Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Establish a Live Connection with PingOne Data using Tableau Bridge
The CData ODBC Driver for PingOne enables you to integrate live PingOne data into Tableau Cloud dashboards using the Tableau Bridge.
The Tableau Bridge enables you to publish dashboards to Tableau Cloud while maintaining live connectivity with any data source. In this article, you will use the Tableau Bridge to maintain data freshness in a published workbook by listening for changes in the underlying PingOne data.
The CData ODBC drivers offer unmatched performance for interacting with live PingOne data in Tableau Cloud due to optimized data processing built into the driver. When you issue complex SQL queries from Tableau Cloud to PingOne, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to PingOne and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations (often SQL functions and JOIN operations) client-side. With built-in dynamic metadata querying, you can visualize and analyze PingOne data using native Tableau data types.
Connect to PingOne as an ODBC Data Source
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
To connect to PingOne, configure these properties:
- Region: The region where the data for your PingOne organization is being hosted.
- AuthScheme: The type of authentication to use when connecting to PingOne.
- Either WorkerAppEnvironmentId (required when using the default PingOne domain) or AuthorizationServerURL, configured as described below.
Configuring WorkerAppEnvironmentId
WorkerAppEnvironmentId is the ID of the PingOne environment in which your Worker application resides. This parameter is used only when the environment is using the default PingOne domain (auth.pingone). It is configured after you have created the custom OAuth application you will use to authenticate to PingOne, as described in Creating a Custom OAuth Application in the Help documentation.
First, find the value for this property:
- From the home page of your PingOne organization, move to the navigation sidebar and click Environments.
- Find the environment in which you have created your custom OAuth/Worker application (usually Administrators), and click Manage Environment. The environment's home page displays.
- In the environment's home page navigation sidebar, click Applications.
- Find your OAuth or Worker application details in the list.
-
Copy the value in the Environment ID field.
It should look similar to:
WorkerAppEnvironmentId='11e96fc7-aa4d-4a60-8196-9acf91424eca'
Now set WorkerAppEnvironmentId to the value of the Environment ID field.
Configuring AuthorizationServerURL
AuthorizationServerURL is the base URL of the PingOne authorization server for the environment where your application is located. This property is only used when you have set up a custom domain for the environment, as described in the PingOne platform API documentation. See Custom Domains.
Authenticating to PingOne with OAuth
PingOne supports both OAuth and OAuthClient authentication. In addition to performing the configuration steps described above, there are two more steps to complete to support OAuth or OAuthCliet authentication:
- Create and configure a custom OAuth application, as described in Creating a Custom OAuth Application in the Help documentation.
- To ensure that the driver can access the entities in Data Model, confirm that you have configured the correct roles for the admin user/worker application you will be using, as described in Administrator Roles in the Help documentation.
- Set the appropriate properties for the authscheme and authflow of your choice, as described in the following subsections.
OAuth (Authorization Code grant)
Set AuthScheme to OAuth.
Desktop Applications
Get and Refresh the OAuth Access Token
After setting the following, you are ready to connect:
- InitiateOAuth: GETANDREFRESH. To avoid the need to repeat the OAuth exchange and manually setting the OAuthAccessToken each time you connect, use InitiateOAuth.
- OAuthClientId: The Client ID you obtained when you created your custom OAuth application.
- OAuthClientSecret: The Client Secret you obtained when you created your custom OAuth application.
- CallbackURL: The redirect URI you defined when you registered your custom OAuth application. For example: https://localhost:3333
When you connect, the driver opens PingOne's OAuth endpoint in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions to the application. The driver then completes the OAuth process:
- The driver obtains an access token from PingOne and uses it to request data.
- The OAuth values are saved in the location specified in OAuthSettingsLocation, to be persisted across connections.
The driver refreshes the access token automatically when it expires.
For other OAuth methods, including Web Applications, Headless Machines, or Client Credentials Grant, refer to the Help documentation.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Add PingOne Data to a Dashboard
- From a new workbook, click Data -> New Data Source -> Other Databases (ODBC).
Select the CData Data Source Name (for example: CData PingOne Source). - In the Database menu, select CData.
- In the Table box, enter a table name or click New Custom SQL to enter an SQL query. This article retrieves the [CData].[Administrators].Users table.
