Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Query Redshift Data in DataGrip
Create a Data Source for Redshift in DataGrip and use SQL to query live Redshift data.
DataGrip is a database IDE that allows SQL developers to query, create, and manage databases. When paired with the CData JDBC Driver for Amazon Redshift, DataGrip can work with live Redshift data. This article shows how to establish a connection to Redshift data in DataGrip and use the table editor to load Redshift data.
Create a New Driver Definition for Redshift
The steps below describe how to create a new Data Source in DataGrip for Redshift.
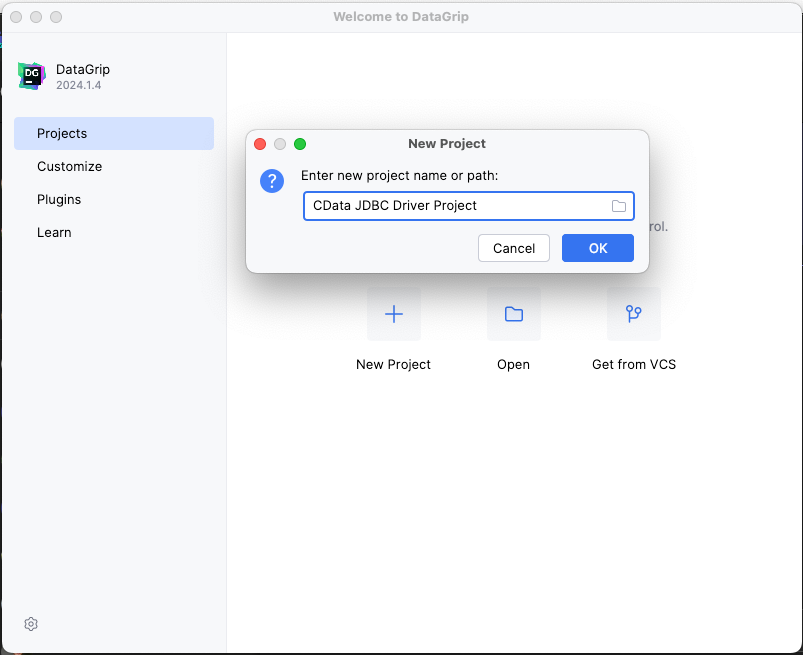
- In DataGrip, click File -> New > Project and name the project
![Creating a new DataGrip project.]()
- In the Database Explorer, click the plus icon () and select Driver.
![Adding a new Driver.]()
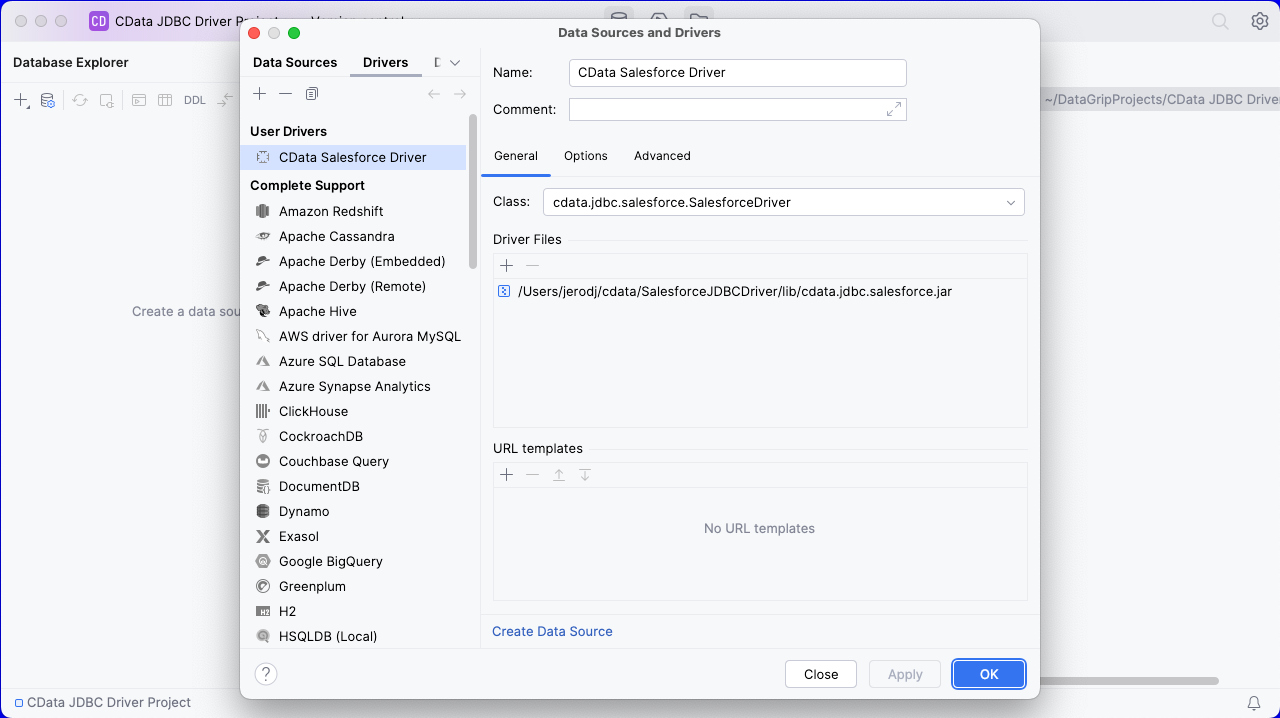
- In the Driver tab:
- Set Name to a user-friendly name (e.g. "CData Redshift Driver")
- Set Driver Files to the appropriate JAR file. To add the file, click the plus (), select "Add Files," navigate to the "lib" folder in the driver's installation directory and select the JAR file (e.g. cdata.jdbc.redshift.jar).
- Set Class to cdata.jdbc.redshift.Redshift.jar
