Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Connect to Oracle Data from Blazor Apps
Build ASP.NET Core Blazor C# apps that integrate with real-time Oracle data using standard SQL.
Blazor is a framework for developing modern, client-side web UIs using .NET technology. Instead of coding in JavaScript, developers can use the familiar C# language and .NET libraries to build app UIs.
The CData ADO.NET Provider for Oracle can be used with standard ADO.NET interfaces, such as LINQ and Entity Framework, to interact with live Oracle data. Since Blazor supports .NET Core, developers can use CData ADO.NET Providers in Blazor apps. In this article, we will guide you to build a simple Blazor app that talks to Oracle using standard SQL queries.
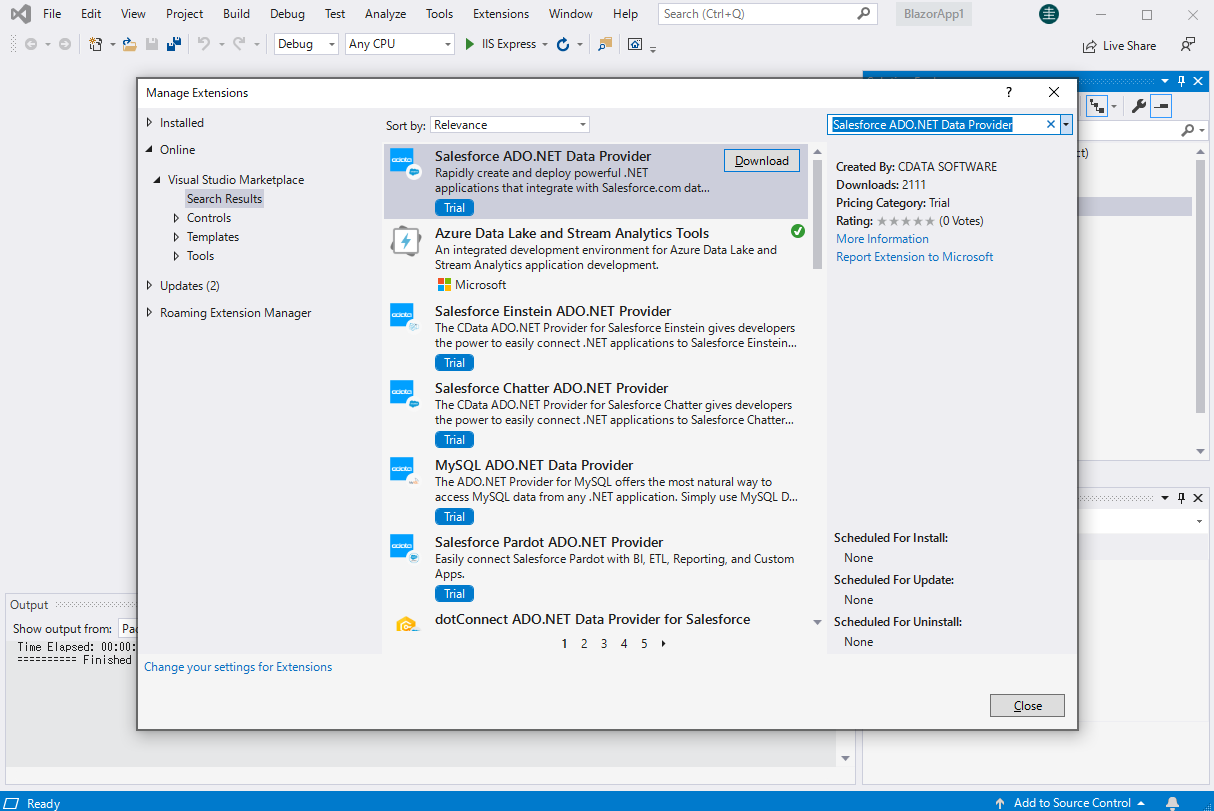
Install the CData ADO.NET Provider for Oracle
CData ADO.NET Providers allow users to access Oracle just like they would access SQL Server, using simple SQL queries.
Install the Oracle ADO.NET Data Provider from the CData website or from NuGet. Search NuGet for "Oracle ADO.NET Data Provider."
