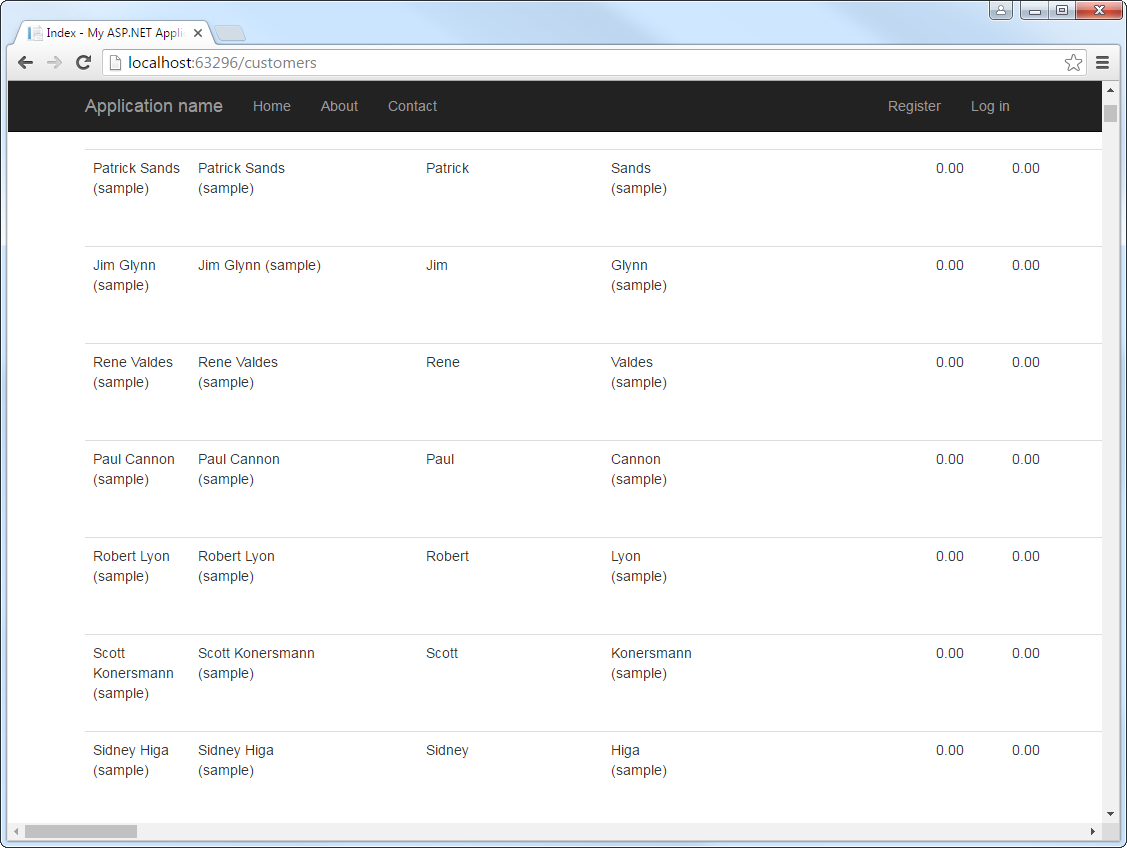
Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Build MVC Applications with Connectivity to Kintone Data
This article shows how to use only the Entity Framework and the CData ADO.NET provider to access Kintone from an ASP.NET MVC application.
In this article, we will guide you through the process of utilizing wizards within Visual Studio to seamlessly integrate the CData ADO.NET Provider for Kintone into a basic MVC (Model, View, Controller) project.
Create the Entity Framework Model
Follow the steps below to save connection properties and map tables to entities in the data model.
- Create a new MVC project in Visual Studio. In this example, the project name is MvcKintoneApp.
If you are using Entity Framework 6, you will need to take the preliminary step of registering the Kintone Entity Framework provider for your project. See the "LINQ and Entity Framework" chapter in the help documentation for a guide.
Note that MVC 3 scaffolding and MVC 4 scaffolding do not support Entity Framework 6. You can use your scaffolding with Entity Framework 6 by upgrading to the latest version of MVC.- To add the .edmx file from the designer, right-click your Models folder and click Add New Item. Select ADO.NET Entity Data Model, name the model, and click Add. In this example, the name of the model is KintoneModel.
- In the Entity Data Model wizard, select the option 'EF Designer from database'. The Entity Data Model wizard is displayed.
- Click New Connection. Select CData Kintone Data Source in the dialog that is displayed.
Specify the required connection string properties.
In addition to the authentication values, set the following parameters to connect to and retrieve data from Kintone:
- Url: The URL of your account.