- Drag the table onto the join area. At this point, you can include multiple tables, leveraging the built-in SQL engine to process complex data requests.
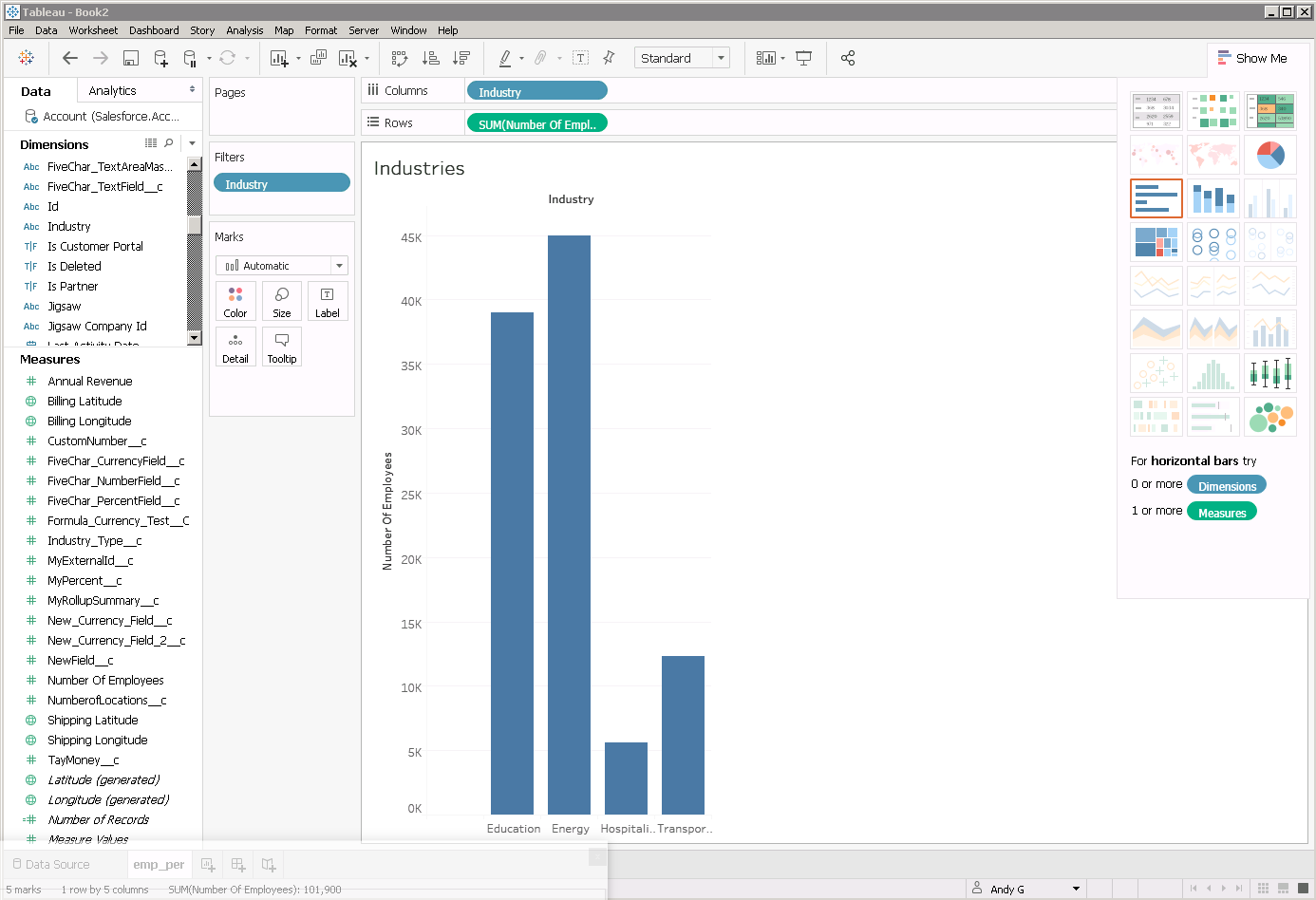
- Click the tab for your worksheet. Columns are listed as Dimensions and Measures, which you can drag and drop onto the dashboard to create visualizations.
