Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Connect to Live MongoDB Data in PostGresSQL Interface through CData Connect Cloud
Create a live connection to MongoDB in CData Connect Cloud and connect to your MongoDB data from PostgreSQL.
There are a vast number of PostgreSQL clients available on the Internet. PostgreSQL is a popular interface for data access. When you pair PostgreSQL with CData Connect Cloud, you gain database-like access to live MongoDB data from PostgreSQL. In this article, we walk through the process of connecting to MongoDB data in Connect Cloud and establishing a connection between Connect Cloud and PostgreSQL using a TDS foreign data wrapper (FDW).
CData Connect Cloud provides a pure SQL Server interface for MongoDB, allowing you to query data from MongoDB without replicating the data to a natively supported database. Using optimized data processing out of the box, CData Connect Cloud pushes all supported SQL operations (filters, JOINs, etc.) directly to MongoDB, leveraging server-side processing to return the requested MongoDB data quickly.
About MongoDB Data Integration
Accessing and integrating live data from MongoDB has never been easier with CData. Customers rely on CData connectivity to:
- Access data from MongoDB 2.6 and above, ensuring broad usability across various MongoDB versions.
- Easily manage unstructured data thanks to flexible NoSQL (learn more here: Leading-Edge Drivers for NoSQL Integration).
- Leverage feature advantages over other NoSQL drivers and realize functional benefits when working with MongoDB data (learn more here: A Feature Comparison of Drivers for NoSQL).
