Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Import Oracle Eloqua Data into Microsoft Power Query
The CData API Server offers standards-based Web service endpoints that allow a variety of applications to access Oracle Eloqua data. In this article, you will use the OData format to import Oracle Eloqua data into Microsoft Power Query.
The API Server, when paired with the ADO.NET Provider for Oracle Eloqua (or any of 200+ other ADO.NET Providers), enables you to use Web services to connect to and query Oracle Eloqua data. This article details how to import an OData feed of Oracle Eloqua data into Microsoft Power Query.
Set Up the API Server
Follow the steps below to begin producing secure Oracle Eloqua OData services:
Deploy
The API Server runs on your own server. On Windows, you can deploy using the stand-alone server or IIS. On a Java servlet container, drop in the API Server WAR file. See the help documentation for more information and how-tos.
The API Server is also easy to deploy on Microsoft Azure, Amazon EC2, and Heroku.
Connect to Oracle Eloqua
After you deploy the API Server and the ADO.NET Provider for Oracle Eloqua, provide authentication values and other connection properties needed to connect to Oracle Eloqua by clicking Settings -> Connections and adding a new connection in the API Server administration console.
There are two authentication methods available for connecting to Oracle Eloqua: Login and OAuth. The Login method requires you to have the Company, User, and Password of the user.
If you do not have access to the username and password or do not wish to require them, you can use OAuth authentication. OAuth is better suited for allowing other users to access their own data. Using login credentials is better suited for accessing your own data.