Set Up Tableau Bridge as a Service
- In the Server menu, select Start Tableau Bridge Client.
- Sign in to the Tableau Bridge using a site admin level account.
- If prompted, select the Tableau Cloud site where you want to publish live data. The bridge client will open and is accessible from the system tray.
- By default, the Tableau Bridge client is set to Application mode. Select 'Switch to service' to enable Tableau Bridge to handle live connections.
- Log in to your Tableau Cloud site as an administrator.
- From your site, click Settings, then Bridge.
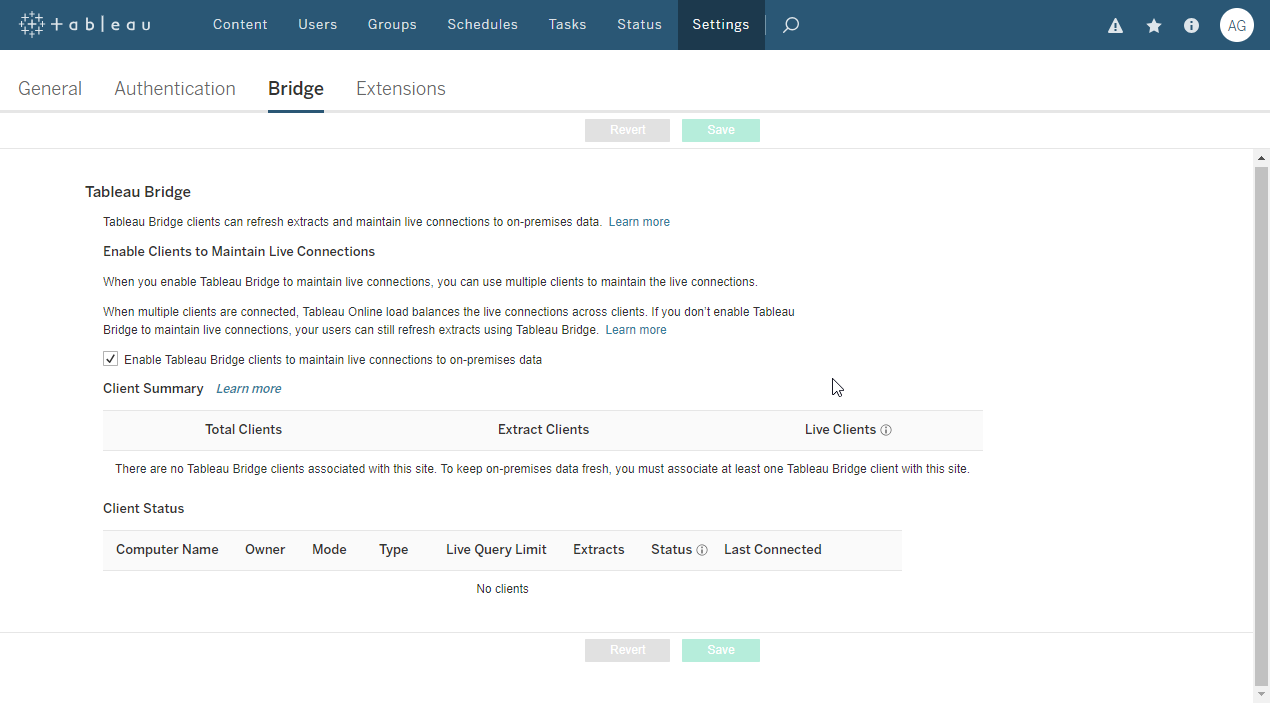
- In the Bridge settings, under Enable Clients to Maintain Live Connections, check the box labeled 'Enable Tableau Bridge clients to maintain live connections to on-premises data.'
Publish a Dashboard Containing the Live Data Source
Having configured both the Tableau Bridge and Tableau Cloud to enable live data connections, you can now publish your workbook to Tableau Cloud. From the Server menu, select Publish Workbook.
