Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Use the CData ODBC Driver for Microsoft Exchange in Microsoft Power Query
You can use the CData Microsoft Exchange ODBC Driver with Microsoft Power Query. In this article, you will use the ODBC driver to import Microsoft Exchange data into Microsoft Power Query.
The CData ODBC Driver for Microsoft Exchange enables you to link to Microsoft Exchange data in Microsoft Power Query, ensuring that you see any updates. This article details how to use the ODBC driver to import Microsoft Exchange data into Microsoft Power Query.
Connect to Microsoft Exchange as an ODBC Data Source
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
Specify the User and Password to connect to Exchange. Additionally, specify the address of the Exchange server you are connecting to and the Platform associated with the server.
Import Microsoft Exchange Data
Follow the steps below to import Microsoft Exchange data using standard SQL:
-
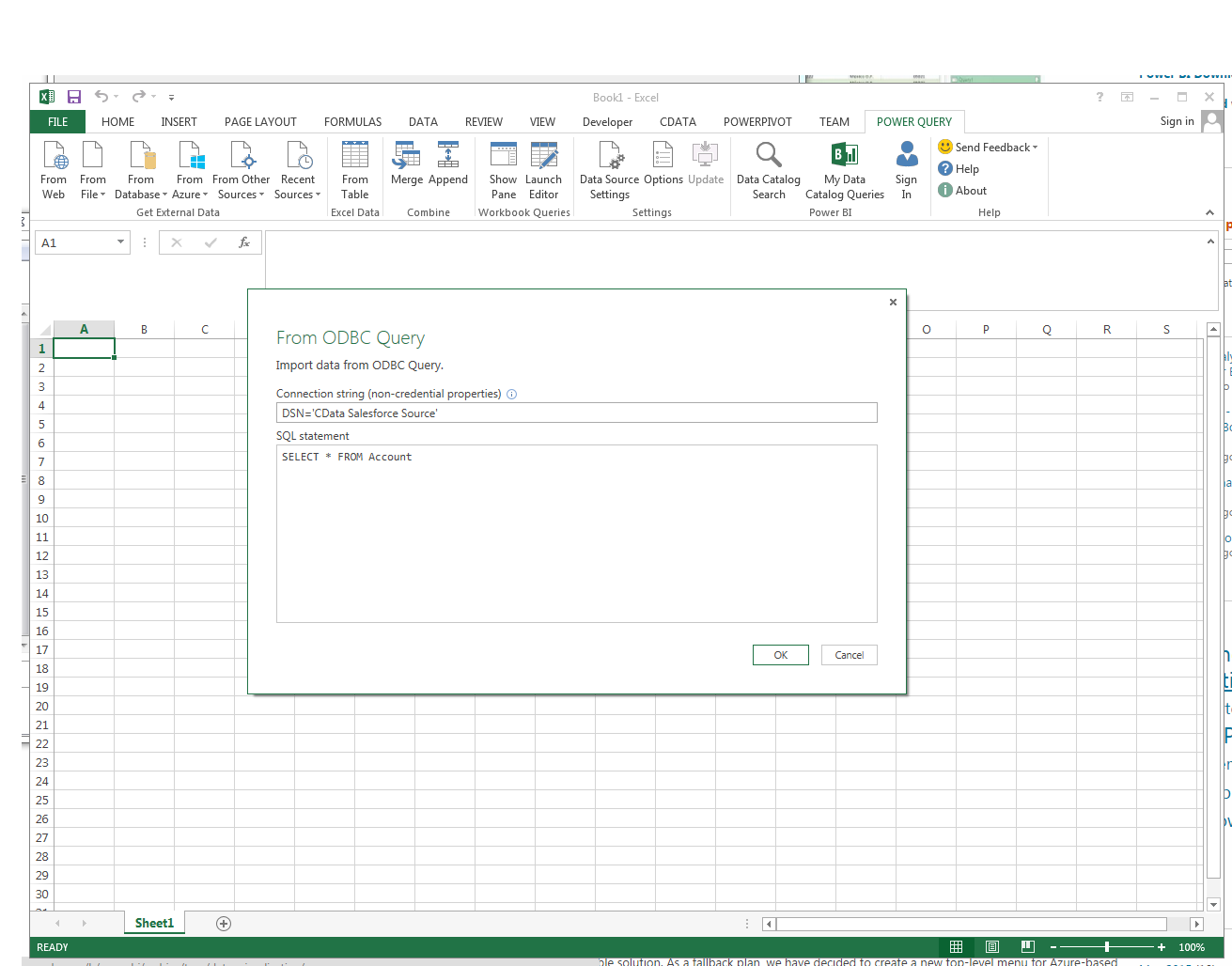
From the ribbon in Excel, click Power Query -> From Other Data Sources -> From ODBC.
- Enter the ODBC connection string. Below is a connection string using the default DSN created when you install the driver:
Provider=MSDASQL.1;Persist Security Info=False;DSN=CData Exchange Source -
Enter the SELECT statement to import data with. For example:
SELECT GivenName, Size FROM Contacts![The ODBC connection string and SELECT query. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
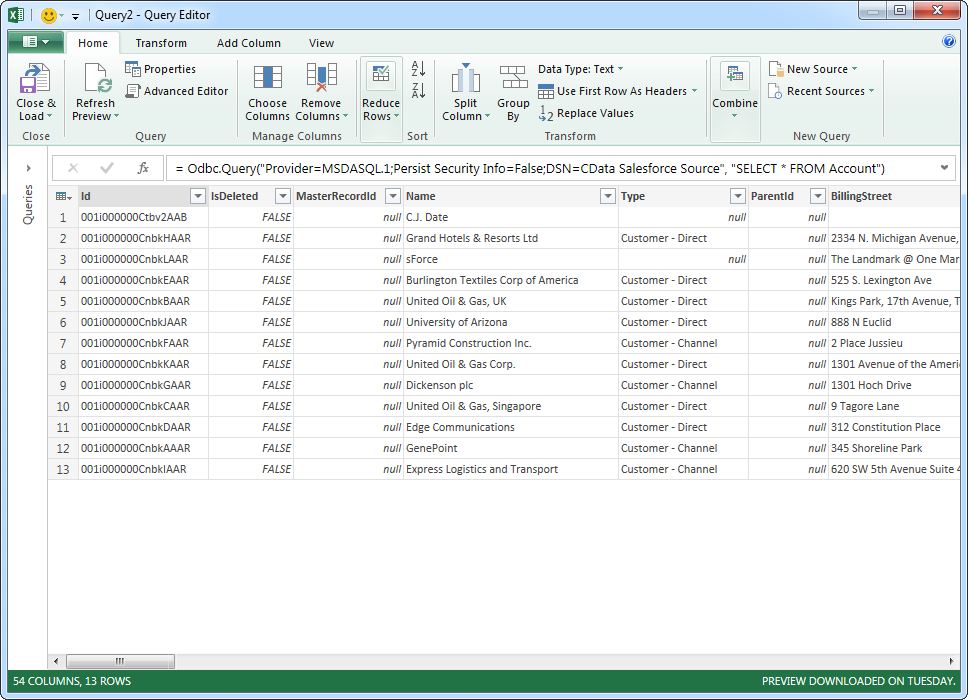
Enter credentials, if required, and click Connect. The results of the query are displayed in the Query Editor Preview. You can combine queries from other data sources or refine the data with Power Query formulas. To load the query to the worksheet, click the Close and Load button.
![Tables loaded in Power Query. (Salesforce is shown.)]()