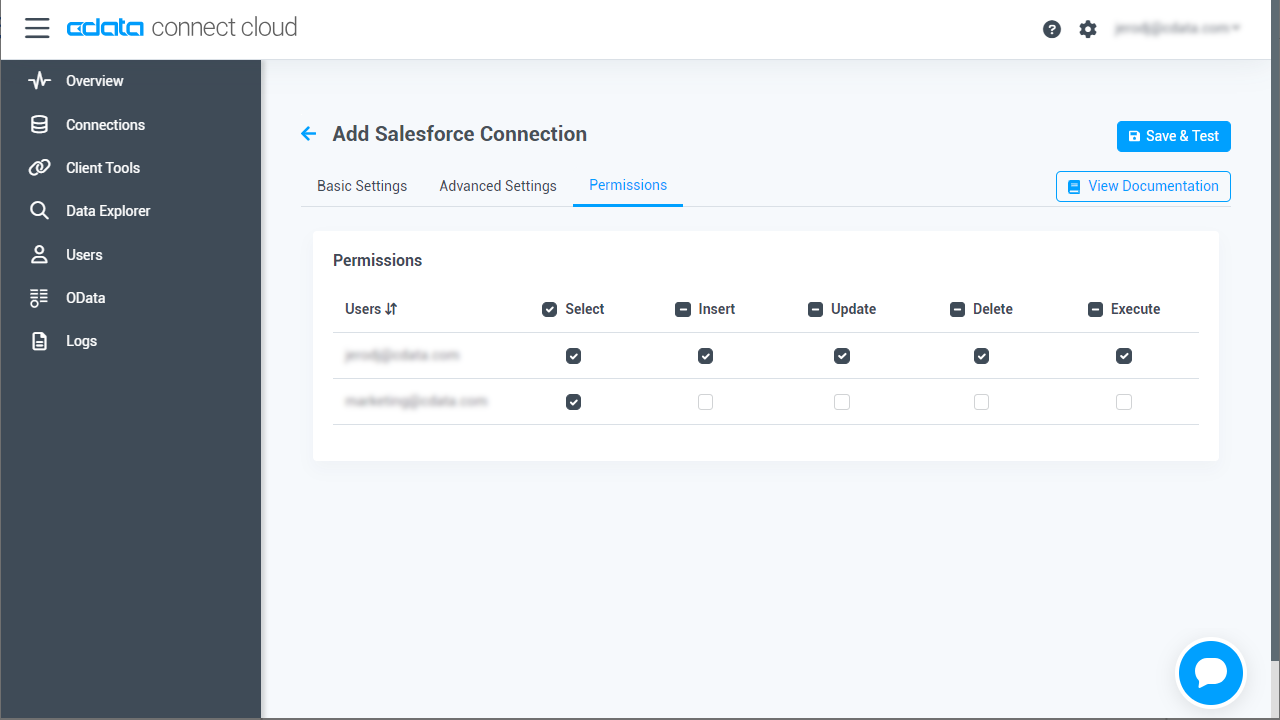
- Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add AlloyDB Connection page and update the User-based permissions
Add a Personal Access Token
If you are connecting from a service, application, platform, or framework that does not support OAuth authentication, you can create a Personal Access Token (PAT) to use for authentication. Best practices would dictate that you create a separate PAT for each service, to maintain granularity of access.
- Click on your username at the top right of the Connect Cloud app and click User Profile
- On the User Profile page, scroll down to the Personal Access Tokens section and click Create PAT
- Give your PAT a name and click Create
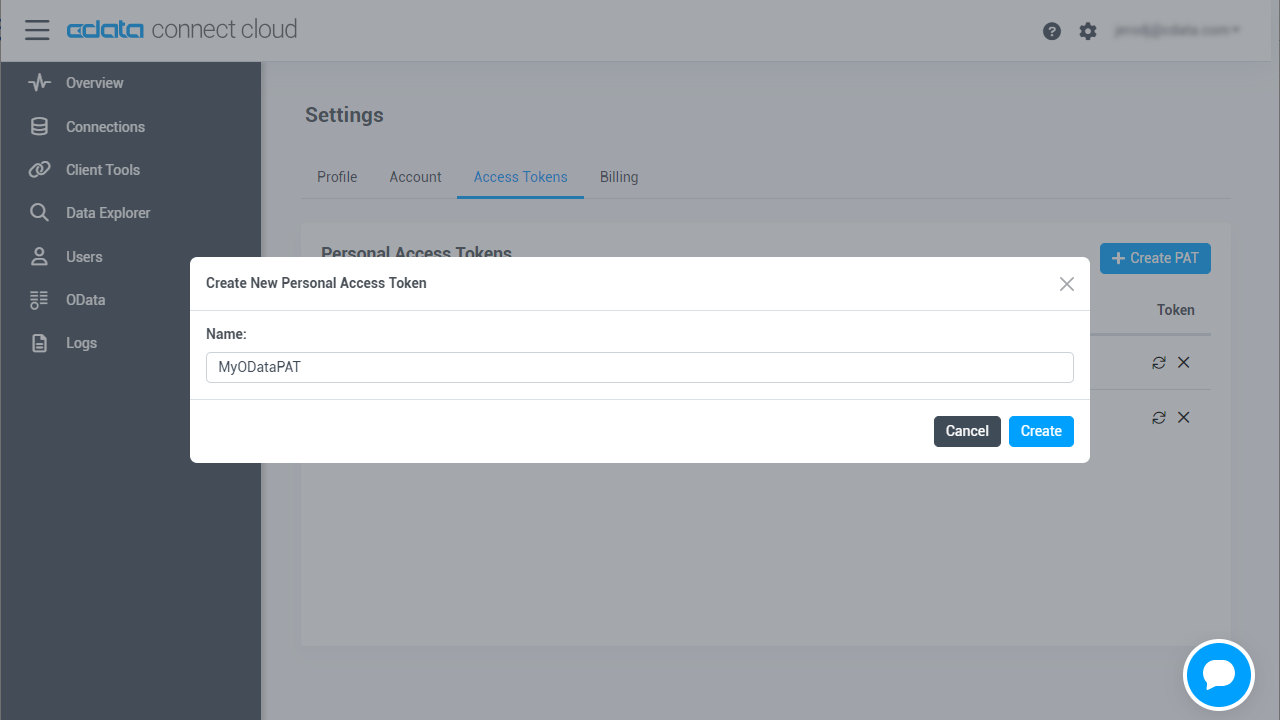
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use
With the connection configured, you are ready to connect to AlloyDB data from Databricks.
Connecting live AlloyDB data in Databricks
Follow these steps to establish a connection from Databricks to the CData Connect Cloud Virtual SQL Server API.