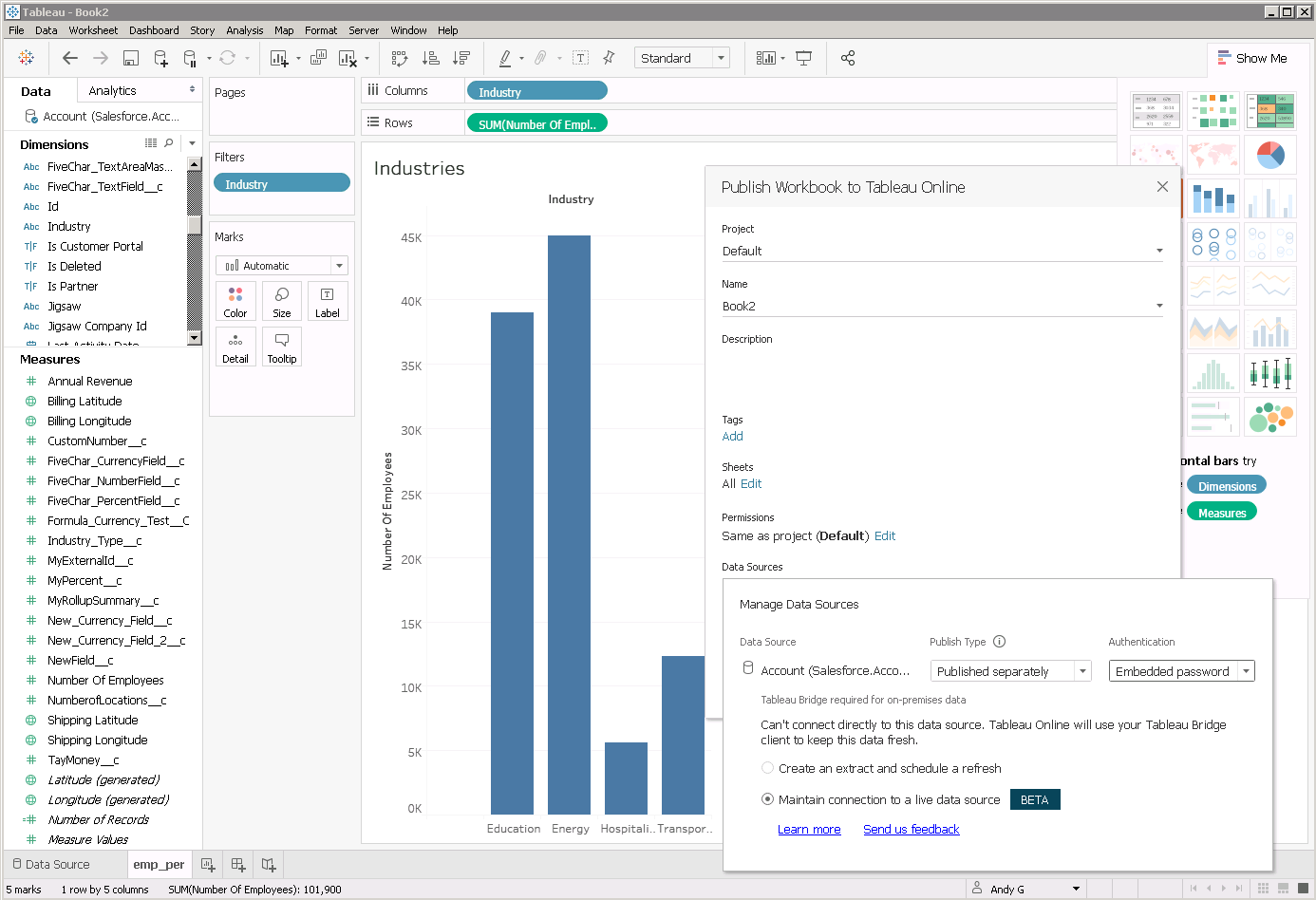
After choosing the workbook name and project that you wish to publish to, configure the deployment so that the CData ODBC driver for PingOne is embedded in your workbook as a separate, live data source.
- Under Data Sources, select the option to Edit the embedded data sources in the workbook.
- Change Publish Type to 'Published separately,' then select a desired means of authentication.
- Last, select 'Maintain connection to a live data source' and click the green Publish Workbook button.
The published workbook now updates alongside the underlying PingOne data. From a published dashboard, simply click the Refresh button to reflect the most recent changes.