MongoDB's flexibility means that it can be used as a transactional, operational, or analytical database. That means CData customers use our solutions to integrate their business data with MongoDB or integrate their MongoDB data with their data warehouse (or both). Customers also leverage our live connectivity options to analyze and report on MongoDB directly from their preferred tools, like Power BI and Tableau.
For more details on MongoDB use case and how CData enhances your MongoDB experience, check out our blog post: The Top 10 Real-World MongoDB Use Cases You Should Know in 2024.
Getting Started
Connect to MongoDB in Connect Cloud
CData Connect Cloud uses a straightforward, point-and-click interface to connect to data sources.
- Log into Connect Cloud, click Connections and click Add Connection
- Select "MongoDB" from the Add Connection panel
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to MongoDB.
Set the Server, Database, User, and Password connection properties to connect to MongoDB. To access MongoDB collections as tables you can use automatic schema discovery or write your own schema definitions. Schemas are defined in .rsd files, which have a simple format. You can also execute free-form queries that are not tied to the schema.
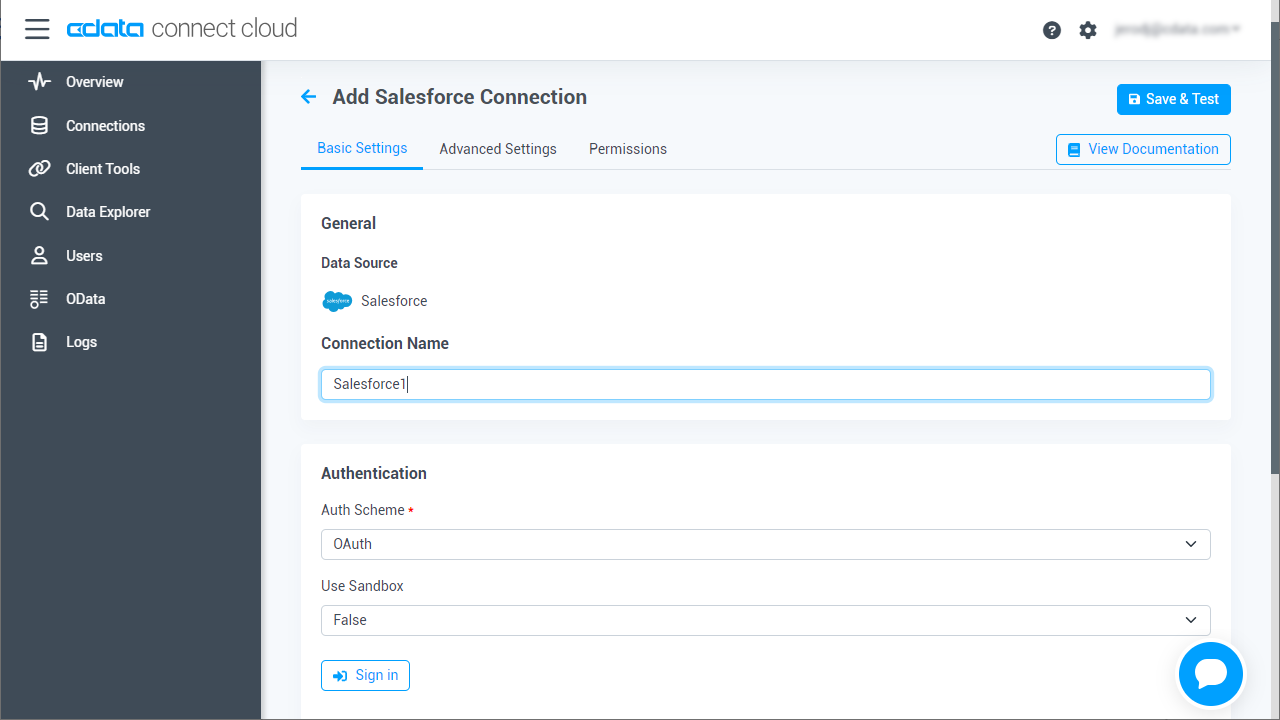
![Configuring a connection (Salesforce is shown) Configuring a connection (Salesforce is shown)]()
- Click Create & Test
-
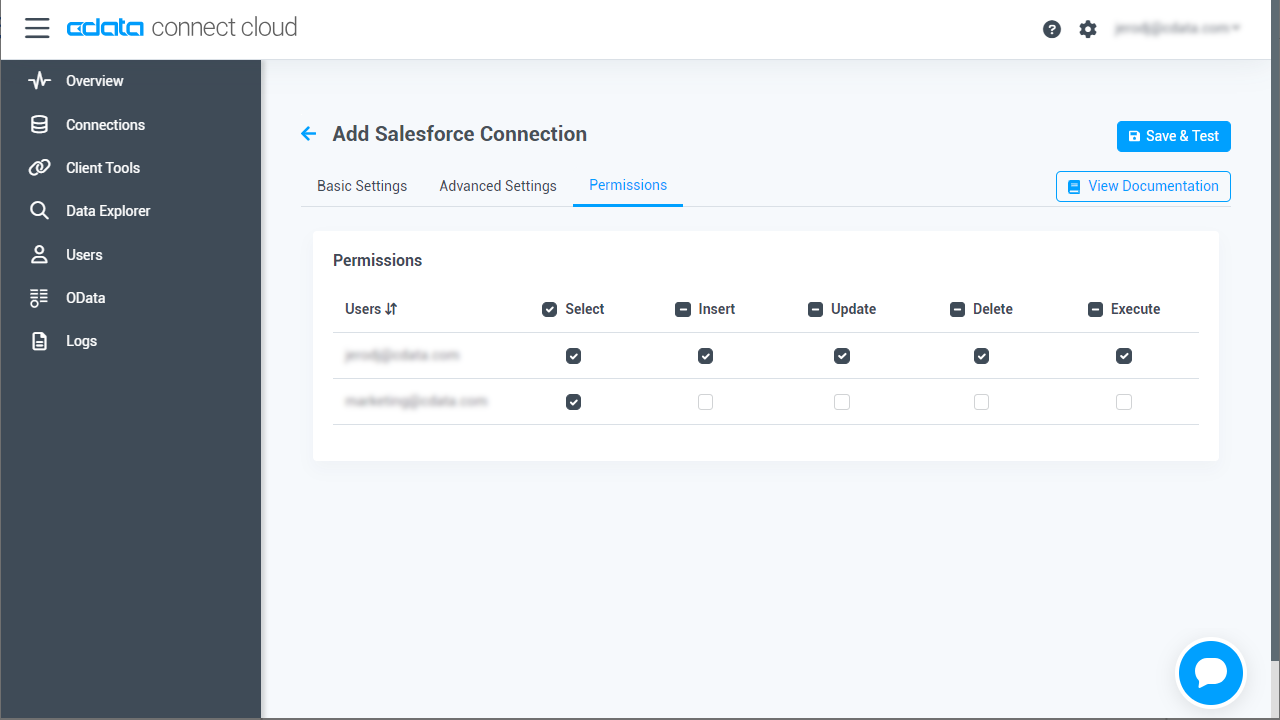
Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add MongoDB Connection page and update the User-based permissions.
![Updating permissions Updating permissions]()
Add a Personal Access Token
If you are connecting from a service, application, platform, or framework that does not support OAuth authentication, you can create a Personal Access Token (PAT) to use for authentication. Best practices would dictate that you create a separate PAT for each service, to maintain granularity of access.
