Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Automate Tasks in Power Automate Using the CData API Server and MongoDB ADO.NET Provider
Automate actions like sending emails to a contact list, posting to social media, or syncing CRM and ERP.
Power Automate (Microsoft Flow) makes it easy to automate tasks that involve data from multiple systems, on premises or in the cloud. With the CData API Server and MongoDB ADO.NET Provider (or any of 200+ other ADO.NET Providers), line-of-business users have a native way to create actions based on MongoDB triggers in Power Automate; the API Server makes it possible for SaaS applications like Power Automate to integrate seamlessly with MongoDB data through data access standards like Swagger and OData. This article shows how to use wizards in Power Automate and the API Server for MongoDB to create a trigger -- entities that match search criteria -- and send an email based on the results.
About MongoDB Data Integration
Accessing and integrating live data from MongoDB has never been easier with CData. Customers rely on CData connectivity to:
- Access data from MongoDB 2.6 and above, ensuring broad usability across various MongoDB versions.
- Easily manage unstructured data thanks to flexible NoSQL (learn more here: Leading-Edge Drivers for NoSQL Integration).
- Leverage feature advantages over other NoSQL drivers and realize functional benefits when working with MongoDB data (learn more here: A Feature Comparison of Drivers for NoSQL).
MongoDB's flexibility means that it can be used as a transactional, operational, or analytical database. That means CData customers use our solutions to integrate their business data with MongoDB or integrate their MongoDB data with their data warehouse (or both). Customers also leverage our live connectivity options to analyze and report on MongoDB directly from their preferred tools, like Power BI and Tableau.
For more details on MongoDB use case and how CData enhances your MongoDB experience, check out our blog post: The Top 10 Real-World MongoDB Use Cases You Should Know in 2024.
Getting Started
Set Up the API Server
Follow the steps below to begin producing secure and Swagger-enabled MongoDB APIs:
Deploy
The API Server runs on your own server. On Windows, you can deploy using the stand-alone server or IIS. On a Java servlet container, drop in the API Server WAR file. See the help documentation for more information and how-tos.
The API Server is also easy to deploy on Microsoft Azure, Amazon EC2, and Heroku.
Connect to MongoDB
After you deploy, provide authentication values and other connection properties by clicking Settings -> Connections in the API Server administration console. You can then choose the entities you want to allow the API Server access to by clicking Settings -> Resources.
Set the Server, Database, User, and Password connection properties to connect to MongoDB. To access MongoDB collections as tables you can use automatic schema discovery or write your own schema definitions. Schemas are defined in .rsd files, which have a simple format. You can also execute free-form queries that are not tied to the schema.
You will also need to enable CORS and define the following sections on the Settings -> Server page. As an alternative, you can select the option to allow all domains without '*'.
- Access-Control-Allow-Origin: Set this to a value of '*' or specify the domains that are allowed to connect.
- Access-Control-Allow-Methods: Set this to a value of "GET,PUT,POST,OPTIONS".
- Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Set this to "x-ms-client-request-id, authorization, content-type".
Authorize API Server Users
After determining the OData services you want to produce, authorize users by clicking Settings -> Users. The API Server uses authtoken-based authentication and supports the major authentication schemes. You can authenticate as well as encrypt connections with SSL. Access can also be restricted by IP address; access is restricted to only the local machine by default.