Create a Oracle-Connected Blazor App
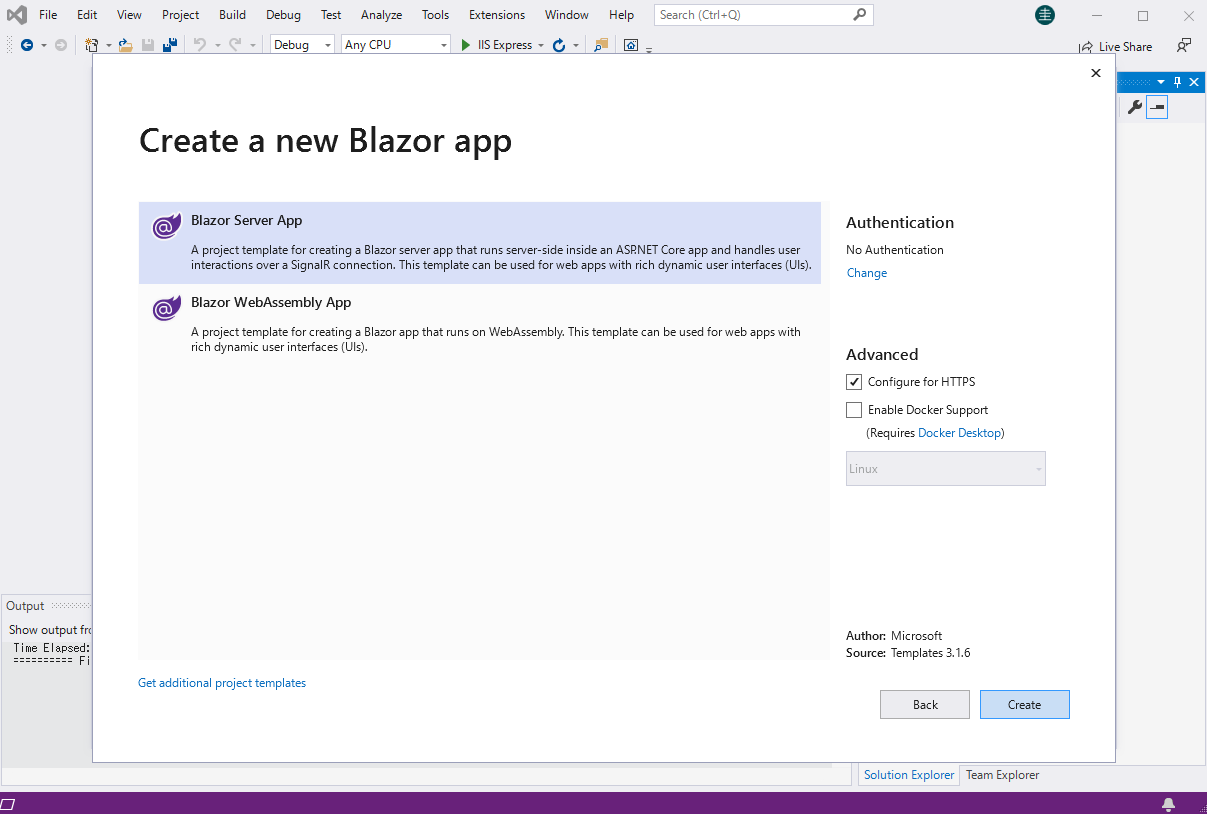
Start by creating a Blazor project that references the CData ADO.NET Provider for Oracle
- Create a Blazor project on Visual Studio.