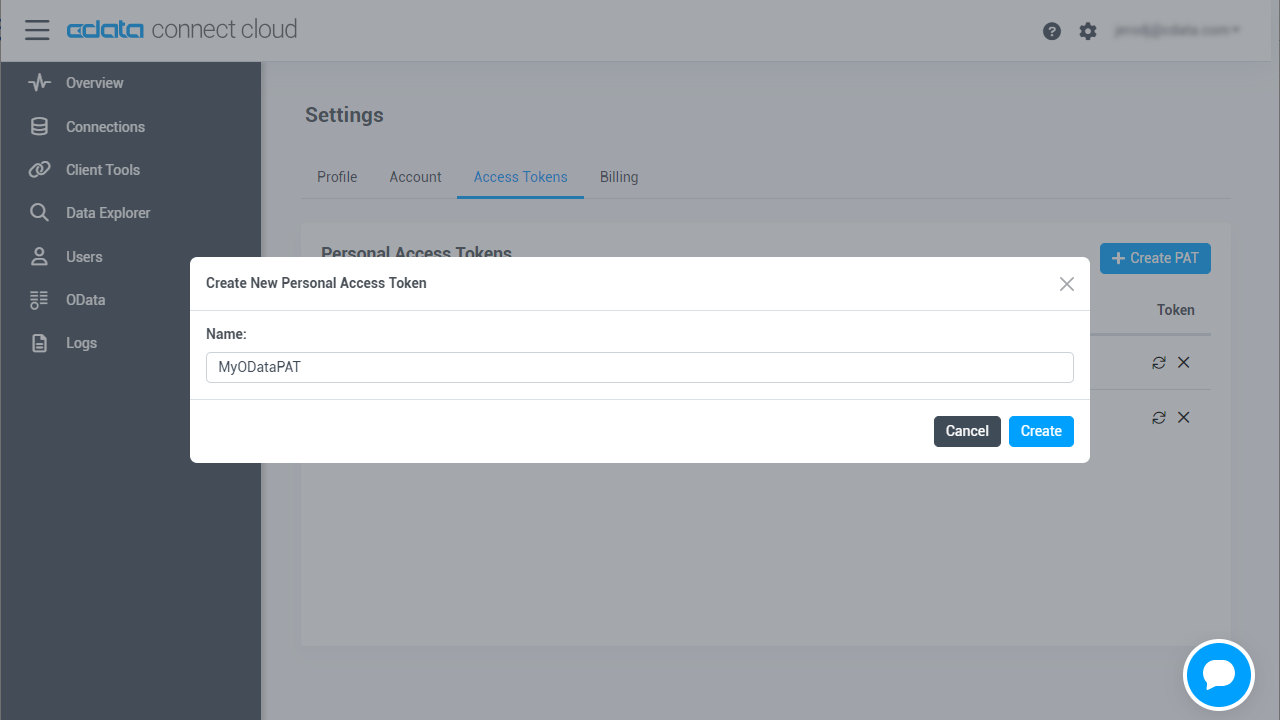
- Click on your username at the top right of the Connect Cloud app and click User Profile.
- On the User Profile page, scroll down to the Personal Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
- Give your PAT a name and click Create.
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
Build the TDS Foreign Data Wrapper
The Foreign Data Wrapper can be installed as an extension to PostgreSQL, without recompiling PostgreSQL. The tds_fdw extension is used as an example (https://github.com/tds-fdw/tds_fdw).
- You can clone and build the git repository via something like the following view source:
sudo apt-get install git git clone https://github.com/tds-fdw/tds_fdw.git cd tds_fdw make USE_PGXS=1 sudo make USE_PGXS=1 installNote: If you have several PostgreSQL versions and you do not want to build for the default one, first locate where the binary for pg_config is, take note of the full path, and then append PG_CONFIG=after USE_PGXS=1 at the make commands. - After you finish the installation, then start the server:
sudo service postgresql start - Then go inside the Postgres database
psql -h localhost -U postgres -d postgresNote: Instead of localhost you can put the IP where your PostgreSQL is hosted.
Connect to MongoDB data as a PostgreSQL Database and query the data!
After you have installed the extension, follow the steps below to start executing queries to MongoDB data:
- Log into your database.
- Load the extension for the database:
CREATE EXTENSION tds_fdw; - Create a server object for MongoDB data:
CREATE SERVER "MongoDB1" FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER tds_fdw OPTIONS (servername'tds.cdata.com', port '14333', database 'MongoDB1'); - Configure user mapping with your email and Personal Access Token from your Connect Cloud account:
CREATE USER MAPPING for postgres SERVER "MongoDB1" OPTIONS (username 'username@cdata.com', password 'your_personal_access_token' ); - Create the local schema:
CREATE SCHEMA "MongoDB1"; - Create a foreign table in your local database:
#Using a table_name definition: CREATE FOREIGN TABLE "MongoDB1".restaurants ( id varchar, cuisine varchar) SERVER "MongoDB1" OPTIONS(table_name 'MongoDB.restaurants', row_estimate_method 'showplan_all'); #Or using a schema_name and table_name definition: CREATE FOREIGN TABLE "MongoDB1".restaurants ( id varchar, cuisine varchar) SERVER "MongoDB1" OPTIONS (schema_name 'MongoDB', table_name 'restaurants', row_estimate_method 'showplan_all'); #Or using a query definition: CREATE FOREIGN TABLE "MongoDB1".restaurants ( id varchar, cuisine varchar) SERVER "MongoDB1" OPTIONS (query 'SELECT * FROM MongoDB.restaurants', row_estimate_method 'showplan_all'); #Or setting a remote column name: CREATE FOREIGN TABLE "MongoDB1".restaurants ( id varchar, col2 varchar OPTIONS (column_name 'cuisine')) SERVER "MongoDB1" OPTIONS (schema_name 'MongoDB', table_name 'restaurants', row_estimate_method 'showplan_all'); - You can now execute read/write commands to MongoDB:
SELECT id, cuisine FROM "MongoDB1".restaurants;
More Information & Free Trial
Now, you have created a simple query from live MongoDB data. For more information on connecting to MongoDB (and more than 100 other data sources), visit the Connect Cloud page. Sign up for a free trial and start working with live MongoDB data in PostgreSQL.