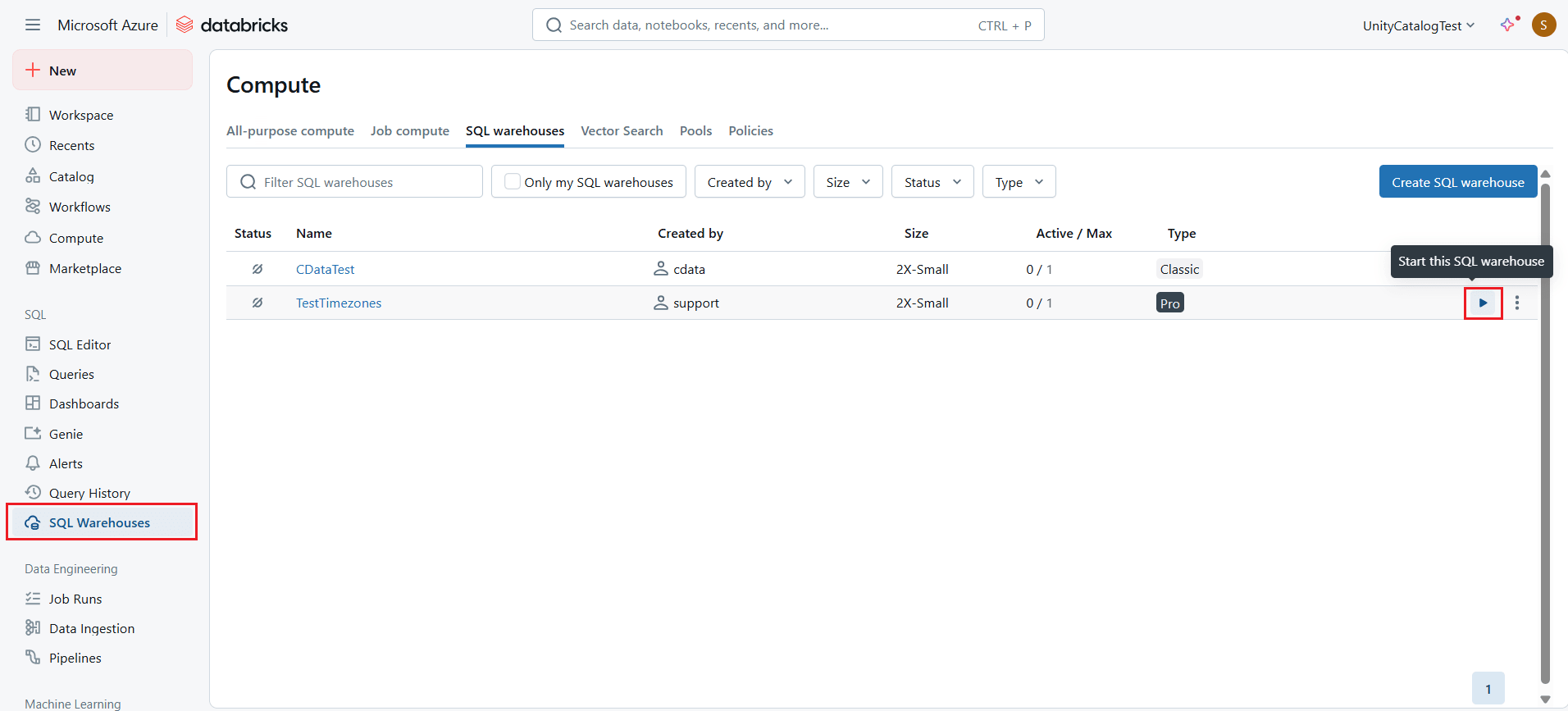
- Log into Databricks.
- Navigate to SQL Warehouses and start any warehouse of your choice.
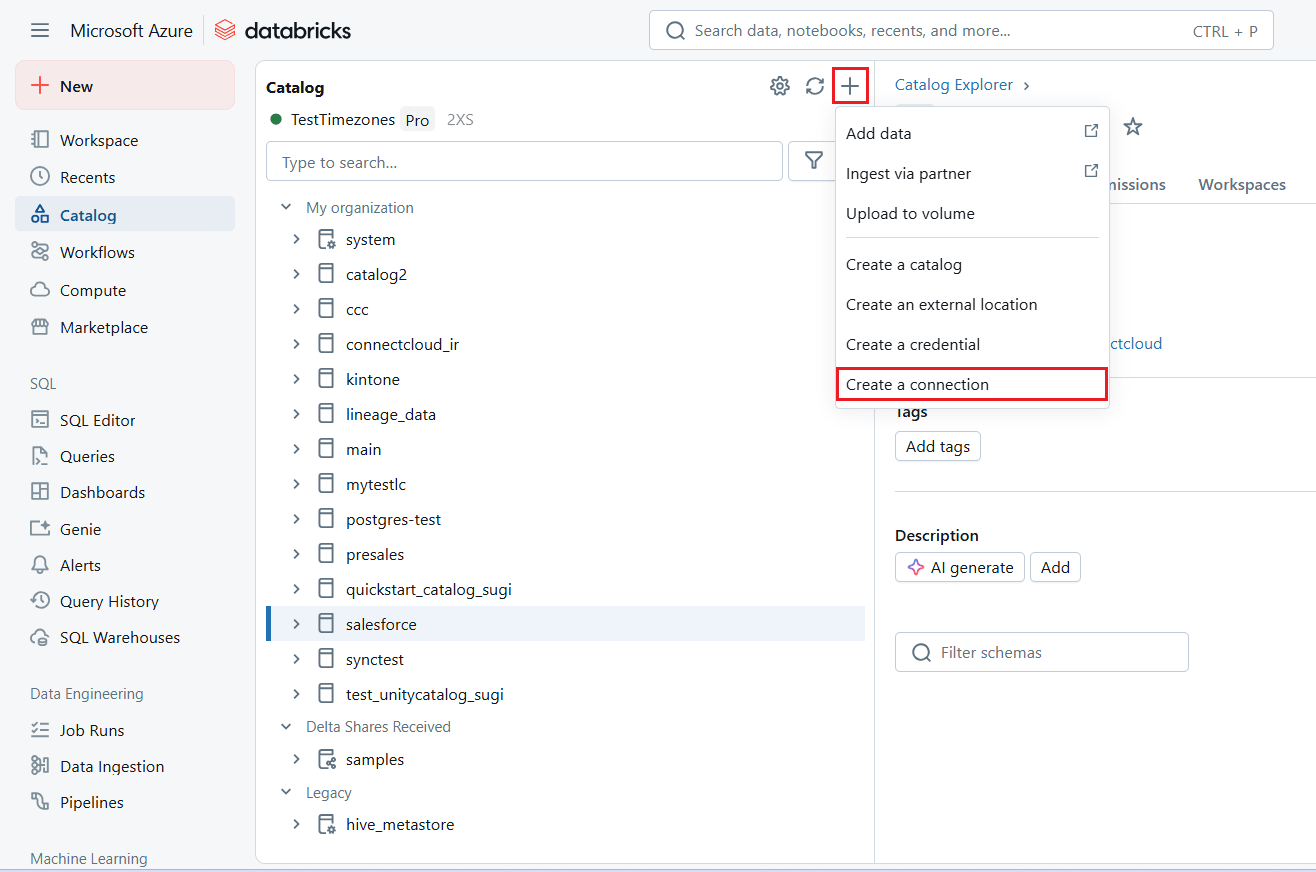
- In the navigation pane, select Catalog. Click and select Create a connection.
