Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Connect to MongoDB in SpagoBI
Create reports featuring live MongoDB data in SpagoBI Studio. Host MongoDB reports on SpagoBI Server.
The CData JDBC Driver for MongoDB enables you to connect to live MongoDB data from business intelligence and data mining tools that support the JDBC standard. This article shows how to integrate MongoDB data into a report in SpagoBI Studio and host it on SpagoBI Server.
About MongoDB Data Integration
Accessing and integrating live data from MongoDB has never been easier with CData. Customers rely on CData connectivity to:
- Access data from MongoDB 2.6 and above, ensuring broad usability across various MongoDB versions.
- Easily manage unstructured data thanks to flexible NoSQL (learn more here: Leading-Edge Drivers for NoSQL Integration).
- Leverage feature advantages over other NoSQL drivers and realize functional benefits when working with MongoDB data (learn more here: A Feature Comparison of Drivers for NoSQL).
MongoDB's flexibility means that it can be used as a transactional, operational, or analytical database. That means CData customers use our solutions to integrate their business data with MongoDB or integrate their MongoDB data with their data warehouse (or both). Customers also leverage our live connectivity options to analyze and report on MongoDB directly from their preferred tools, like Power BI and Tableau.
For more details on MongoDB use case and how CData enhances your MongoDB experience, check out our blog post: The Top 10 Real-World MongoDB Use Cases You Should Know in 2024.
Getting Started
- Deploy the Driver in SpagoBI Server
- Create a Report in SpagoBI Studio
- Host MongoDB Reports on SpagoBI Server
Deploy the JDBC Driver in SpagoBI Server
Follow the steps to create a JDBC data source for MongoDB in SpagoBI Server.
- Copy the driver JAR into %CATALINA_BASE%/lib. These files are located in the lib subfolder of the installation directory.
Add a MongoDB driver resource to the context. The following resource definition can be added to the GlobalNamingResources element in server.xml:
<Resource name="jdbc/mongodb" auth="Container" type="javax.sql.DataSource" driverclassname="cdata.jdbc.mongodb.MongoDBDriver" factory="org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSourceFactory" maxactive="20" maxidle="10" maxwait="-1"/>- Add the following resource link to give access to Web applications. For this article, add the following line to META-INF\context.xml for SpagoBI.
<ResourceLink global="jdbc/mongodb" name="jdbc/mongodb" type="javax.sql.DataSource"/> - Restart the server.
After adding the driver to the resources for the SpagoBI server, add the data source: In SpagoBI, click Resources -> Data Source -> Add and enter the following information:
- Label: Enter a unique identifier for the driver.
- Description: Enter a description for the driver.
- Dialect: Select Default Dialect.
- Read Only: Select the read-only option. This option determines whether the data source is the default database to save datasets created by the end user.
- Type: Select JDBC.
- URL: Enter the JDBC URL using the required connection string properties:
Set the Server, Database, User, and Password connection properties to connect to MongoDB. To access MongoDB collections as tables you can use automatic schema discovery or write your own schema definitions. Schemas are defined in .rsd files, which have a simple format. You can also execute free-form queries that are not tied to the schema.
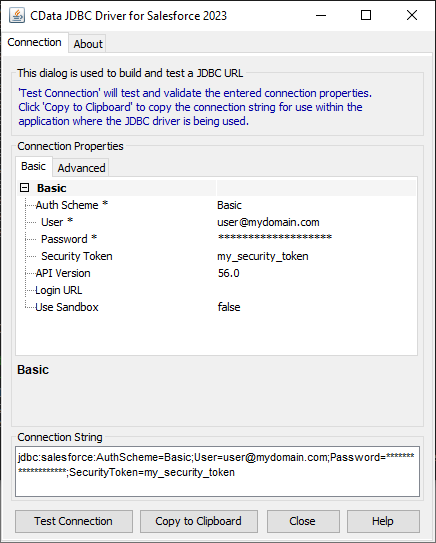
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the MongoDB JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.mongodb.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
A typical JDBC URL is below:
jdbc:mongodb:Server=MyServer;Port=27017;Database=test;User=test;Password=Password; - Driver: Enter the class name for the driver: cdata.jdbc.mongodb.MongoDBDriver

Create Reports in SpagoBI Studio
Follow the steps below to populate reports based on MongoDB data in SpagoBI Studio. You will create a dataset that populates a chart with the results of an SQL query. In the next section, you will host this report on SpagoBI Server.
