Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Excel Spreadsheet Automation with the QUERY Formula
Pull data, automate spreadsheets, and more with the QUERY formula.
The CData Excel Add-In for BigQuery provides formulas that can edit, save, and delete BigQuery data. The following three steps show how you can automate the following task: Search BigQuery data for a user-specified value and then organize the results into an Excel spreadsheet.
About BigQuery Data Integration
CData simplifies access and integration of live Google BigQuery data. Our customers leverage CData connectivity to:
- Simplify access to BigQuery with broad out-of-the-box support for authentication schemes, including OAuth, OAuth JWT, and GCP Instance.
- Enhance data workflows with Bi-directional data access between BigQuery and other applications.
- Perform key BigQuery actions like starting, retrieving, and canceling jobs; deleting tables; or insert job loads through SQL stored procedures.
Most CData customers are using Google BigQuery as their data warehouse and so use CData solutions to migrate business data from separate sources into BigQuery for comprehensive analytics. Other customers use our connectivity to analyze and report on their Google BigQuery data, with many customers using both solutions.
For more details on how CData enhances your Google BigQuery experience, check out our blog post: https://www.cdata.com/blog/what-is-bigquery
Getting Started
The syntax of the CDATAQUERY formula is the following:
=CDATAQUERY(Query, [Connection], [Parameters], [ResultLocation]);
This formula requires three inputs:
- Query: The declaration of the BigQuery data records you want to retrieve or the modifications to be made, written in standard SQL.
Connection: Either the connection name, such as GoogleBigQueryConnection1, or a connection string. The connection string consists of the required properties for connecting to BigQuery data, separated by semicolons.
Google uses the OAuth authentication standard. To access Google APIs on behalf of individual users, you can use the embedded credentials or you can register your own OAuth app.
OAuth also enables you to use a service account to connect on behalf of users in a Google Apps domain. To authenticate with a service account, you will need to register an application to obtain the OAuth JWT values.
In addition to the OAuth values, you will need to specify the DatasetId and ProjectId. See the "Getting Started" chapter of the help documentation for a guide to using OAuth.
- ResultLocation: The cell that the output of results should start from.
Pass Spreadsheet Cells as Inputs to the Query
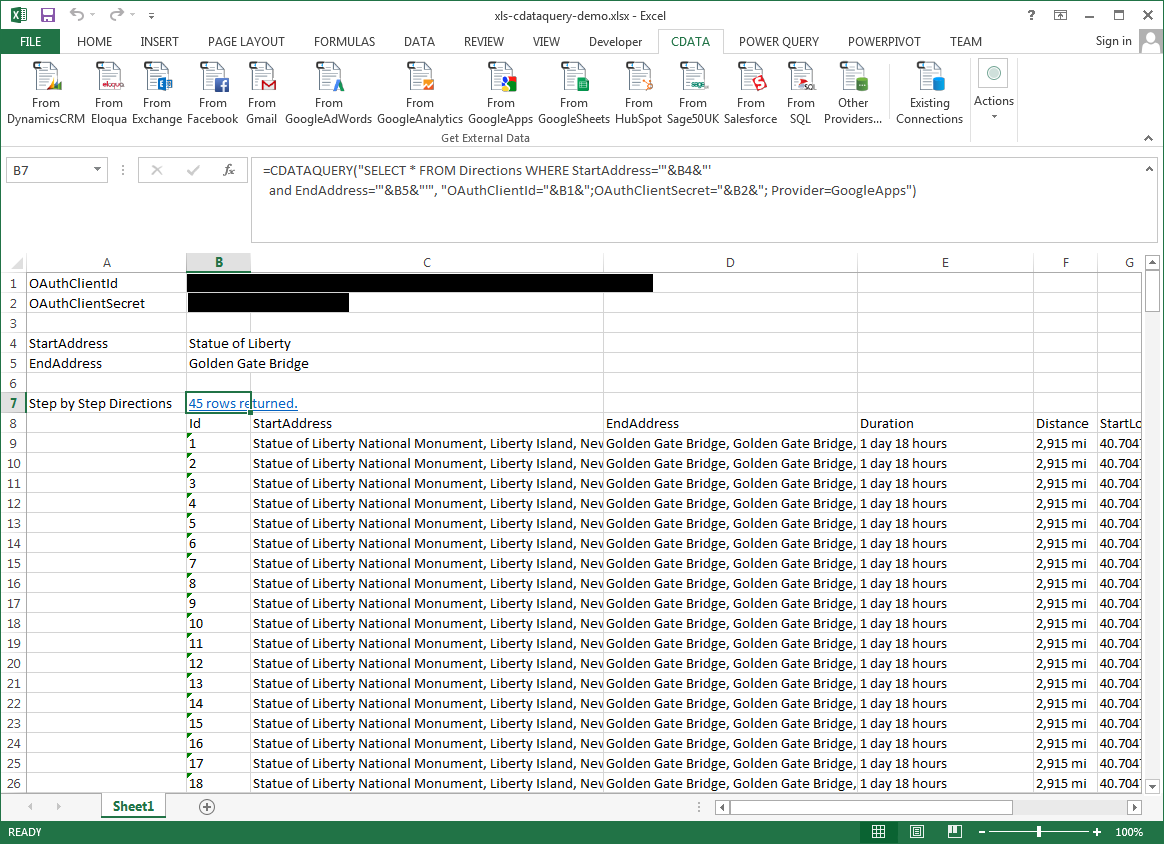
The procedure below results in a spreadsheet that organizes all the formula inputs in the first column.
- Define cells for the formula inputs. In addition to the connection inputs, add another input to define a criterion for a filter to be used to search BigQuery data, such as ShipCity.
- In another cell, write the formula, referencing the cell values from the user input cells defined above. Single quotes are used to enclose values such as addresses that may contain spaces.
- Change the filter to change the data.
![The outputs of the formula. (Google Apps is shown.)]()
=CDATAQUERY("SELECT * FROM Orders WHERE ShipCity = '"&B3&"'","DataSetId="&B1&";ProjectId="&B2&";Provider=GoogleBigQuery",B4)