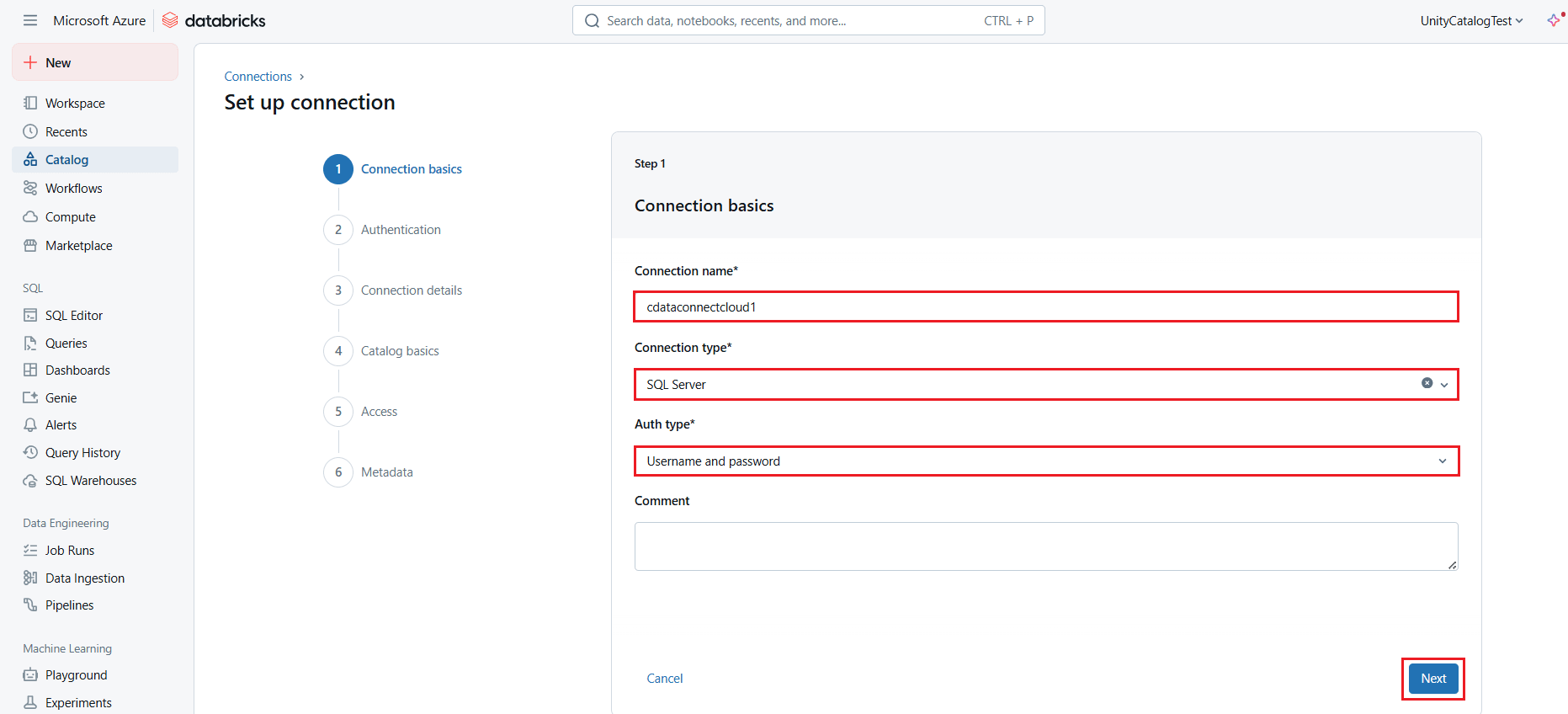
- In the Connection basics section (or Step 1 of Set up connection page), enter the following connection details and click Next:
- Connection name: a user-defined connection name.
- Connection type: select SQL Server from the drop-down list.
- Auth type: select Username and password.
- In the Authentication section (or Step 2), enter the required authentication details, and click Next:
- Host: tds.cdata.com
- Port: 14333
- User: enter your CData Connect Cloud username, displayed in the top-right corner of the CData Connect Cloud interface. For example, test@cdata.com
- Password: enter the PAT generated and copied in the previous section.
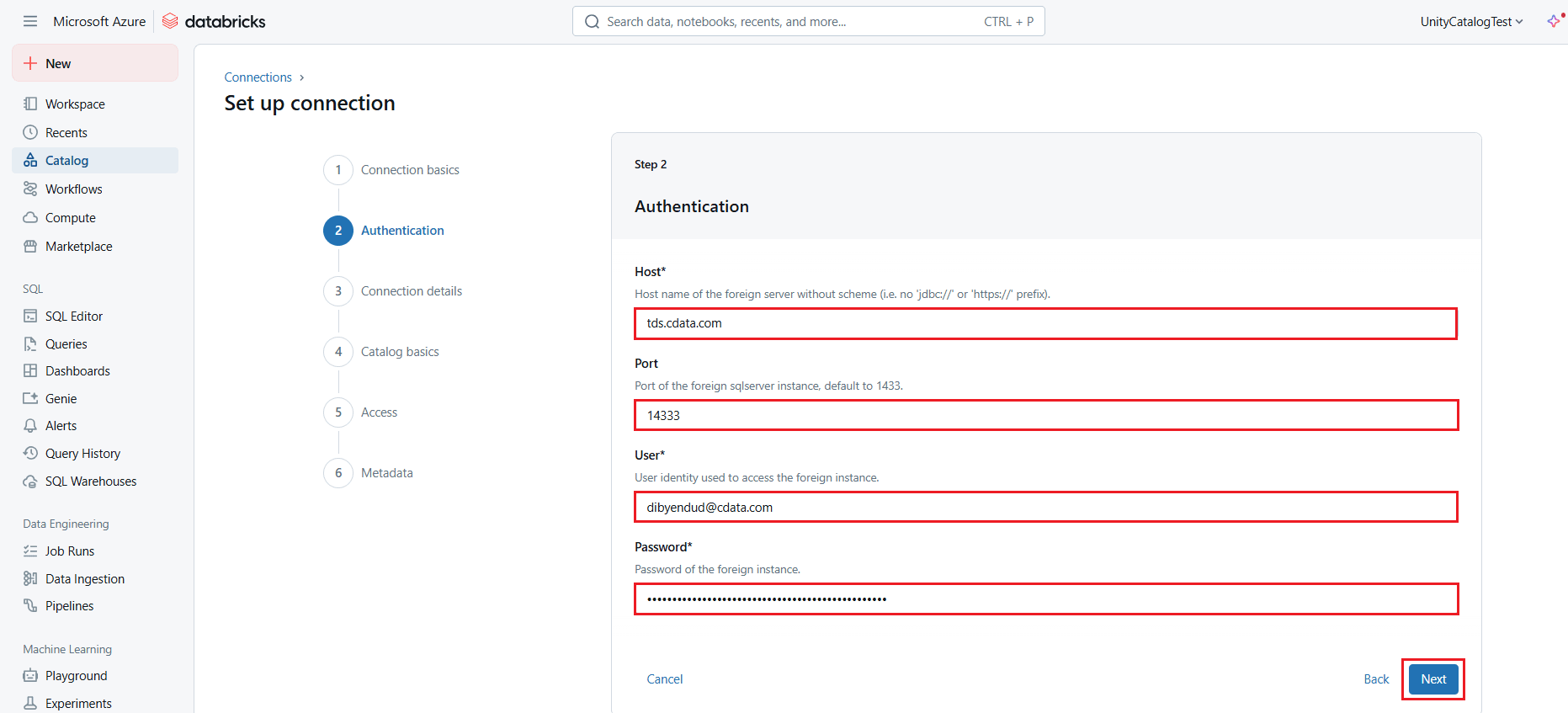
- In the Connection details section (or Step 3), enable the Trust server certificate checkbox and select the appropriate Application intent. Click Create Connection.