- GuestSpaceId: Optional. Set this when using a guest space.
Authenticating with Kintone
Kintone supports the following authentication methods.
Using Password Authentication
You must set the following to authenticate:
- User: The username of your account.
- Password: The password of your account.
Using Basic Authentication
If the basic authentication security feature is set on the domain, supply the additional login credentials with BasicAuthUser and BasicAuthPassword. Basic authentication requires these credentials in addition to User and Password.
Using Client SSL
Instead of basic authentication, you can specify a client certificate to authenticate. Set SSLClientCert, SSLClientCertType, SSLClientCertSubject, and SSLClientCertPassword. Additionally, set User and Password to your login credentials.
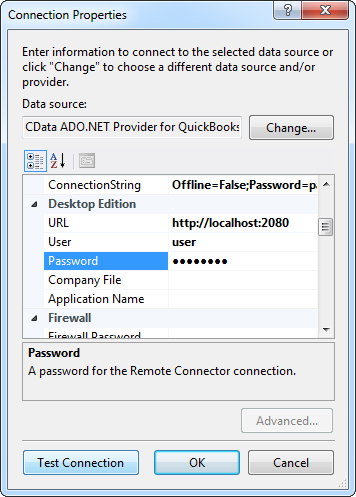
A typical connection string is below:
User=myuseraccount;Password=mypassword;Url=http://subdomain.domain.com;GuestSpaceId=myspaceid![The connection for the model. (QuickBooks is shown.)]()
Name the connection and select whether to include sensitive information, such as connection credentials, in the connection string. For simplicity, this example saves sensitive information in Web.config. The connection settings are saved as KintoneEntities.
![The completed connection step in the ADO.NET Entity Data Model wizard. (A QuickBooks connection is shown.)]()
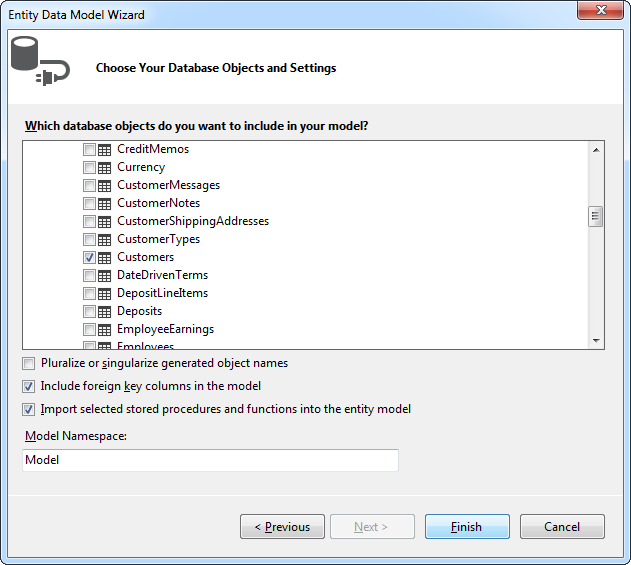
- Select the tables and views you need. In this example, Comments is imported. Also, the option to pluralize object names is deselected in this example. Click Finish to create the .edmx file.
![Tables to be imported into the .edmx file. (QuickBooks is shown.)]()
- Build your project to complete this step.
Scaffold the Controller and Views
Once you've established the model and completed the project build, you can employ ASP.NET Scaffolding wizards to generate both the controller and the views.
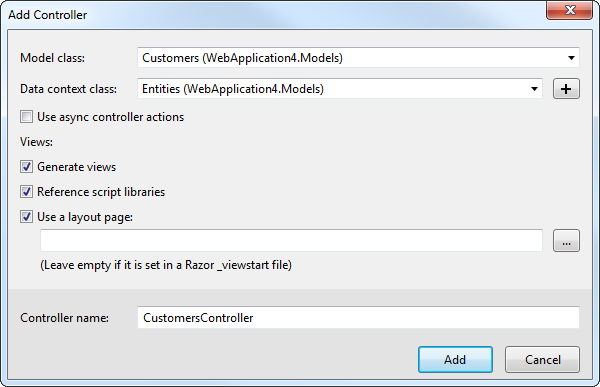
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the controllers folder and click Add -> Controller. Select MVC 5 Controller with views, using Entity Framework.
- In the Add Controller dialog that is then displayed, select the following options:
- Model class: Select a table you imported; for example, Comments.
- Data context class: Select your context class.
-
Leave the default values for the other fields.
![Creating a new controller from an existing entity data model in the Add Controller dialog in MVC 5. (QuickBooks is shown.)]()