Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) with Odoo Data Entities in Java
Object-relational mapping (ORM) techniques make it easier to work with relational data sources and can bridge your logical business model with your physical storage model. Follow this tutorial to integrate connectivity to Odoo data into a Java-based ORM framework, Hibernate.
You can use Hibernate to map object-oriented domain models to a traditional relational database. The tutorial below shows how to use the CData JDBC Driver for Odoo to generate an ORM of your Odoo repository with Hibernate.
Though Eclipse is the IDE of choice for this article, the CData JDBC Driver for Odoo works in any product that supports the Java Runtime Environment. In the Knowledge Base you will find tutorials to connect to Odoo data from IntelliJ IDEA and NetBeans.
About Odoo Data Integration
Accessing and integrating live data from Odoo has never been easier with CData. Customers rely on CData connectivity to:
- Access live data from both Odoo API 8.0+ and Odoo.sh Cloud ERP.
-
Extend the native Odoo features with intelligent handling of many-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many data properties. CData's connectivity solutions also intelligently handle complex data properties within Odoo. In addition to columns with simple values like text and dates, there are also columns that contain multiple values on each row. The driver decodes these kinds of values differently, depending upon the type of column the value comes from:
- Many-to-one columns are references to a single row within another model. Within CData solutions, many-to-one columns are represented as integers, whose value is the ID to which they refer in the other model.
- Many-to-many columns are references to many rows within another model. Within CData solutions, many-to-many columns are represented as text containing a comma-separated list of integers. Each value in that list is the ID of a row that is being referenced.
- One-to-many columns are references to many rows within another model - they are similar to many-to-many columns (comma-separated lists of integers), except that each row in the referenced model must belong to only one in the main model.
- Use SQL stored procedures to call server-side RFCs within Odoo.
Users frequently integrate Odoo with analytics tools such as Power BI and Qlik Sense, and leverage our tools to replicate Odoo data to databases or data warehouses.
Getting Started
Install Hibernate
Follow the steps below to install the Hibernate plug-in in Eclipse.
- In Eclipse, navigate to Help -> Install New Software.
- Enter "http://download.jboss.org/jbosstools/neon/stable/updates/" in the Work With box.
- Enter "Hibernate" into the filter box.
- Select Hibernate Tools.
Start A New Project
Follow the steps below to add the driver JARs in a new project.
- Create a new project. Select Java Project as your project type and click Next. Enter a project name and click Finish.
- Right-click the project and click Properties. Click Java Build Path and then open the Libraries tab.
- Click Add External JARs to add the cdata.jdbc.odoo.jar library, located in the lib subfolder of the installation directory.
Add a Hibernate Configuration File
Follow the steps below to configure connection properties to Odoo data.
- Right-click on the new project and select New -> Hibernate -> Hibernate Configuration File (cfg.xml).
- Select src as the parent folder and click Next.
Input the following values:
- Hibernate version:: 5.2
- Database dialect: Derby
- Driver class: cdata.jdbc.odoo.OdooDriver
Connection URL: A JDBC URL, starting with jdbc:odoo: and followed by a semicolon-separated list of connection properties.
To connect, set the Url to a valid Odoo site, User and Password to the connection details of the user you are connecting with, and Database to the Odoo database.
Built-in Connection String Designer
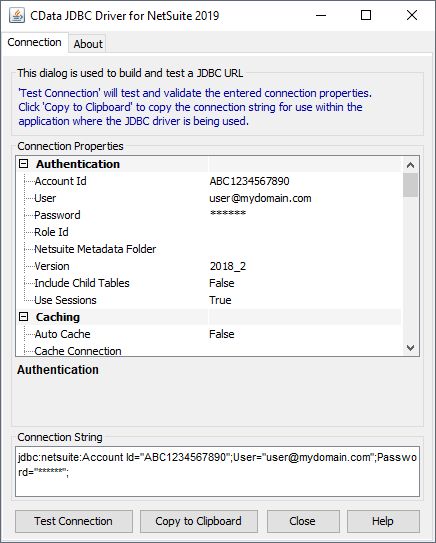
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Odoo JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.odoo.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
A typical JDBC URL is below:
jdbc:odoo:User=MyUser;Password=MyPassword;URL=http://MyOdooSite/;Database=MyDatabase;
Connect Hibernate to Odoo Data
Follow the steps below to select the configuration you created in the previous step.