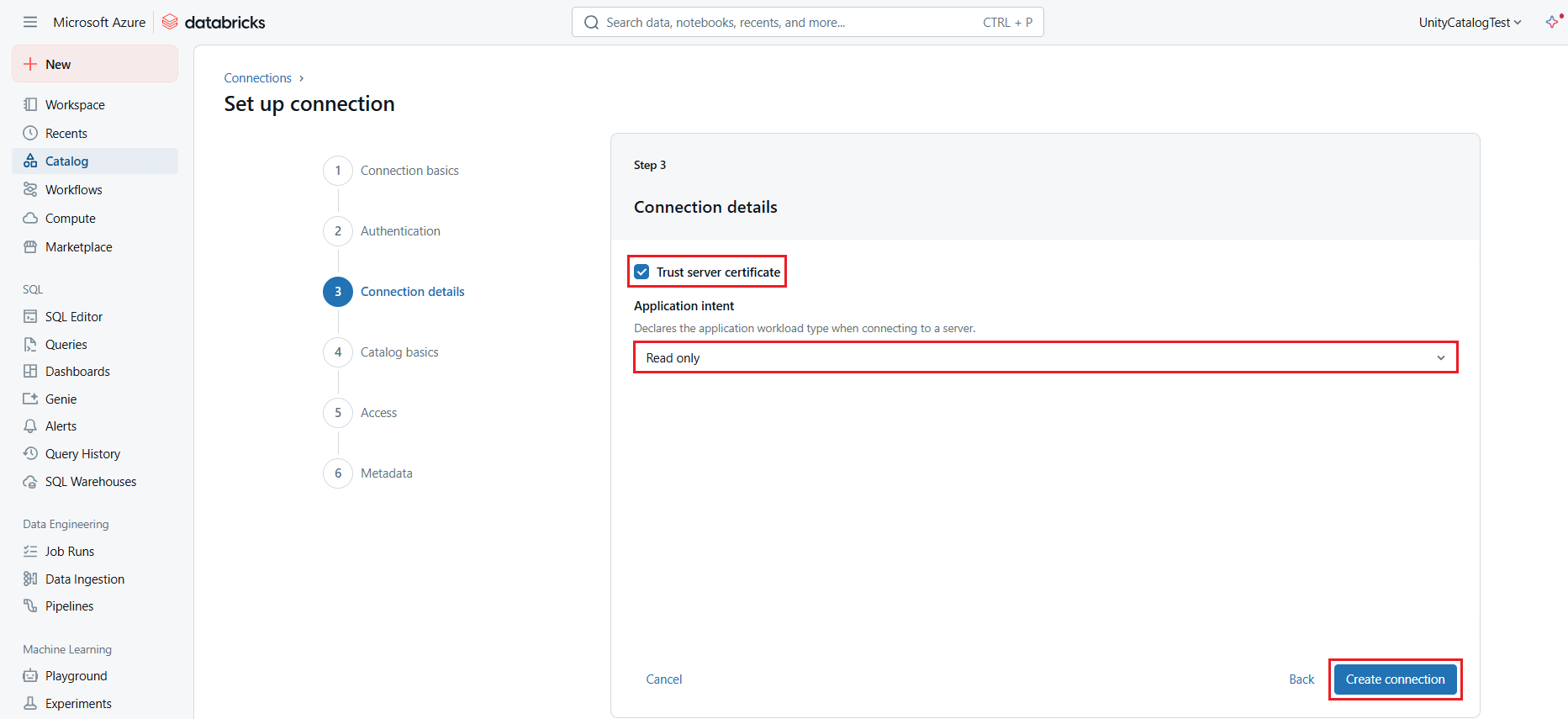
- In the Catalog basics section (or Step 4), enter the required details and click Create catalog:
- Catalog name: enter a name of your choice
- Connection: this will be the Databricks connection you defined earlier
- Database: enter your AlloyDB connection name (for example, AlloyDB1)
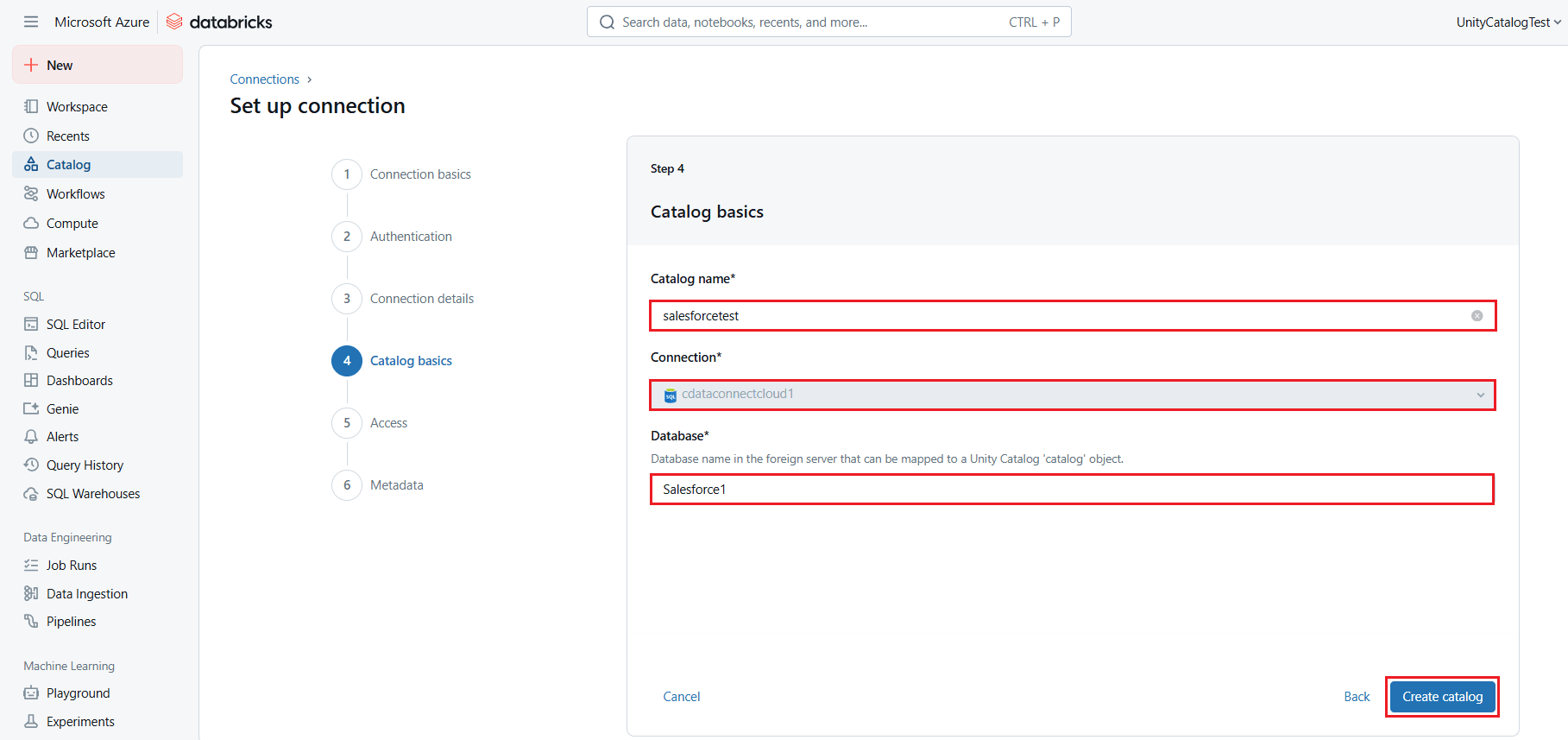
- In the Access section (or Step 5), assign the Workspace, User access rights, and Grant read or edit privileges to the catalog.