Additionally, in the advanced tab you can change driver properties and some other settings like VM Options, VM environment, VM home path, DBMS, etc - For most cases, change the DBMS type to "Unknown" in Expert options to avoid native SQL Server queries (Transact-SQL), which might result in an invalid function error
- Click "Apply" then "OK" to save the Connection
![A configured Driver (Salesforce is shown).]()
Configure a Connection to Redshift
- Once the connection is saved, click the plus (), then "Data Source" then "CData Redshift Driver" to create a new Redshift Data Source.
- In the new window, configure the connection to Redshift with a JDBC URL.
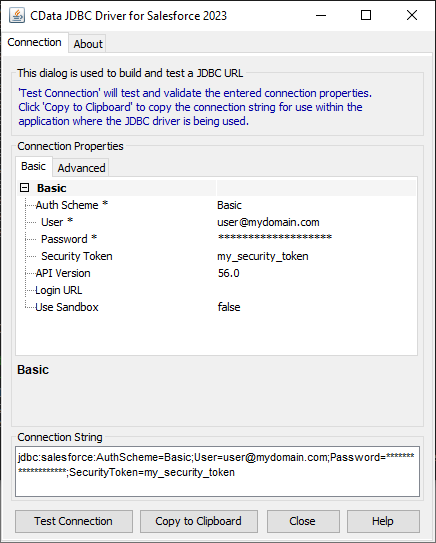
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Redshift JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.redshift.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
To connect to Redshift, set the following:
- Server: Set this to the host name or IP address of the cluster hosting the Database you want to connect to.
- Port: Set this to the port of the cluster.
- Database: Set this to the name of the database. Or, leave this blank to use the default database of the authenticated user.
- User: Set this to the username you want to use to authenticate to the Server.
- Password: Set this to the password you want to use to authenticate to the Server.
You can obtain the Server and Port values in the AWS Management Console:
- Open the Amazon Redshift console (http://console.aws.amazon.com/redshift).
- On the Clusters page, click the name of the cluster.