- Switch to the Hibernate Configurations perspective: Window -> Open Perspective -> Hibernate.
- Right-click on the Hibernate Configurations panel and click Add Configuration.
- Set the Hibernate version to 5.2.
- Click the Browse button and select the project.
- For the Configuration file field, click Setup -> Use Existing and select the location of the hibernate.cfg.xml file (inside src folder in this demo).
- In the Classpath tab, if there is nothing under User Entries, click Add External JARS and add the driver jar once more. Click OK once the configuration is done.
- Expand the Database node of the newly created Hibernate configurations file.
Reverse Engineer Odoo Data
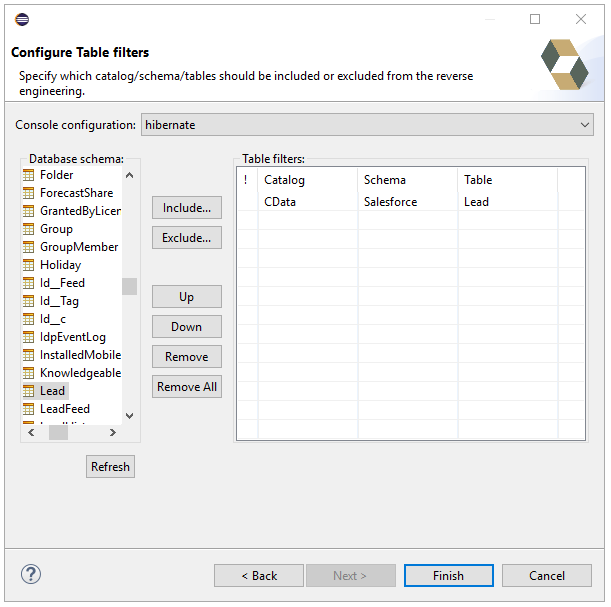
Follow the steps below to generate the reveng.xml configuration file. You will specify the tables you want to access as objects.
- Switch back to the Package Explorer.
- Right-click your project, select New -> Hibernate -> Hibernate Reverse Engineering File (reveng.xml). Click Next.
- Select src as the parent folder and click Next.
- In the Console configuration drop-down menu, select the Hibernate configuration file you created above and click Refresh.
- Expand the node and choose the tables you want to reverse engineer. Click Finish when you are done.
Configure Hibernate to Run
Follow the steps below to generate plain old Java objects (POJO) for the Odoo tables.
- From the menu bar, click Run -> Hibernate Code Generation -> Hibernate Code Generation Configurations.
- In the Console configuration drop-down menu, select the Hibernate configuration file you created in the previous section. Click Browse by Output directory and select src.
- Enable the Reverse Engineer from JDBC Connection checkbox. Click the Setup button, click Use Existing, and select the location of the hibernate.reveng.xml file (inside src folder in this demo).
- In the Exporters tab, check Domain code (.java) and Hibernate XML Mappings (hbm.xml).
- Click Run.
One or more POJOs are created based on the reverse-engineering setting in the previous step.
Insert Mapping Tags
For each mapping you have generated, you will need to create a mapping tag in hibernate.cfg.xml to point Hibernate to your mapping resource. Open hibernate.cfg.xml and insert the mapping tags as so:
cdata.odoo.OdooDriver
jdbc:odoo:User=MyUser;Password=MyPassword;URL=http://MyOdooSite/;Database=MyDatabase;
org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServerDialect
Execute SQL
Using the entity you created from the last step, you can now search and modify Odoo data:
import java.util.*;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.query.Query;
public class App {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
Session session = new
Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory().openSession();
String SELECT = "FROM res_users r WHERE id = :id";
Query q = session.createQuery(SELECT, res_users.class);
q.setParameter("id","1");
List<res_users> resultList = (List<res_users>) q.list();
for(res_users s: resultList){
System.out.println(s.getname());
System.out.println(s.getemail());
}
}
}