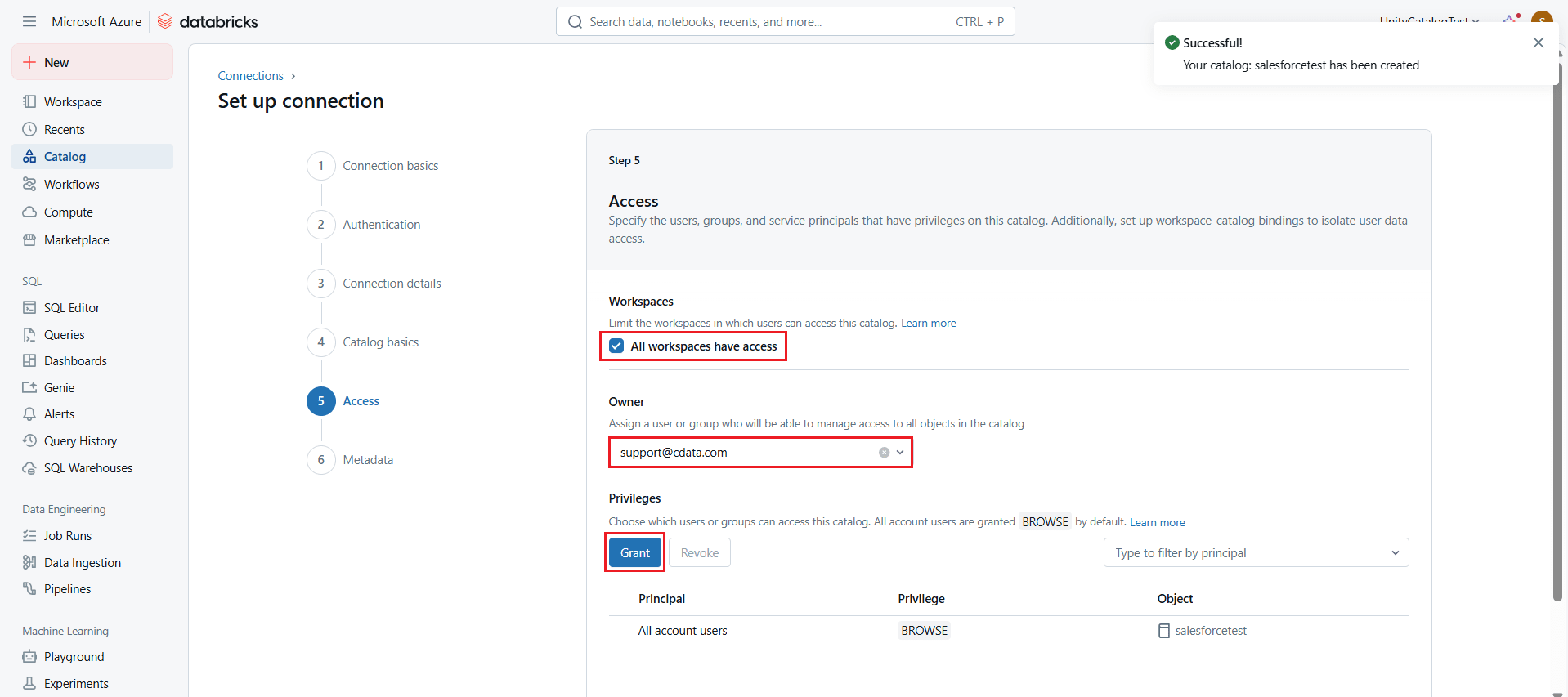
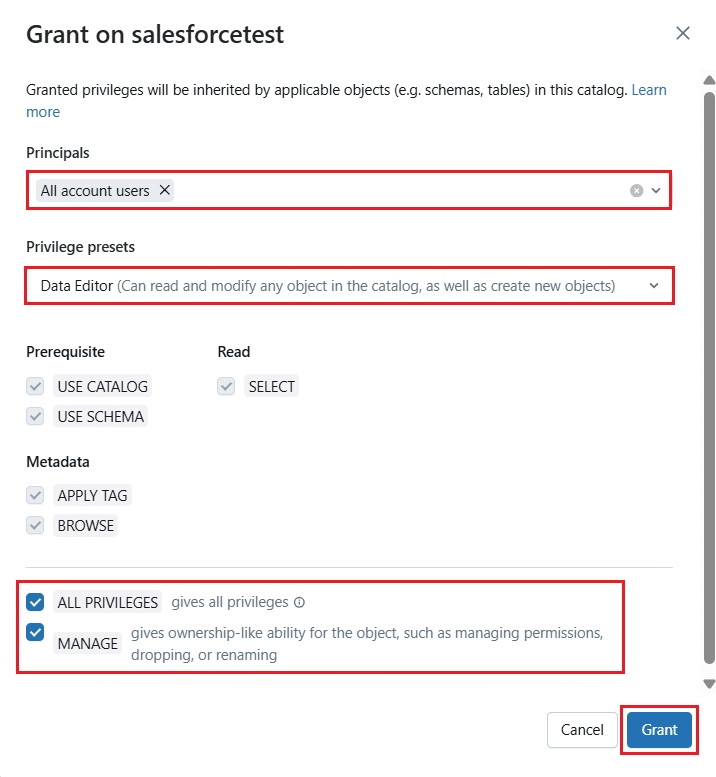
- Click Next > Save to save all the details for the catalog.
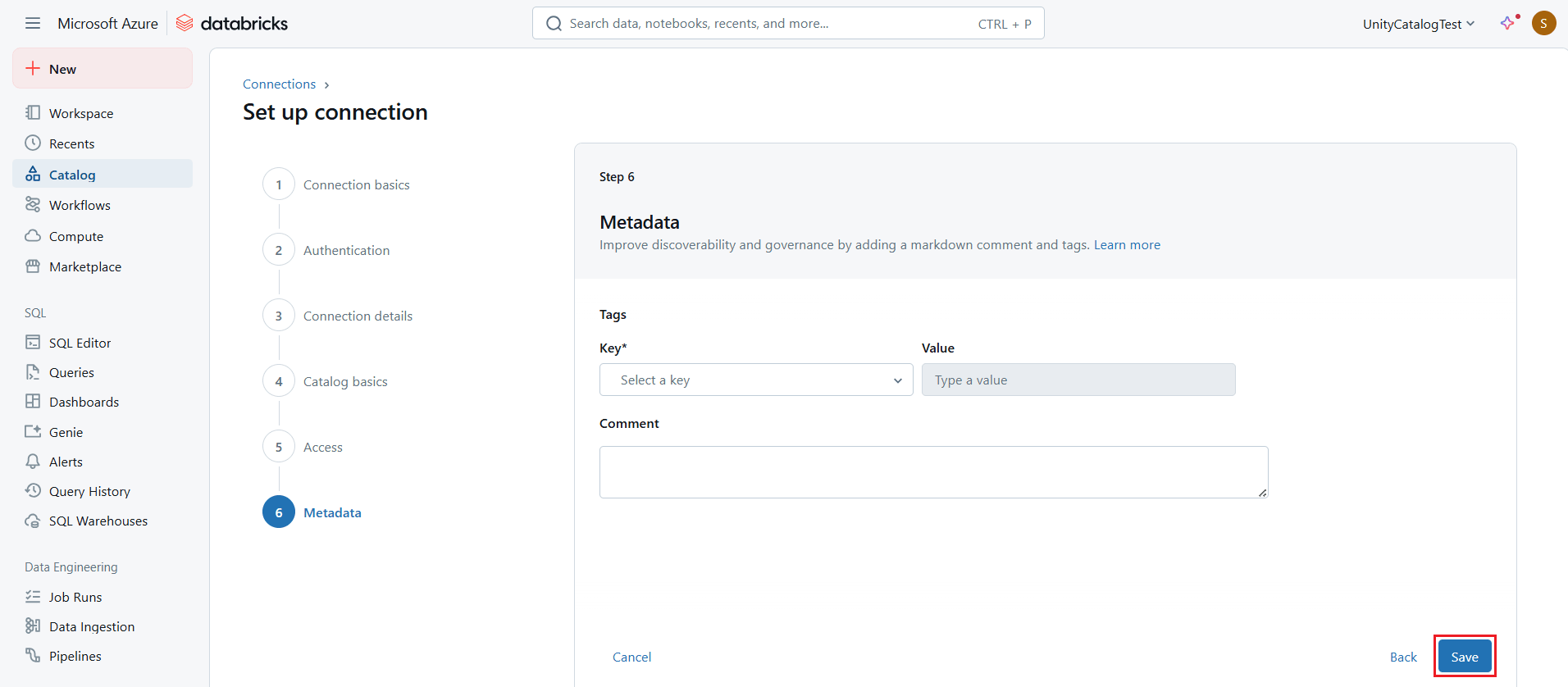
Access the catalog and visualize live AlloyDB data in Databricks
To access the newly created catalog and create a dashboard to visualize live AlloyDB data in Databricks, follow these steps:
- Select the catalog and expand it. A list of tables from AlloyDB will appear on the screen.