- On the Configuration tab for the cluster, copy the cluster URL from the connection strings displayed.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
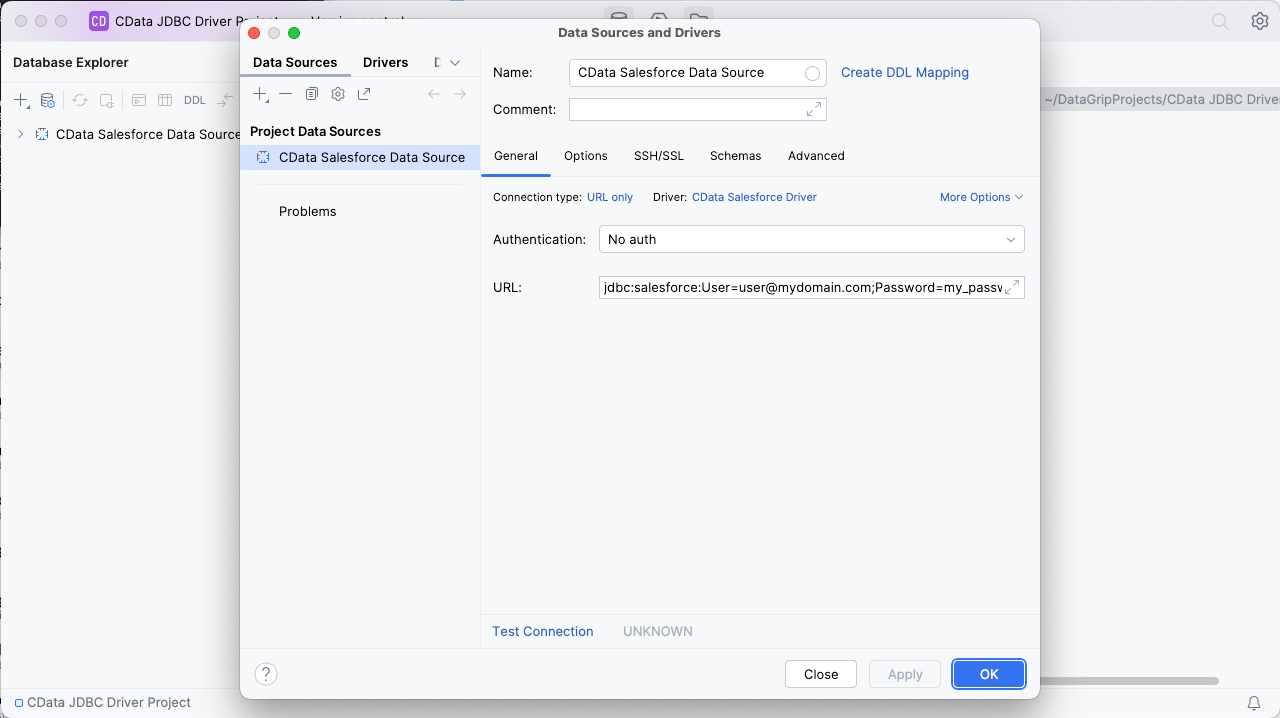
- Set URL to the connection string, e.g.,
jdbc:redshift:User=admin;Password=admin;Database=dev;Server=examplecluster.my.us-west-2.redshift.amazonaws.com;Port=5439; - Click "Apply" and "OK" to save the connection string
![A configured Data Source (Salesforce is shown).]()
At this point, you will see the data source in the Data Explorer.
Execute SQL Queries Against Redshift
To browse through the Redshift entities (available as tables) accessible through the JDBC Driver, expand the Data Source.
