Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →How to Connect to & Open Salesforce Data in Microsoft Excel
This article uses the CData ODBC driver for Salesforce to import data in Excel with Microsoft Query. This article also demonstrates how to use parameters with Microsoft Query.
The CData ODBC driver for Salesforce uses the standard ODBC interface to link Salesforce data with applications like Microsoft Access and Excel. Follow the steps below to use Microsoft Query to import Salesforce data into a spreadsheet and provide values to a parameterized query from cells in a spreadsheet.
About Salesforce Data Integration
Accessing and integrating live data from Salesforce has never been easier with CData. Customers rely on CData connectivity to:
- Access to custom entities and fields means Salesforce users get access to all of Salesforce.
- Create atomic and batch update operations.
- Read, write, update, and delete their Salesforce data.
- Leverage the latest Salesforce features and functionalities with support for SOAP API versions 30.0.
- See improved performance based on SOQL support to push complex queries down to Salesforce servers.
- Use SQL stored procedures to perform actions like creating, retrieving, aborting, and deleting jobs, uploading and downloading attachments and documents, and more.
Users frequently integrate Salesforce data with:
- other ERPs, marketing automation, HCMs, and more.
- preferred data tools like Power BI, Tableau, Looker, and more.
- databases and data warehouses.
For more information on how CData solutions work with Salesforce, check out our Salesforce integration page.
Getting Started
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
There are several authentication methods available for connecting to Salesforce: Login, OAuth, and SSO. The Login method requires you to have the username, password, and security token of the user.
If you do not have access to the username and password or do not wish to require them, you can use OAuth authentication.
SSO (single sign-on) can be used by setting the SSOProperties, SSOLoginUrl, and TokenUrl connection properties, which allow you to authenticate to an identity provider. See the "Getting Started" chapter in the help documentation for more information.
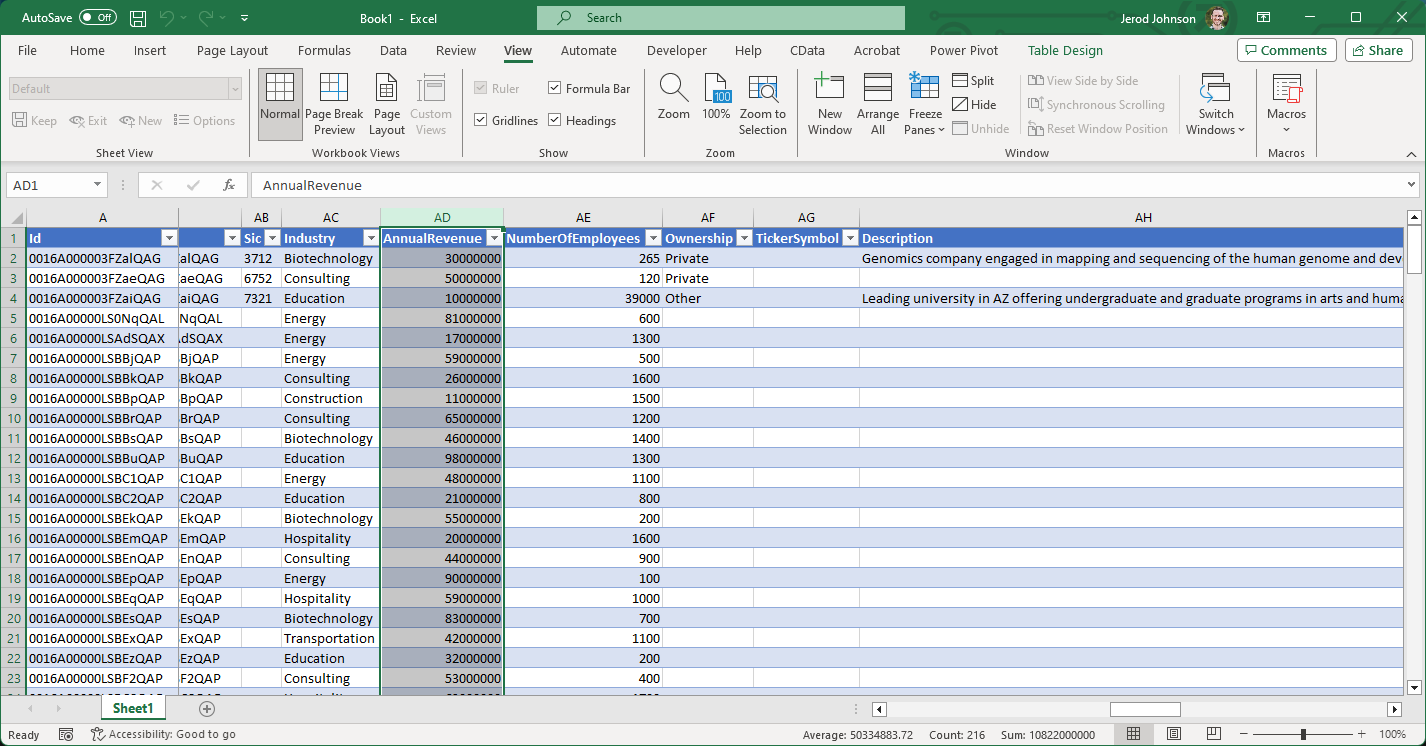
You can then work with live Salesforce data in Excel.