You can then choose the Oracle Eloqua entities you want to allow the API Server access to by clicking Settings -> Resources.
Authorize API Server Users
After determining the OData services you want to produce, authorize users by clicking Settings -> Users. The API Server uses authtoken-based authentication and supports the major authentication schemes. Access can also be restricted based on IP address; by default, only connections to the local machine are allowed. You can authenticate as well as encrypt connections with SSL.
Connect to Oracle Eloqua Data from Power Query
Follow the steps below to import tables that can be refreshed on demand:
- Configure the API Server to use a version of the OData protocol that is recognized by Power Query. In the API Server administration console, click Settings -> Server and change the value of the Default Version property to 3.0.
-
From the ribbon in Excel, click Power Query -> From Other Data Sources -> From OData Feed, and enter the OData URL:
https://your-server:8032/api.rsc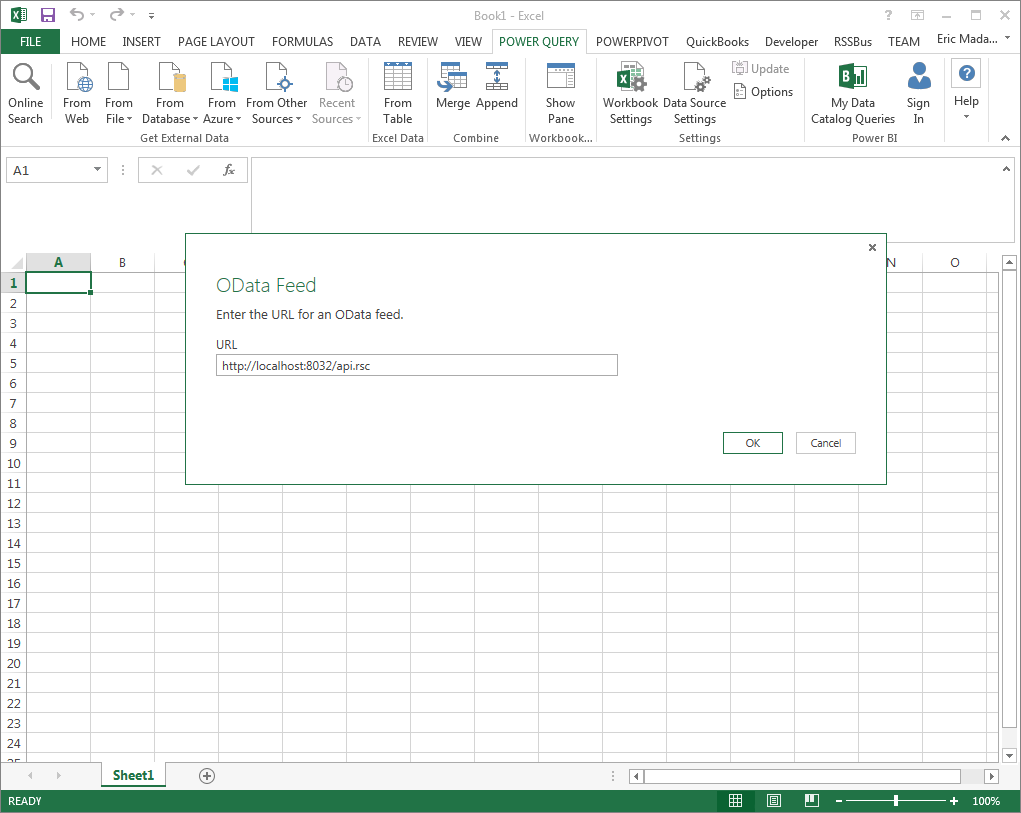
-
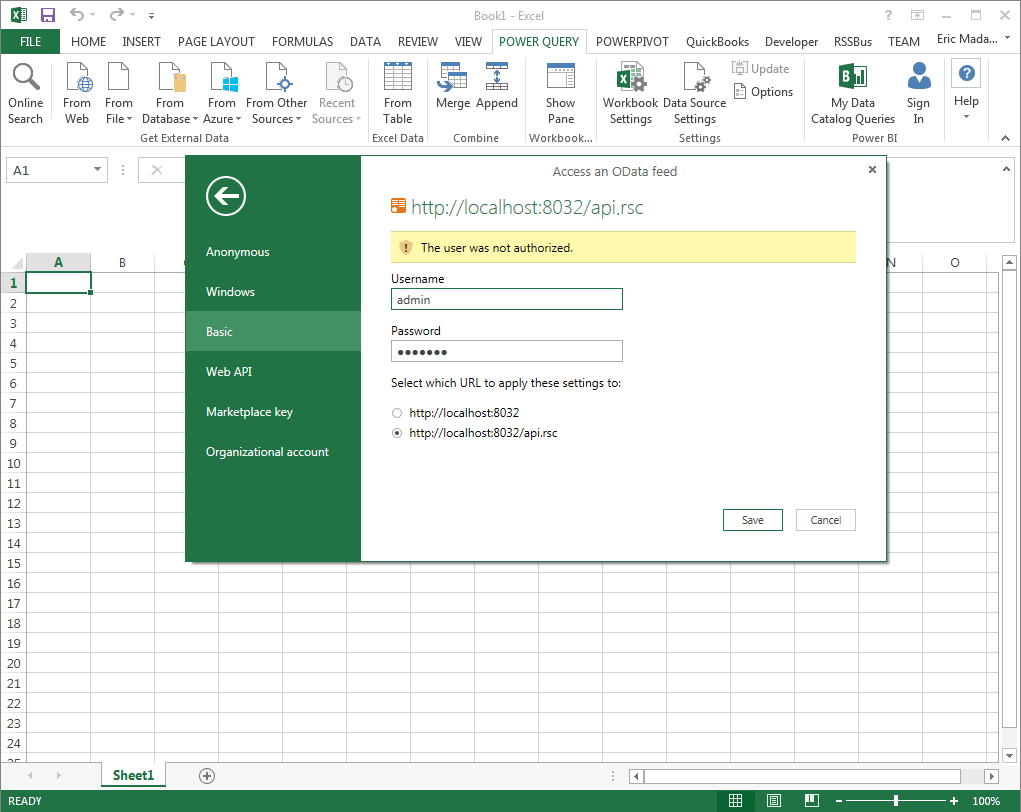
In the next step of the wizard, define authentication credentials and set privacy levels. Select Basic authentication and enter the credentials for a user authorized to make requests. Specify the Username field and enter the user's authtoken in the Password field.
To change the authentication scheme that Power Query will use, click Power Query -> Data Source Settings. Select the OData feed from the list and then click Edit Credential. Select the privacy level from the menu on the Data Source Settings page.