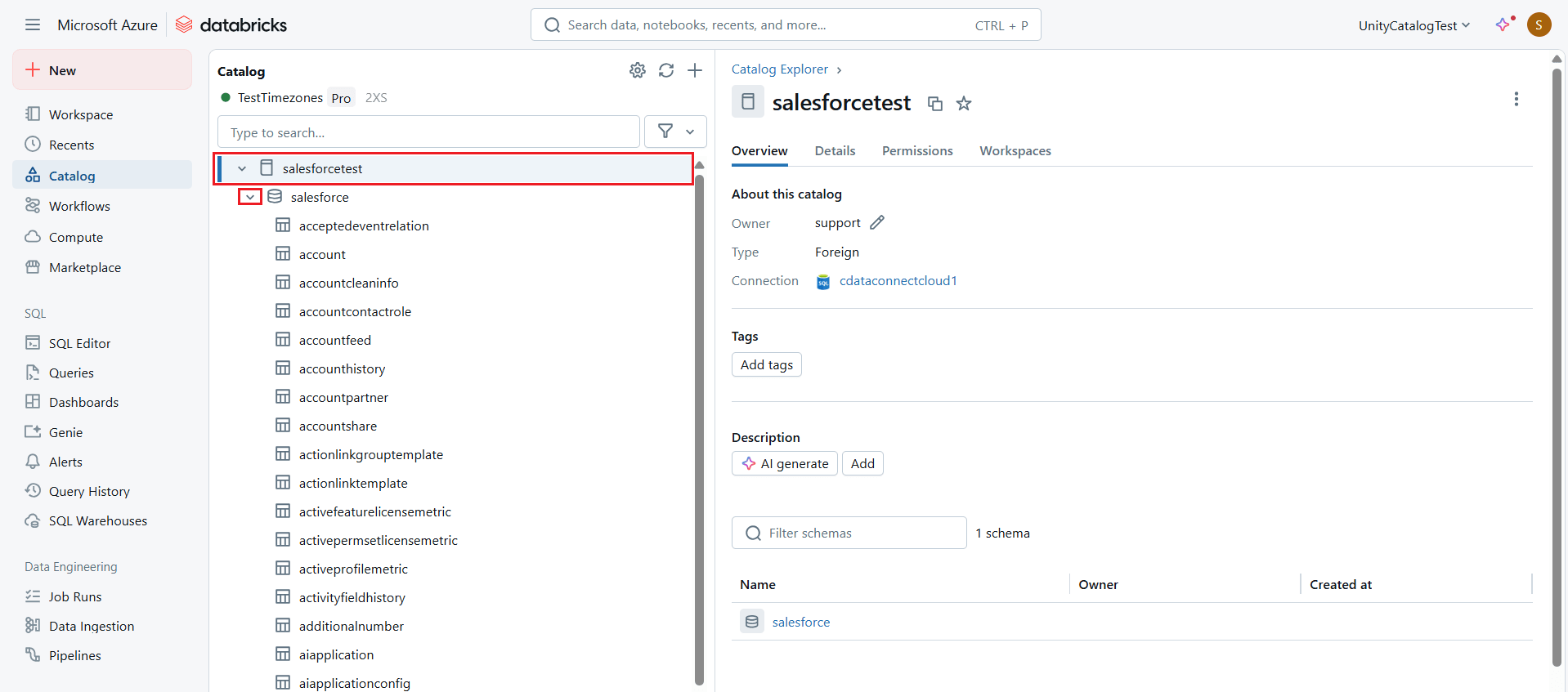
- Choose the desired table and click the Overview tab to view the table metadata.
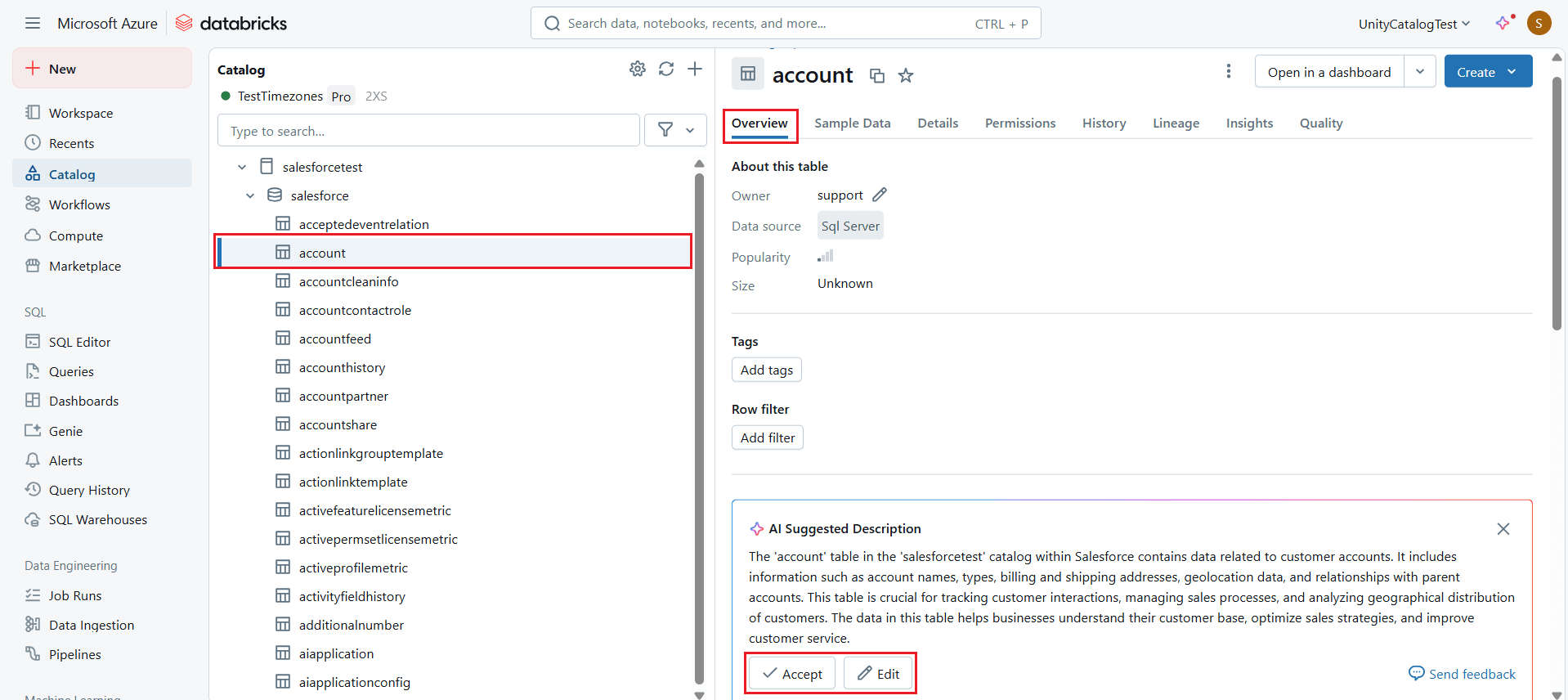

- Click the Sample Data tab to view real-time data in the table.