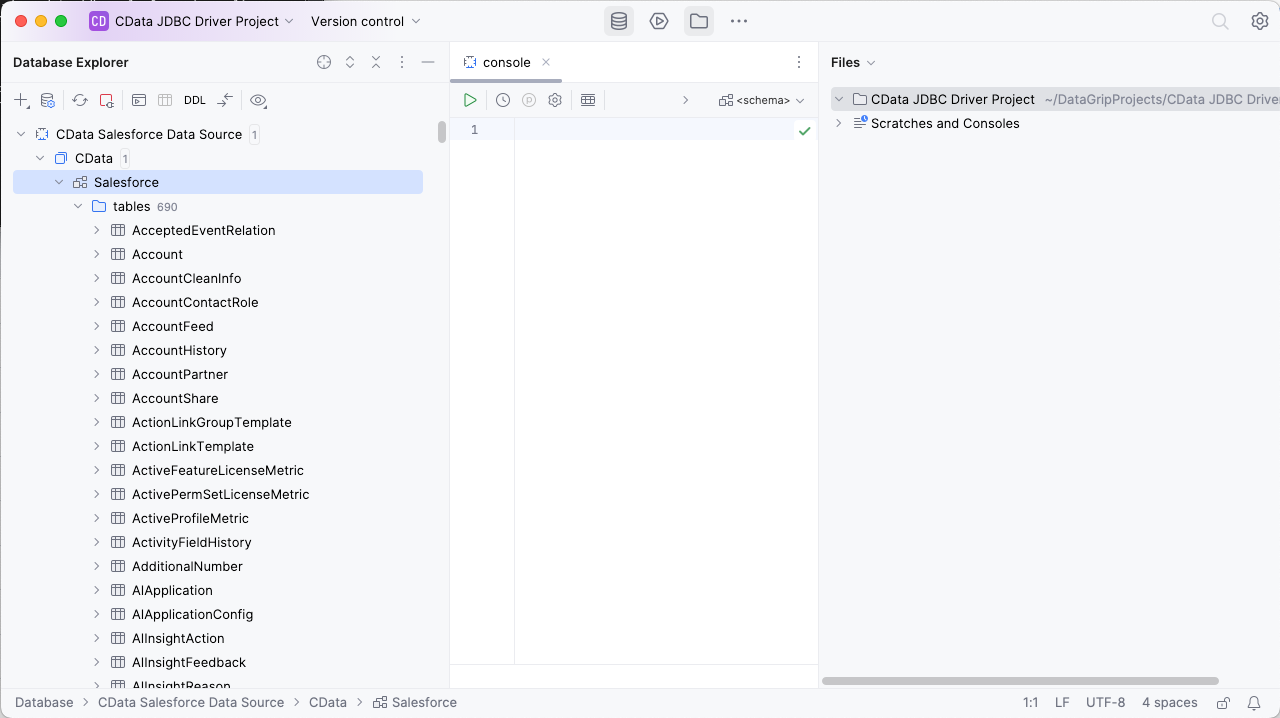
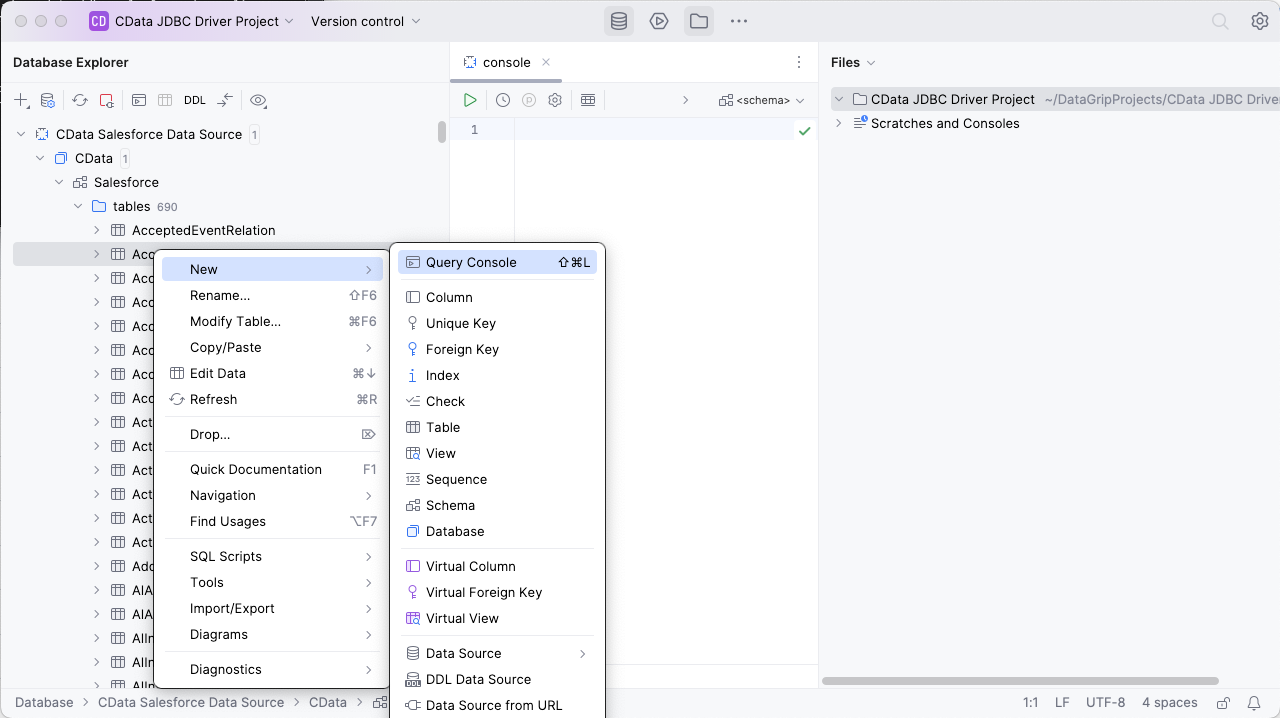
To execute queries, right click on any table and select "New" -> "Query Console."
