Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Query SAP Ariba Source Data as a MySQL Database in Node.js
Execute MySQL queries against SAP Ariba Source data from Node.js.
You can use the SQL Gateway from the ODBC Driver for SAP Ariba Source to query SAP Ariba Source data through a MySQL interface. Follow the procedure below to start the MySQL remoting service of the SQL Gateway and start querying using Node.js.
Connect to SAP Ariba Source Data
If you have not already done so, provide values for the required connection properties in the data source name (DSN). You can use the built-in Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to configure the DSN. This is also the last step of the driver installation. See the "Getting Started" chapter in the help documentation for a guide to using the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure a DSN.
In order to connect with SAP Ariba Source, set the following:
- API: Specify which API you would like the provider to retrieve SAP Ariba data from. Select the Supplier, Sourcing Project Management, or Contract API based on your business role (possible values are SupplierDataAPIWithPaginationV4, SourcingProjectManagementAPIV2, or ContractAPIV1).
- DataCenter: The data center where your account's data is hosted.
- Realm: The name of the site you want to access.
- Environment: Indicate whether you are connecting to a test or production environment (possible values are TEST or PRODUCTION).
If you are connecting to the Supplier Data API or the Contract API, additionally set the following:
- User: Id of the user on whose behalf API calls are invoked.
- PasswordAdapter: The password associated with the authenticating User.
If you're connecting to the Supplier API, set ProjectId to the Id of the sourcing project you want to retrieve data from.
Authenticating with OAuth
After setting connection properties, you need to configure OAuth connectivity to authenticate.
- Set AuthScheme to OAuthClient.
- Register an application with the service to obtain the APIKey, OAuthClientId and OAuthClientSecret.
For more information on creating an OAuth application, refer to the Help documentation.
Automatic OAuth
After setting the following, you are ready to connect:
-
APIKey: The Application key in your app settings.
OAuthClientId: The OAuth Client Id in your app settings.
OAuthClientSecret: The OAuth Secret in your app settings.
When you connect, the provider automatically completes the OAuth process:
- The provider obtains an access token from SAP Ariba and uses it to request data.
- The provider refreshes the access token automatically when it expires.
- The OAuth values are saved in memory relative to the location specified in OAuthSettingsLocation.
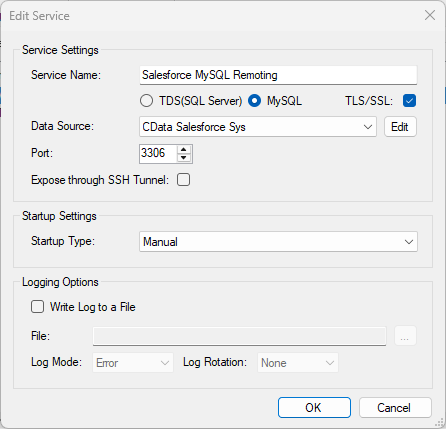
Configure the SQL Gateway
See the SQL Gateway Overview to set up connectivity to SAP Ariba Source data as a virtual MySQL database. You will configure a MySQL remoting service that listens for MySQL requests from clients. The service can be configured in the SQL Gateway UI.
Query SAP Ariba Source from Node.js
The following example shows how to define a connection and execute queries to SAP Ariba Source with the mysql module. You will need the following information:
- Host name or address, and port: The machine and port where the MySQL remoting service is listening for MySQL connections.
- Username and password: The username and password of a user you authorized on the Users tab of the SQL Gateway.
- Database name: The DSN you configured for the MySQL remoting service.
Connect to SAP Ariba Source data and start executing queries with the code below:
var mysql = require('mysql');
var connection = mysql.createConnection({
host : 'localhost',
database : 'CData SAPAribaSource Sys',
port : '3306',
user : 'mysql_user',
password : 'test'
});
connection.connect();
connection.query('SELECT * FROM Vendors', function(err, rows, fields) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(rows);
});
connection.end();