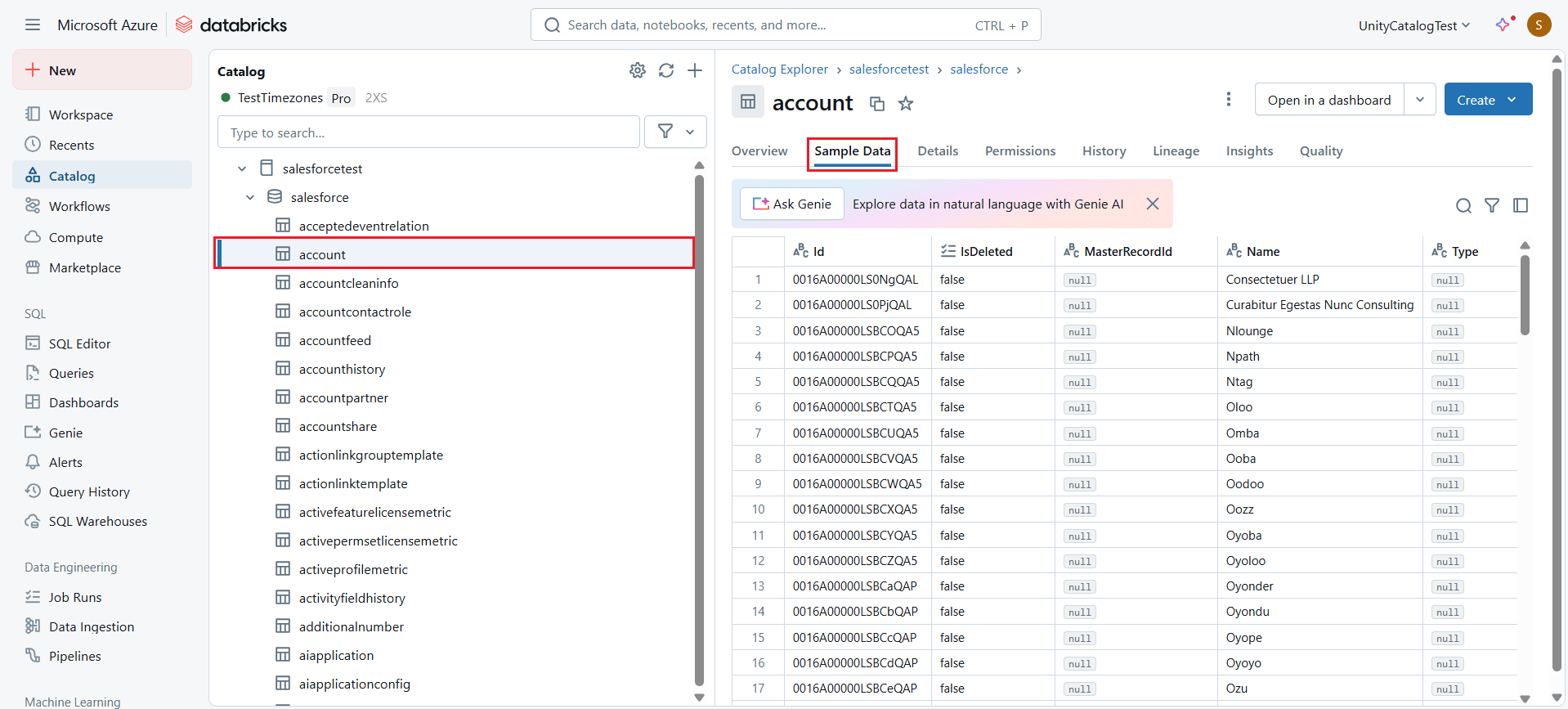
- Now, click Create at the top right corner and select Dashboard.
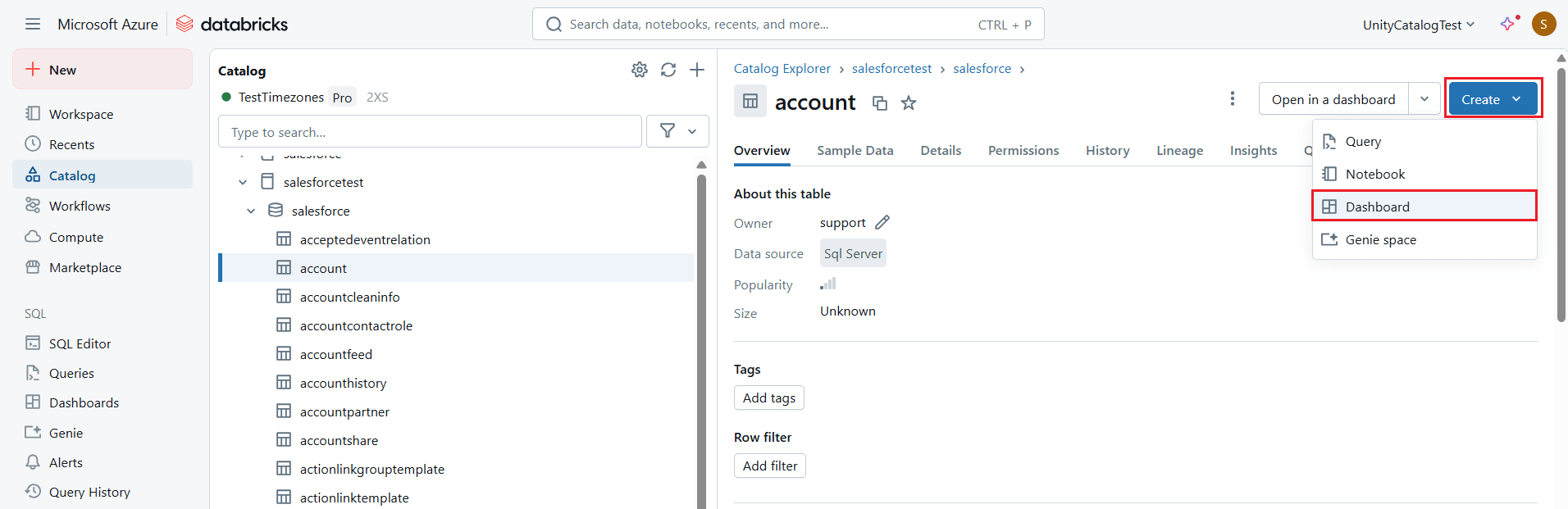
- Manually create a visualization by selecting at least one field in the visualization editor from the widget, or choose one of the visualization options suggested by Databricks AI.