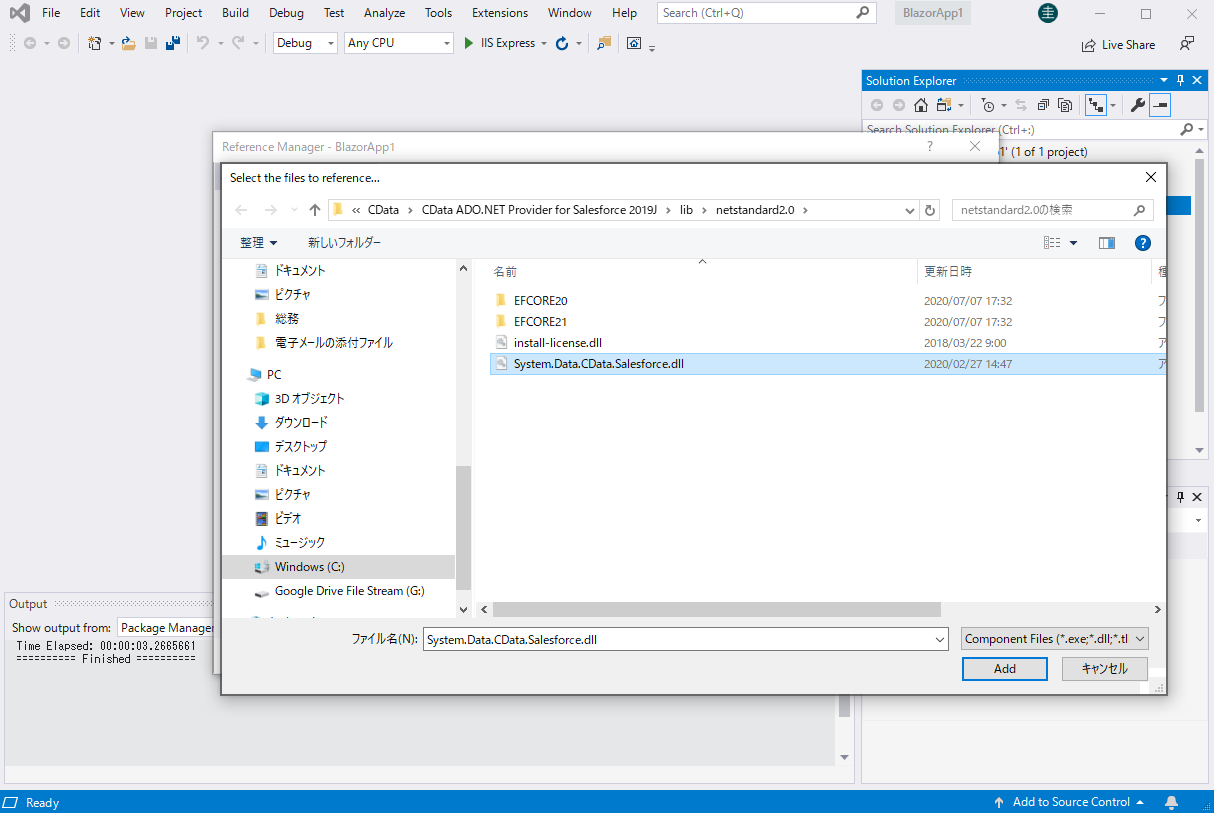
- From the Solution Explorer, right click Dependencies, then click Add Project Reference.
- In the Reference Manager, click the Browse button, and choose the .dll file of the installed ADO.NET Provider (e.g. System.Data.CData.OracleOCI.dll, typically located at C:\Program Files\CData\CData ADO.NET Provider for Oracle\lib etstandard2.0).
SELECT Oracle Data from the Blazor App
- Open the Index.razor file from the Project page.
- In a OracleOCIConnection object, set the connection string:
To connect to Oracle, you'll first need to update your PATH variable and ensure it contains a folder location that includes the native DLLs. The native DLLs can be found in the lib folder inside the installation directory. Once you've done this, set the following to connect:
- Port: The port used to connect to the server hosting the Oracle database.
- User: The user Id provided for authentication with the Oracle database.
- Password: The password provided for authentication with the Oracle database.
- Service Name: The service name of the Oracle database.
For example: User=myuser;Password=mypassword;Server=localhost;Port=1521;
- The code below creates a simple Blazor app for displaying Oracle data, using standard SQL to query Oracle just like SQL Server.
@page "/" @using System.Data; @using System.Data.CData.OracleOCI; <h1>Hello, world!</h1> Welcome to your Data app. <div class="row"> <div class="col-12"> @using (OracleOCIConnection connection = new OracleOCIConnection( "User=myuser;Password=mypassword;Server=localhost;Port=1521;")) { var sql = "SELECT CompanyName, City FROM Customers WHERE Country = US"; var results = new DataTable(); OracleOCIDataAdapter dataAdapter = new OracleOCIDataAdapter(sql, connection); dataAdapter.Fill(results); <table class="table table-bordered"> <thead class="thead-light"> <tr> @foreach (DataColumn item in results.Rows[0].Table.Columns) { <th scope="col">@item.ColumnName</th> } </tr> </thead> <tbody> @foreach (DataRow row in results.Rows) { <tr> @foreach (var column in row.ItemArray) { <td>@column.ToString()</td> } </tr> } </tbody> </table> } </div> </div> - Rebuild and run the project. The ADO.NET Provider renders Oracle data as an HTML table in the Blazor app.