For simplicity, we will allow the authtoken for API users to be passed in the URL. You will need to add a setting in the Application section of the settings.cfg file, located in the data directory. On Windows, this is the app_data subfolder in the application root. In the Java edition, the location of the data directory depends on your operation system:
- Windows: C:\ProgramData\CData
- Unix or Mac OS X: ~/cdata
[Application]
AllowAuthtokenInURL = true
Add MongoDB Data to a Flow
You can use the built-in HTTP + Swagger connector to use a wizard to design a MongoDB process flow:
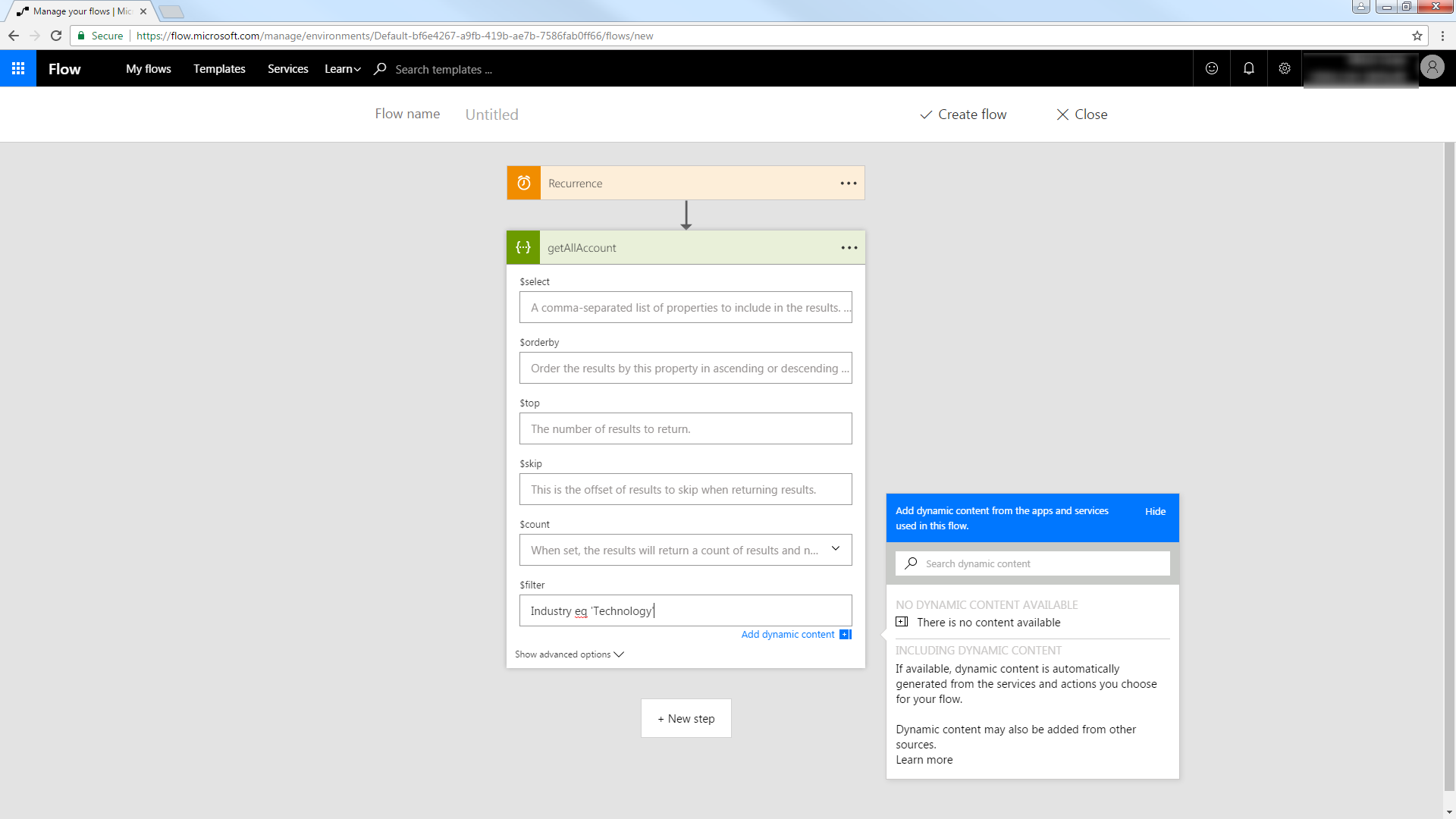
- In Power Automate, click My Flows -> Create from Blank.
- Select the Recurrence action and select a time interval for sending emails. This article uses 1 day.
- Add an HTTP + Swagger action by searching for Swagger.
- Enter the URL to the Swagger metadata document:
https://MySite:MyPort/api.rsc/@MyAuthtoken/$oas - Select the "Return restaurants" operation.
Build the OData query to retrieve MongoDB data. This article defines the following OData filter expression in the $filter box:
Name eq 'Morris Park Bake Shop'
See the API Server help documentation for more on filtering and examples of the supported OData.