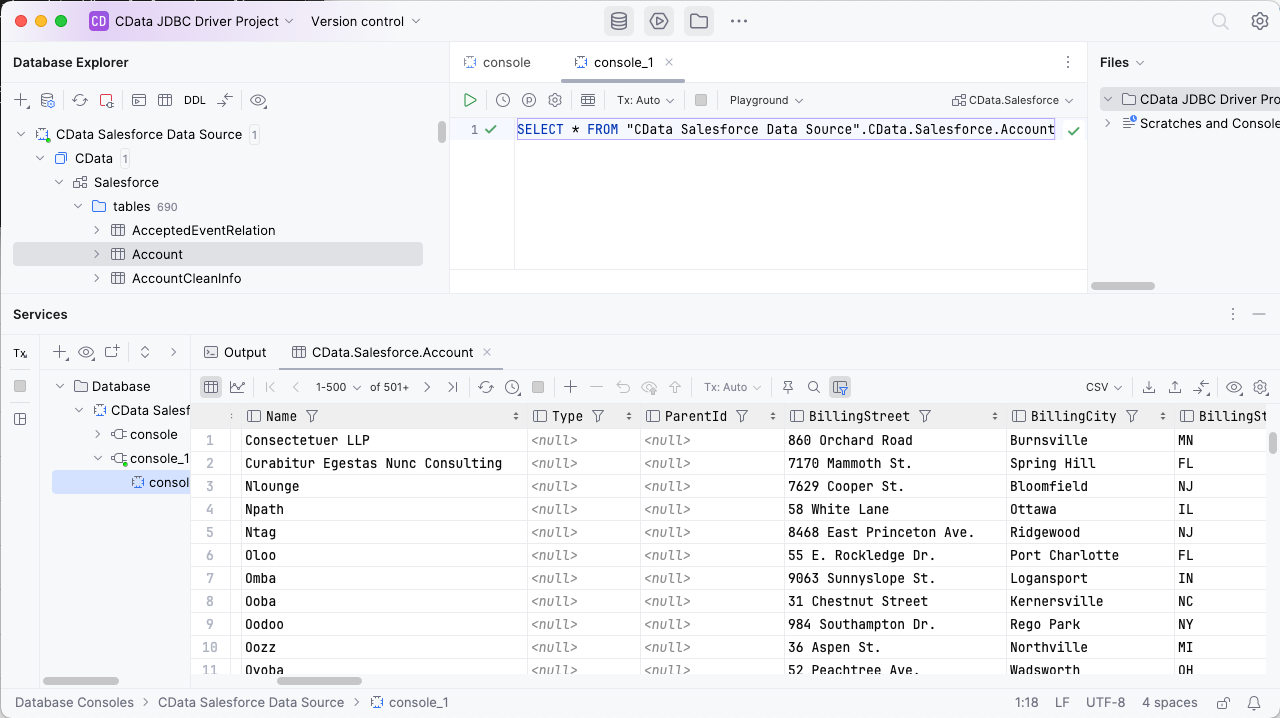
In the Console, write the SQL query you wish to execute. For example: SELECT ShipName, ShipCity FROM Orders
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for Amazon Redshift and start working with your live Redshift data in DataGrip. Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.