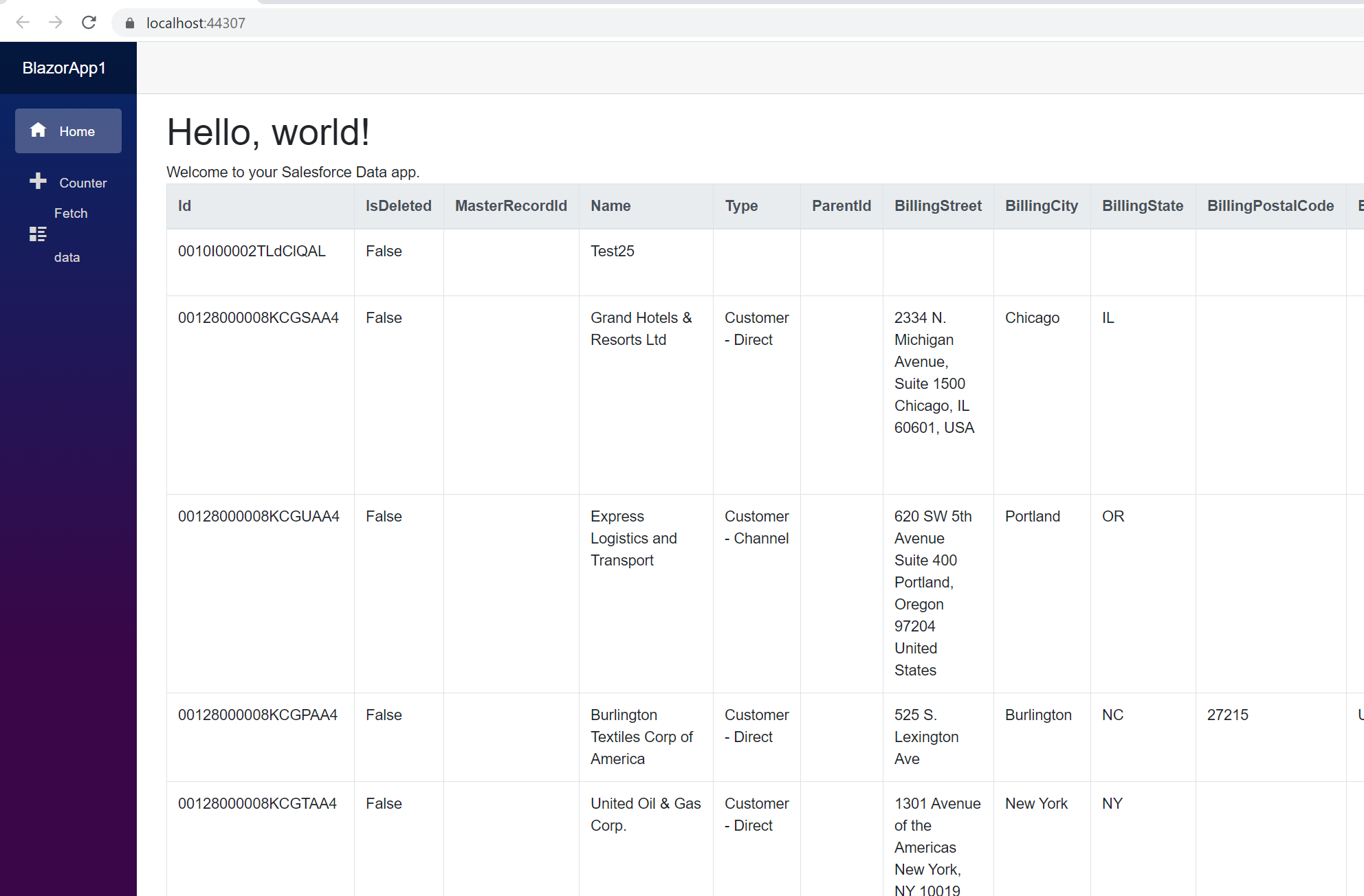
At this point, you have a Oracle-connected Blazor app, capable of working with live Oracle data just like you would work with a SQL Server instance. Download a free, 30-day trial and start working with live Oracle data in your Blazor apps today.