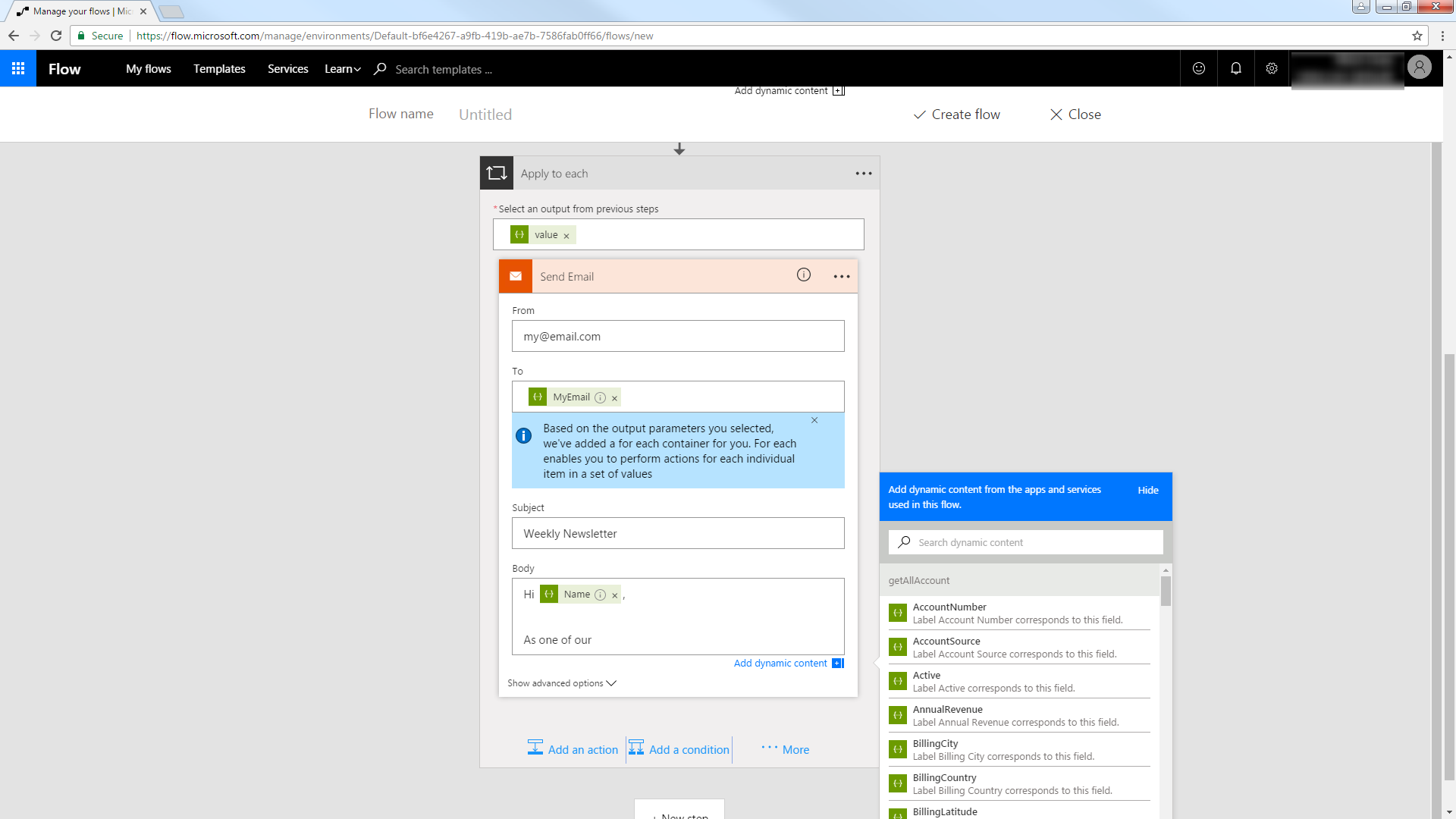
Trigger an Action
You can now work with restaurants entities in your process flow. Follow the steps to send an automated email:
- Add an SMTP - Send Email action.
- Enter the address and credentials for the SMTP server and name the connection. Be sure to enable encryption if supported by your server.
- Enter the message headers and body. You can add MongoDB columns in these boxes.