Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →How to connect to Salesforce Data from IntelliJ
Integrate connectivity to Salesforce data with wizards in IntelliJ.
The CData JDBC Driver for Salesforce enables you to access Salesforce as a JDBC data source, providing integration with rapid development tools in IDEs. This article shows how to use the data source configuration wizard to connect to Salesforce data in IntelliJ.
About Salesforce Data Integration
Accessing and integrating live data from Salesforce has never been easier with CData. Customers rely on CData connectivity to:
- Access to custom entities and fields means Salesforce users get access to all of Salesforce.
- Create atomic and batch update operations.
- Read, write, update, and delete their Salesforce data.
- Leverage the latest Salesforce features and functionalities with support for SOAP API versions 30.0.
- See improved performance based on SOQL support to push complex queries down to Salesforce servers.
- Use SQL stored procedures to perform actions like creating, retrieving, aborting, and deleting jobs, uploading and downloading attachments and documents, and more.
Users frequently integrate Salesforce data with:
- other ERPs, marketing automation, HCMs, and more.
- preferred data tools like Power BI, Tableau, Looker, and more.
- databases and data warehouses.
For more information on how CData solutions work with Salesforce, check out our Salesforce integration page.
Getting Started
Create a JBDC Data Source for Salesforce
Follow the steps below to add the driver JAR and define connection properties required to connect to Salesforce data.
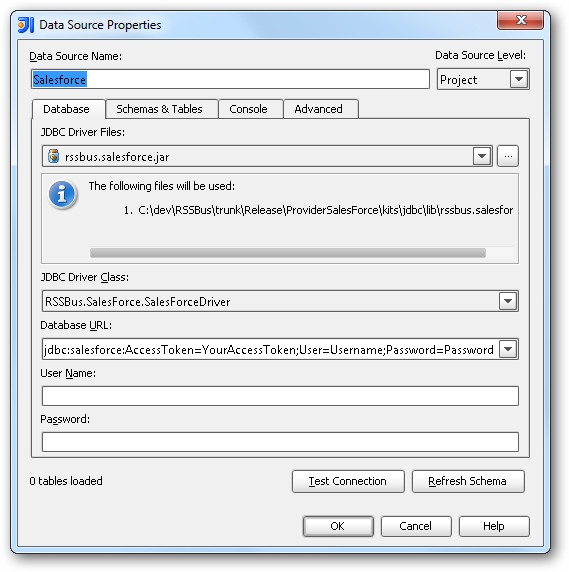
- In the Data Sources window, right-click and then click Add Data Source -> DB Data Source.
In the Data Source Properties dialog that appears, the following properties are required:
- JDBC Driver Files: Click the button next to this menu to add the JDBC Driver file cdata.jdbc.salesforce.jar, located in the installation directory.
- JDBC Driver Class: In this menu, select cdata.jdbc.salesforce.SalesforceDriver from the list.
Database URL: Enter the connection URL in the JDBC URL property. The URL must start with jdbc:salesforce: and includes connection properties separated with semicolons.
There are several authentication methods available for connecting to Salesforce: Login, OAuth, and SSO. The Login method requires you to have the username, password, and security token of the user.
If you do not have access to the username and password or do not wish to require them, you can use OAuth authentication.
SSO (single sign-on) can be used by setting the SSOProperties, SSOLoginUrl, and TokenUrl connection properties, which allow you to authenticate to an identity provider. See the "Getting Started" chapter in the help documentation for more information.
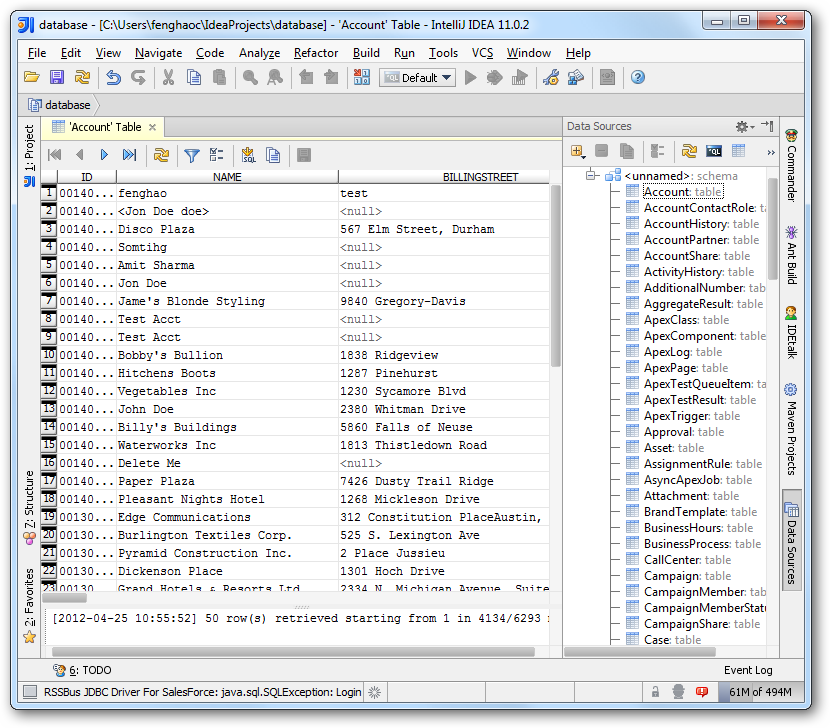
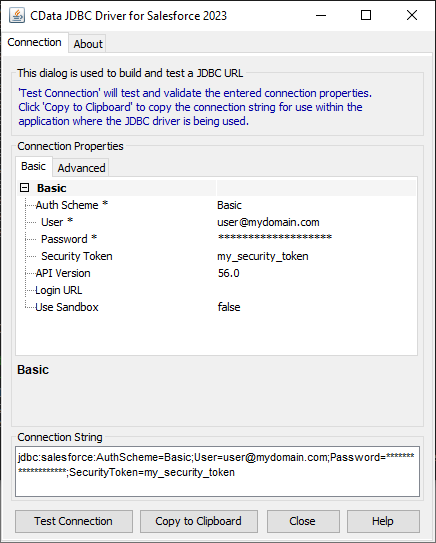
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Salesforce JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.salesforce.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
A typical JDBC URL is the following:
jdbc:salesforce:User=username;Password=password;SecurityToken=Your_Security_Token;
Edit and Save Salesforce Data
To discover schema information, right-click the data source you just created and click Refresh Tables. To query a table, right-click it and then click Open Tables Editor. You can also modify records in the Table Editor.