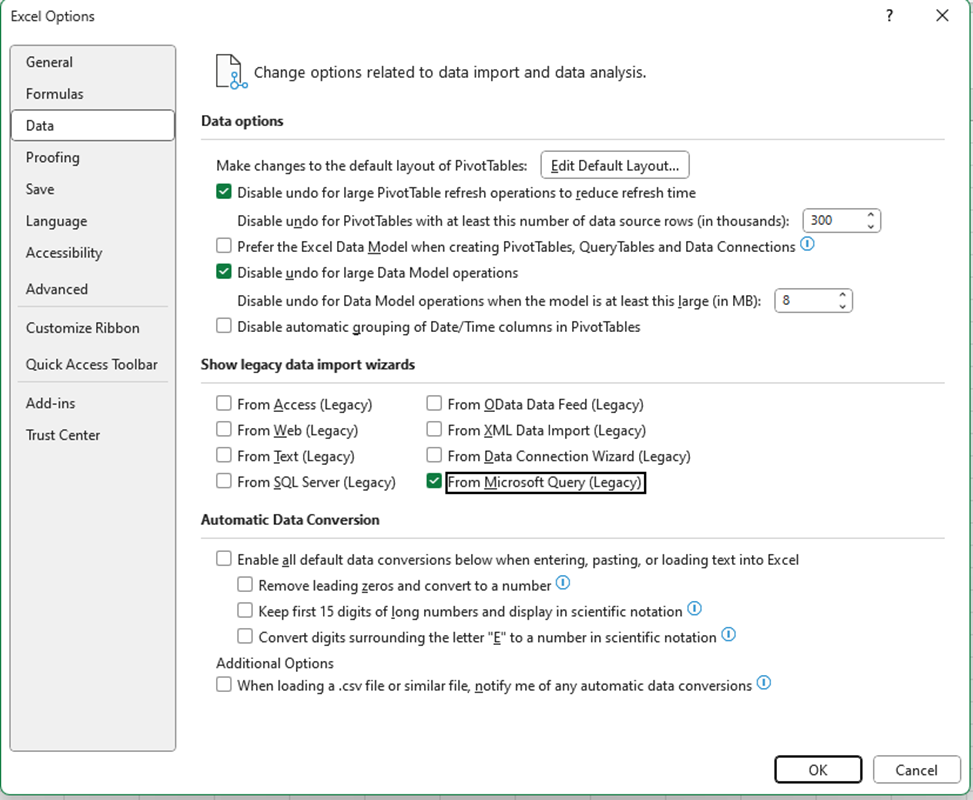
NOTE: In recent versions of Excel, Microsoft Query is not visible by default. To enable visibility, Navigate to Options > Data and check From Microsoft Query (Legacy) under the Show legacy data import wizards section.
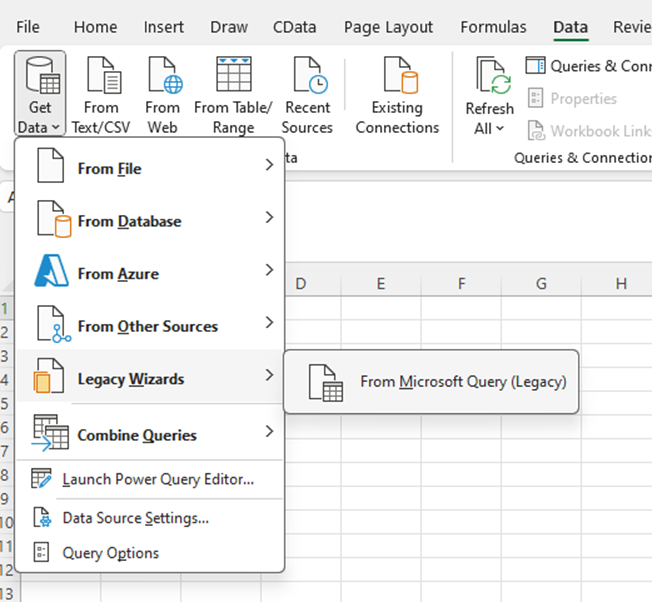
- In Excel, open the Data tab and choose Get Data -> Legacy Wizards -> From Microsoft Query (Legacy).
