Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →How to connect to BigQuery Data from IntelliJ
Integrate connectivity to BigQuery data with wizards in IntelliJ.
The CData JDBC Driver for BigQuery enables you to access BigQuery as a JDBC data source, providing integration with rapid development tools in IDEs. This article shows how to use the data source configuration wizard to connect to BigQuery data in IntelliJ.
About BigQuery Data Integration
CData simplifies access and integration of live Google BigQuery data. Our customers leverage CData connectivity to:
- Simplify access to BigQuery with broad out-of-the-box support for authentication schemes, including OAuth, OAuth JWT, and GCP Instance.
- Enhance data workflows with Bi-directional data access between BigQuery and other applications.
- Perform key BigQuery actions like starting, retrieving, and canceling jobs; deleting tables; or insert job loads through SQL stored procedures.
Most CData customers are using Google BigQuery as their data warehouse and so use CData solutions to migrate business data from separate sources into BigQuery for comprehensive analytics. Other customers use our connectivity to analyze and report on their Google BigQuery data, with many customers using both solutions.
For more details on how CData enhances your Google BigQuery experience, check out our blog post: https://www.cdata.com/blog/what-is-bigquery
Getting Started
Create a JBDC Data Source for BigQuery
Follow the steps below to add the driver JAR and define connection properties required to connect to BigQuery data.
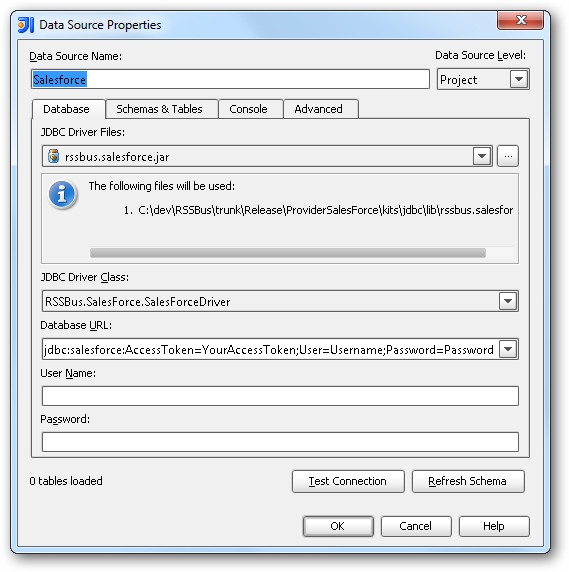
- In the Data Sources window, right-click and then click Add Data Source -> DB Data Source.
In the Data Source Properties dialog that appears, the following properties are required:
- JDBC Driver Files: Click the button next to this menu to add the JDBC Driver file cdata.jdbc.googlebigquery.jar, located in the installation directory.
- JDBC Driver Class: In this menu, select cdata.jdbc.googlebigquery.GoogleBigQueryDriver from the list.
Database URL: Enter the connection URL in the JDBC URL property. The URL must start with jdbc:googlebigquery: and includes connection properties separated with semicolons.
Google uses the OAuth authentication standard. To access Google APIs on behalf of individual users, you can use the embedded credentials or you can register your own OAuth app.
OAuth also enables you to use a service account to connect on behalf of users in a Google Apps domain. To authenticate with a service account, you will need to register an application to obtain the OAuth JWT values.
In addition to the OAuth values, you will need to specify the DatasetId and ProjectId. See the "Getting Started" chapter of the help documentation for a guide to using OAuth.
Built-in Connection String Designer
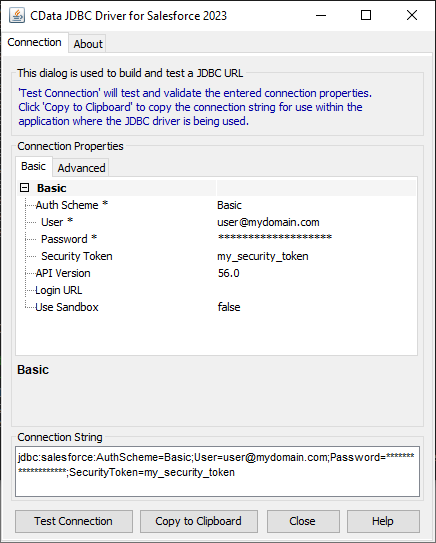
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the BigQuery JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.googlebigquery.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
A typical JDBC URL is the following:
jdbc:googlebigquery:DataSetId=MyDataSetId;ProjectId=MyProjectId;InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH
Edit and Save BigQuery Data
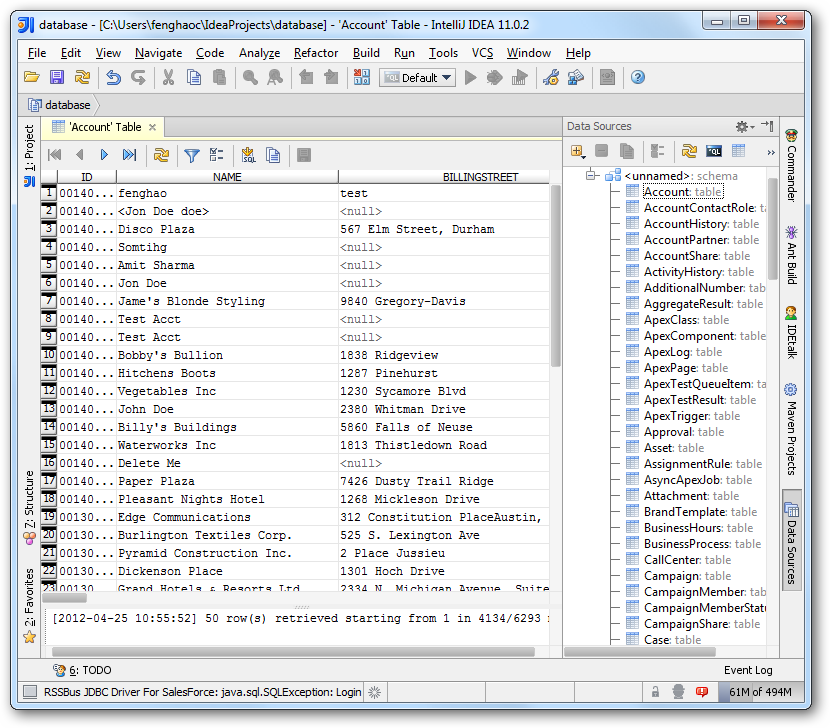
To discover schema information, right-click the data source you just created and click Refresh Tables. To query a table, right-click it and then click Open Tables Editor. You can also modify records in the Table Editor.