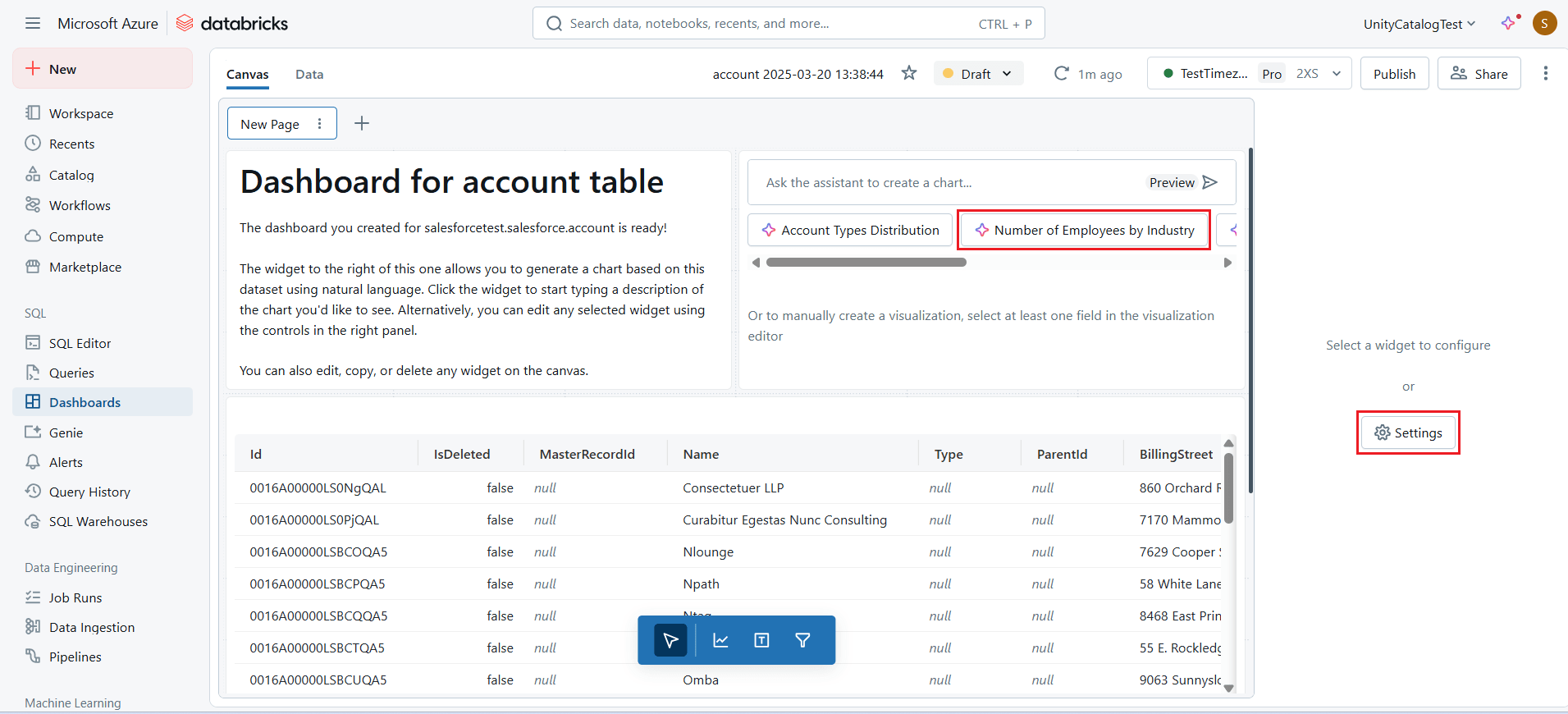
- Once the visualization is created, edit the details in the widget settings of the dashboard.
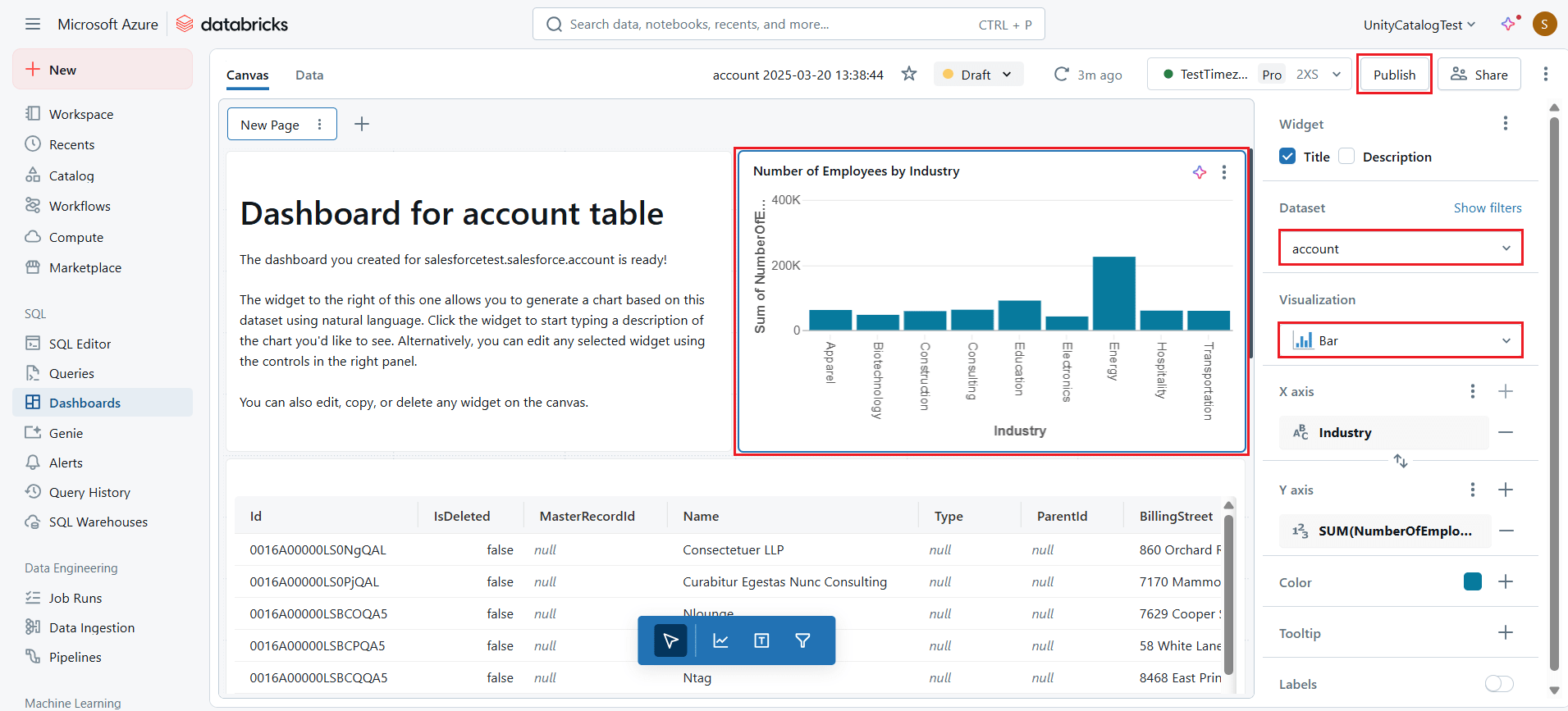
- Click Publish to publish the dashboard report.
Live access to AlloyDB data from cloud applications
At this stage, you have established a direct, cloud-to-cloud connection to live AlloyDB data in Databricks. This enables you to create dashboards to monitor and visualize your data seamlessly.
For more details on accessing live data from over 100 SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources through cloud applications like Databricks, visit our Connect Cloud page. As always, let us know if you have any questions during your evaluation. Our world-class CData Support Team is always available to help!

