Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →DataBind Redshift Data to the DevExpress Data Grid
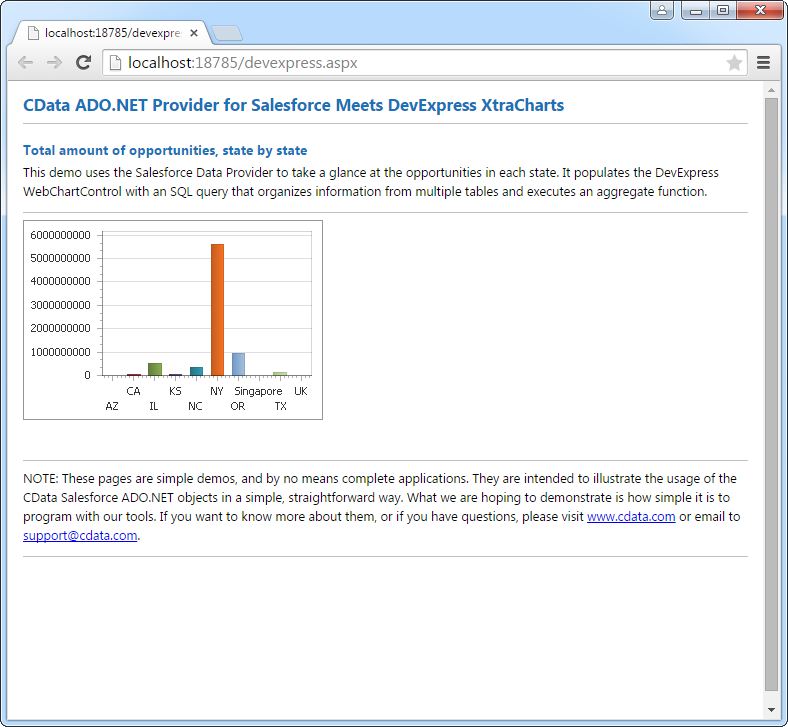
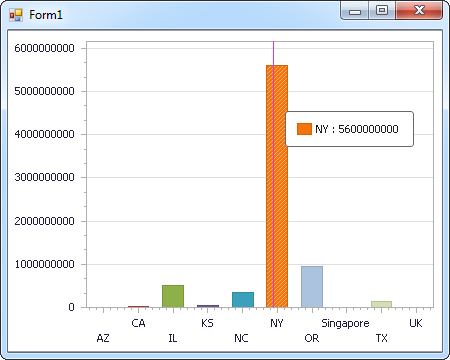
Use the CData ADO.NET Provider for Redshift with the DevExpress Windows Forms and Web controls to provide Redshift data to a chart.
The ADO.NET Provider for Redshift by CData incorporates conventional ADO.NET data access components compatible with third-party controls. You can adhere to the standard ADO.NET data binding procedures to establish two-way access to real-time data through UI controls. This article will demonstrate the utilization of CData components for data binding with DevExpress UI Controls (Windows Forms and Web controls), specifically binding to a chart that visualizes live data.
To connect to Redshift, set the following:
- Server: Set this to the host name or IP address of the cluster hosting the Database you want to connect to.
- Port: Set this to the port of the cluster.
- Database: Set this to the name of the database. Or, leave this blank to use the default database of the authenticated user.
- User: Set this to the username you want to use to authenticate to the Server.
- Password: Set this to the password you want to use to authenticate to the Server.
You can obtain the Server and Port values in the AWS Management Console:
- Open the Amazon Redshift console (http://console.aws.amazon.com/redshift).
- On the Clusters page, click the name of the cluster.
- On the Configuration tab for the cluster, copy the cluster URL from the connection strings displayed.
Windows Forms Controls
The code below shows how to populate a DevExpress chart with Redshift data. The RedshiftDataAdapter binds to the Series property of the chart control. The Diagram property of the control defines the x- and y-axes as the column names.
using (RedshiftConnection connection = new RedshiftConnection(
"User=admin;Password=admin;Database=dev;Server=examplecluster.my.us-west-2.redshift.amazonaws.com;Port=5439;")) {
RedshiftDataAdapter dataAdapter = new RedshiftDataAdapter(
"SELECT ShipName, ShipCity FROM Orders", connection);
DataTable table = new DataTable();
dataAdapter.Fill(table);
DevExpress.XtraCharts.Series series = new DevExpress.XtraCharts.Series();
chartControl1.Series.Add(series);
series.DataSource = table;
series.ValueDataMembers.AddRange(new string[] { "ShipCity" });
series.ArgumentScaleType = DevExpress.XtraCharts.ScaleType.Qualitative;
series.ArgumentDataMember = "ShipName";
series.ValueScaleType = DevExpress.XtraCharts.ScaleType.Numerical;
chartControl1.Legend.Visibility = DevExpress.Utils.DefaultBoolean.False;
((DevExpress.XtraCharts.SideBySideBarSeriesView)series.View).ColorEach = true;
}
Web Controls
The code below shows how to populate a DevExpress Web control with Redshift data. The RedshiftDataAdapter binds to the Series property of the chart; the Diagram property defines the x- and y-axes as the column names.
using DevExpress.XtraCharts;
using (RedshiftConnection connection = new RedshiftConnection(
"User=admin;Password=admin;Database=dev;Server=examplecluster.my.us-west-2.redshift.amazonaws.com;Port=5439;"))
{
RedshiftDataAdapter RedshiftDataAdapter1 = new RedshiftDataAdapter("SELECT ShipName, ShipCity FROM Orders", connection);
DataTable table = new DataTable();
RedshiftDataAdapter1.Fill(table);
DevExpress.XtraCharts.Series series = new Series("Series1", ViewType.Bar);
WebChartControl1.Series.Add(series);
series.DataSource = table;
series.ValueDataMembers.AddRange(new string[] { "ShipCity" });
series.ArgumentScaleType = ScaleType.Qualitative;
series.ArgumentDataMember = "ShipName";
series.ValueScaleType = ScaleType.Numerical;
((DevExpress.XtraCharts.SideBySideBarSeriesView)series.View).ColorEach = true;
}