-
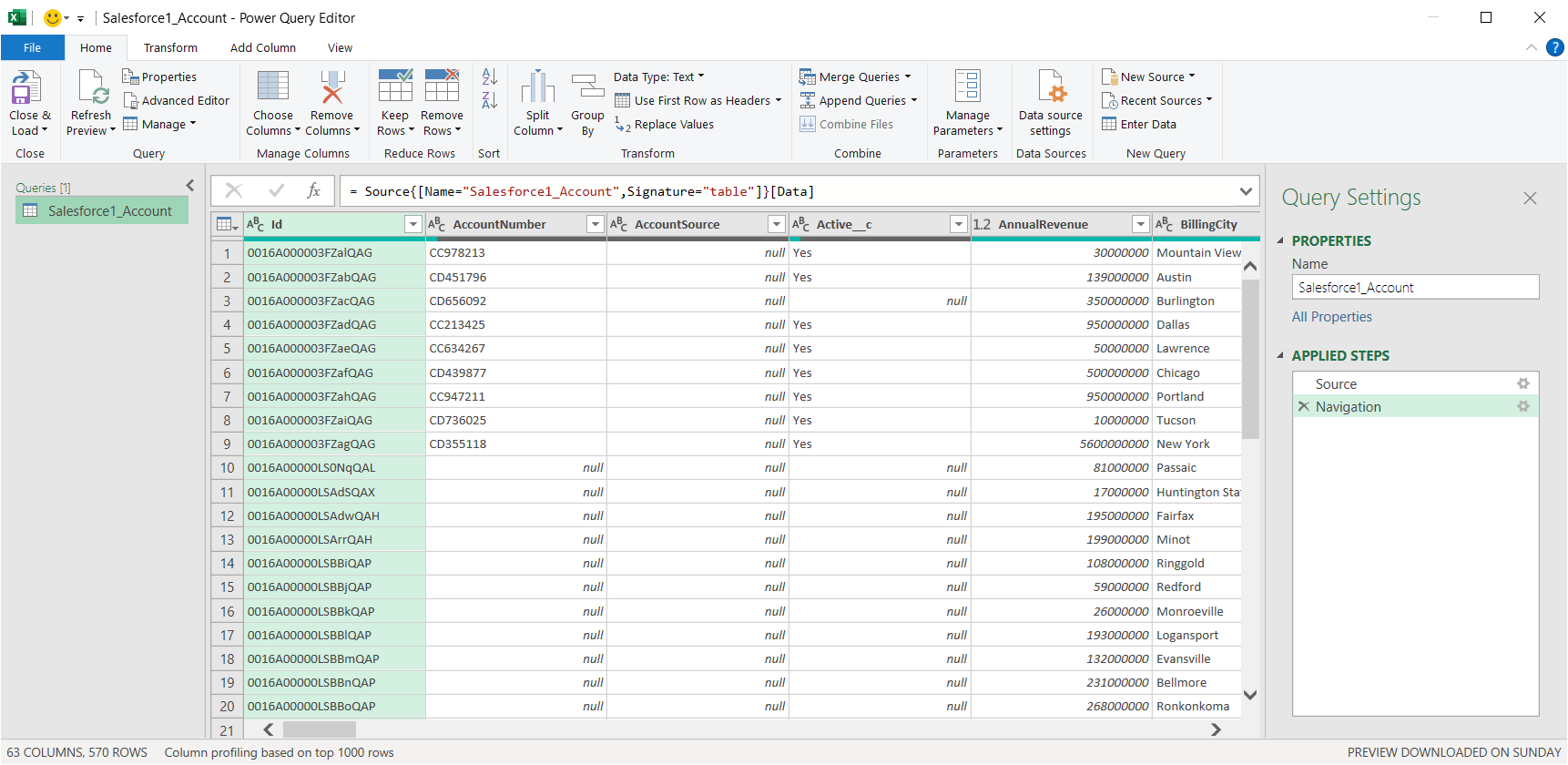
You can now access Oracle Eloqua data in Power Query. In the Navigator expand the node for the OData feed, right-click a table, and click Edit to open the Query Editor. This will display the table data.