First, you will need to connect to MongoDB data from a report in SpagoBI Studio:
- In SpagoBI Studio, click File -> New -> Project and select Report Project in the Business Intelligence and Reporting Tools folder.
- Click File -> New -> Report and select Blank Report.
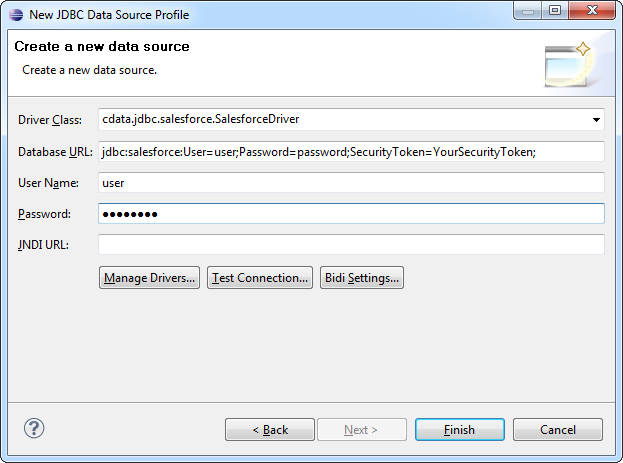
- In the Data Explorer view, right-click Data Sources and click New Data Source.
- Select JDBC Data Source and enter a name for the data source.
- Click Manage Drivers and click Add to add the driver JAR, cdata.jdbc.mongodb.jar. The driver JAR is located in the lib subfolder of the installation directory.
- In the Driver Class menu, select the driver class, cdata.jdbc.mongodb.MongoDBDriver.
- In the Database URL box, enter the JDBC URL. A typical JDBC URL is below:
jdbc:mongodb:Server=MyServer;Port=27017;Database=test;User=test;Password=Password;See the "Getting Started" chapter of the driver help for a guide to obtaining the required connection properties.![The JDBC data source. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
After you have connected to MongoDB data, create a dataset that contains the results of an SQL query:
- Right-click the DataSet folder and click New Data Set. Select the JDBC data source for MongoDB and enter a name for the dataset.
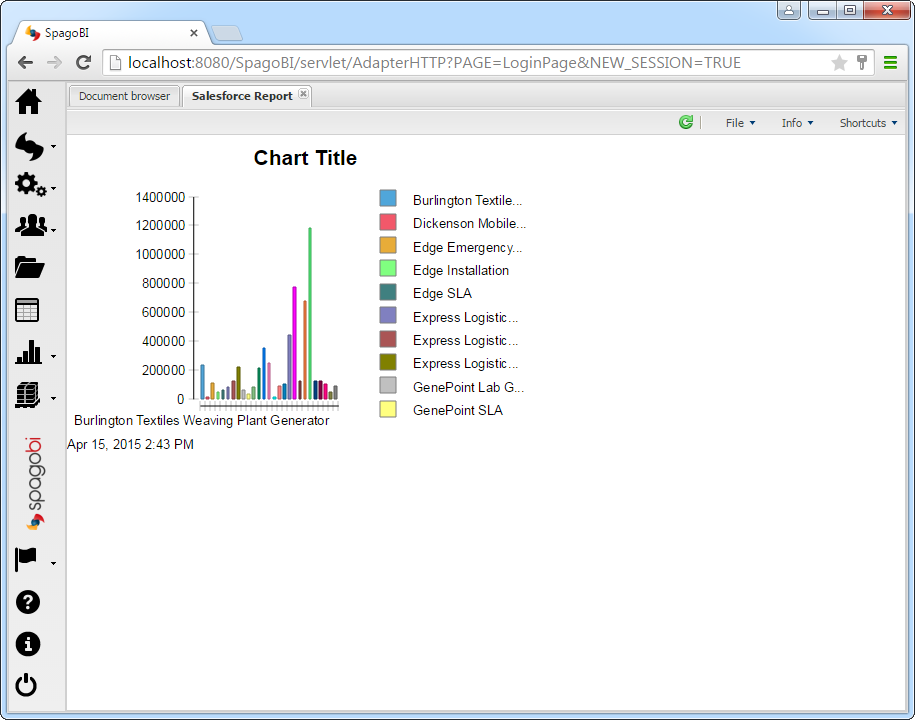
- Build the SQL query. In this example, this query will be used to add a chart to the dashboard. For example:
SELECT borough, cuisine FROM restaurants![The query to be used to populate a chart. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
You can use the dataset to populate report objects. Follow the steps below to create a chart.