![Open Microsoft Query from the Data tab.]()
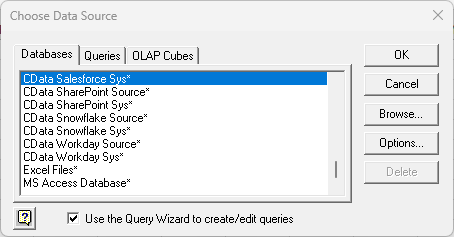
- Choose the Salesforce DSN. Select the option to use Query Wizard to create/edit queries.
![The list of available ODBC DSNs in the Choose Data Source dialog.]()
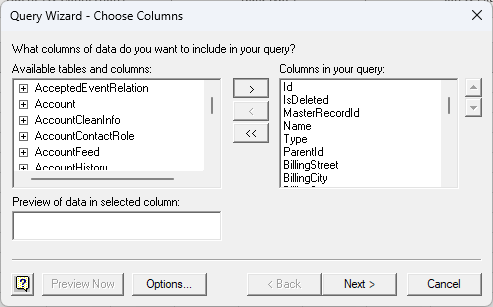
- In the Query Wizard, expand the node for the table you would like to import into your spreadsheet. Select the columns you want to import and click the arrow to add them to your query. Alternatively, select the table name to add all columns for that table.
![Available tables and columns in the Choose Columns step of the Query Wizard. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
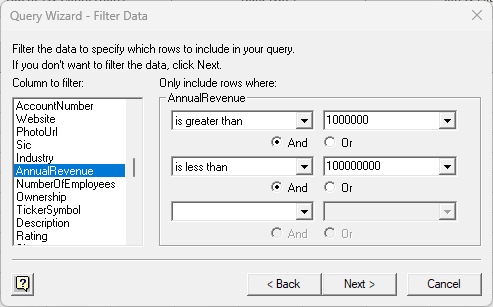
- The Filter Data page allows you to specify criteria. For example, you can limit results by setting a date range.
![The Filter Data step of the Query Wizard. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
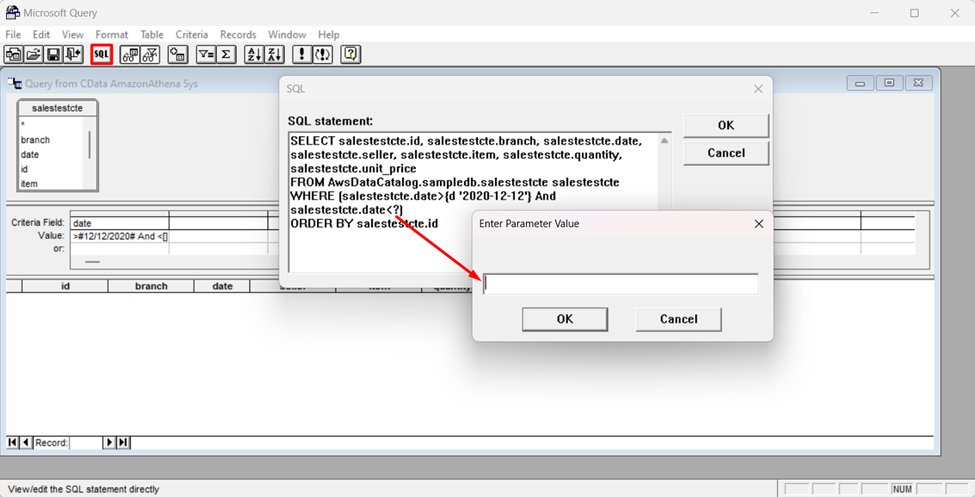
- If you want to use parameters in your query, select the option to edit the query in Microsoft Query.
To set a parameter in the query, you will need to modify the SQL statement directly. To do this, click the SQL button in the Query Editor. If you set filter criteria earlier, you should have a WHERE clause already in the query.
To use a parameter, use a "?" character as the wildcard character for a field's value in the WHERE clause. For example, if you are importing the Account, you can set "Name=?".
- Close the SQL dialog when you are finished editing the SQL statement. You will be prompted to enter a parameter value. In the next step, you will select a cell to provide this value. So, leave the box in the dialog blank.
![The generated SQL statement. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
-
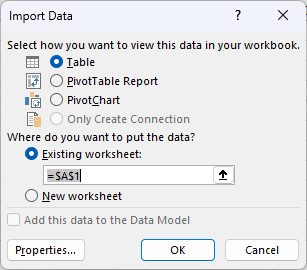
Click File -> Return Data to Microsoft Excel. The Import Data dialog is displayed. Enter a cell where results should be imported.
![The Import Data dialog.]()
- Close the Import Data dialog. You will be prompted to enter a parameter value. Click the button next to the parameter box to select a cell. Select the option to automatically refresh the spreadsheet when the value changes.