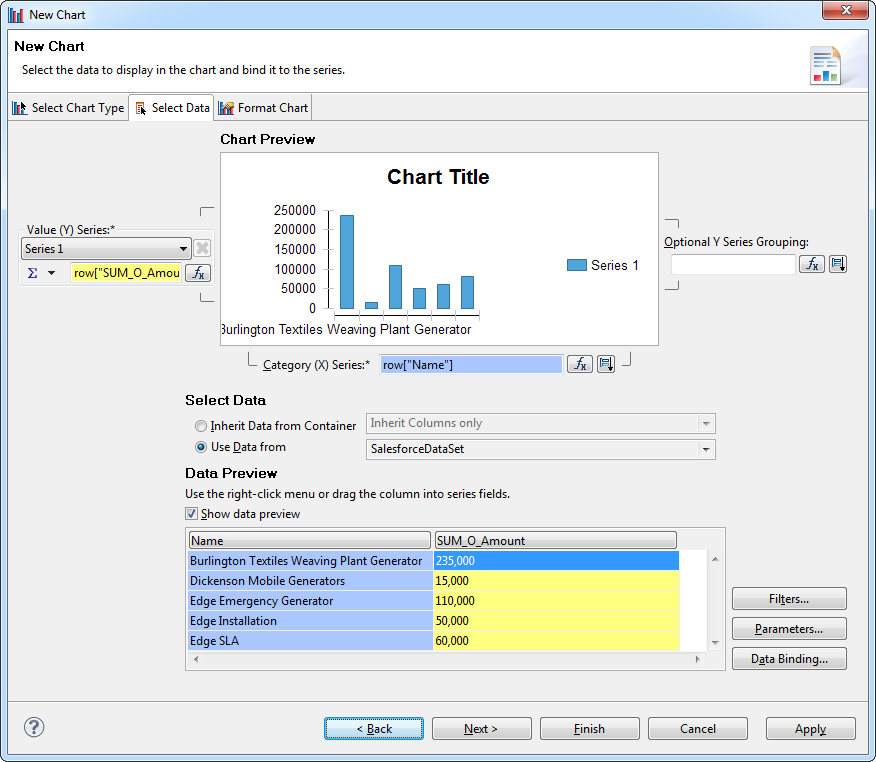
- In the Palette view, drag a chart onto the canvas.
- In the Select Chart Type tab, select a bar chart.
- In the Select Data tab, click the Use Data From option and select the MongoDB data set from the menu.
- Drag borough from the table to the series for the x-axis.
- Drag cuisine from the table to the series for the y-axis.
![Columns in the dataset defined as the x- and y-axes for the chart. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
Host MongoDB Reports on SpagoBI Server
Follow the steps below to host documents based on live MongoDB data on SpagoBI Server. You will use the report you created in the previous section as a template. To enable report users to access the live data, create placeholder parameters to be replaced by the MongoDB JDBC data source on the server:
- If you have not already done so, open the Report Design perspective in SpagoBI Studio.
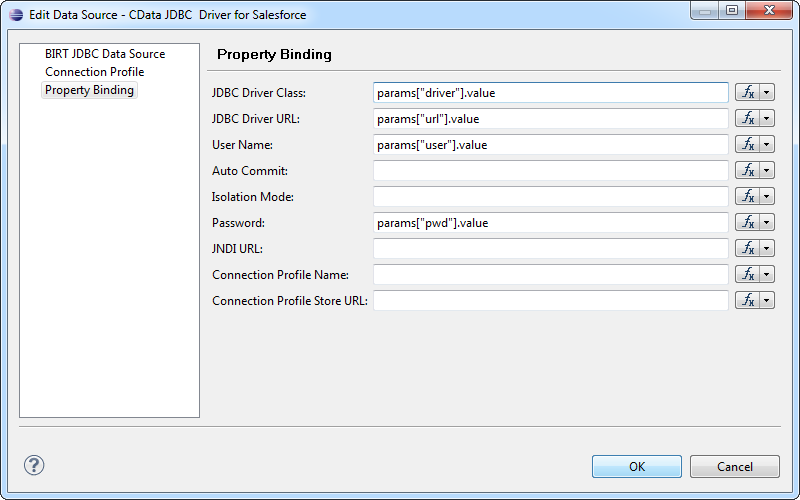
- In the Data Explorer view, right-click the Report Parameters folder and click New Parameter. Add the url parameter and assign an empty value to it. This parameter is a placeholder for the JDBC data source on the SpagoBI Server.
- Right-click the MongoDB data source and click Edit.
-
In the Property Binding node, set the JDBC Driver URL binding property to the url parameter: Click the box for the property. In the Category section, select Report Parameters. Select All in the Subcategory section and double-click the parameter.
You can also enter the following in the JavaScript syntax:
params["url"].value![Placeholder values in the report for the JDBC data source on the server.]()
Next, create a new document for the report on SpagoBI Server.
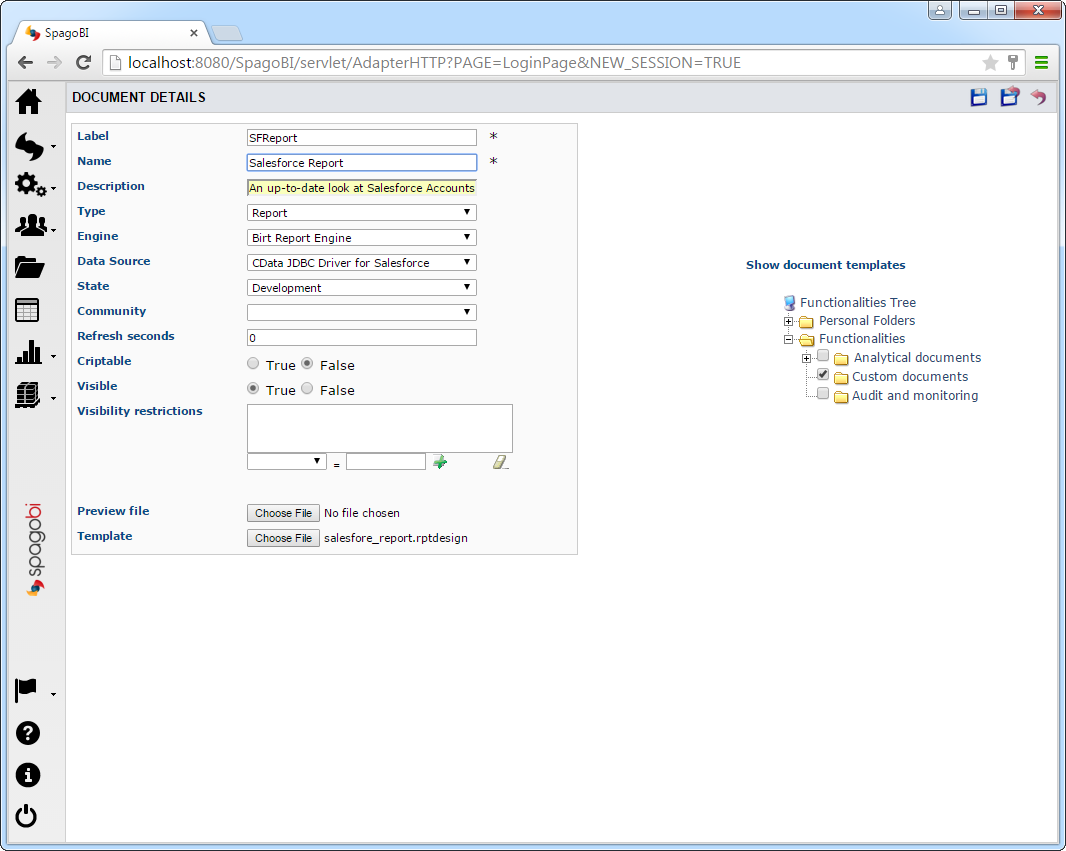
- In SpagoBI Server, click Documents Development -> Create Document -> Generic Document. The Document Details page is displayed.
- To create the document, enter the following:
- Label: Enter a unique identifier for the document.
- Name: Enter a user-friendly name for the document.
- Type: Select Report from the menu.
- Engine: Select BIRT Report Engine.
- Data Source: Select the MongoDB Data Source you created in Create a JDBC Data Source for MongoDB in SpagoBI Server.
- In the Show Document Templates section, select the folder where you want the document to be stored.
In the Template section, click Choose File. Navigate to the folder containing your report project. Select the .rptdesign file.
Note: You can find the path to the project in the project properties.
- Click the Save button.
When you run the report on the server, the placeholder url parameter is replaced with the JDBC URL defined on the server.