Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Connect to ServiceNow Data in CloverDX (formerly CloverETL)
Transfer ServiceNow data using the visual workflow in the CloverDX data integration tool.
The CData JDBC Driver for ServiceNow enables you to use the data transformation components in CloverDX (formerly CloverETL) to work with ServiceNow as sources. In this article, you will use the JDBC Driver for ServiceNow to set up a simple transfer into a flat file. The CData JDBC Driver for ServiceNow enables you to use the data transformation components in CloverDX (formerly CloverETL) to work with ServiceNow as sources. In this article, you will use the JDBC Driver for ServiceNow to set up a simple transfer into a flat file.
About ServiceNow Data Integration
CData simplifies access and integration of live ServiceNow data. Our customers leverage CData connectivity to:
- Get optimized performance since CData uses the REST API for data and the SOAP API for schema.
- Read, write, update, and delete ServiceNow objects like Schedules, Timelines, Questions, Syslogs and more.
- Use SQL stored procedures for actions like adding items to a cart, submitting orders, and downloading attachments.
- Securely authenticate with ServiceNow, including basic (username and password), OKTA, ADFS, OneLogin, and PingFederate authentication schemes.
Many users access live ServiceNow data from preferred analytics tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Excel, and use CData solutions to integrate ServiceNow data with their database or data warehouse.
Getting Started
Connect to ServiceNow as a JDBC Data Source
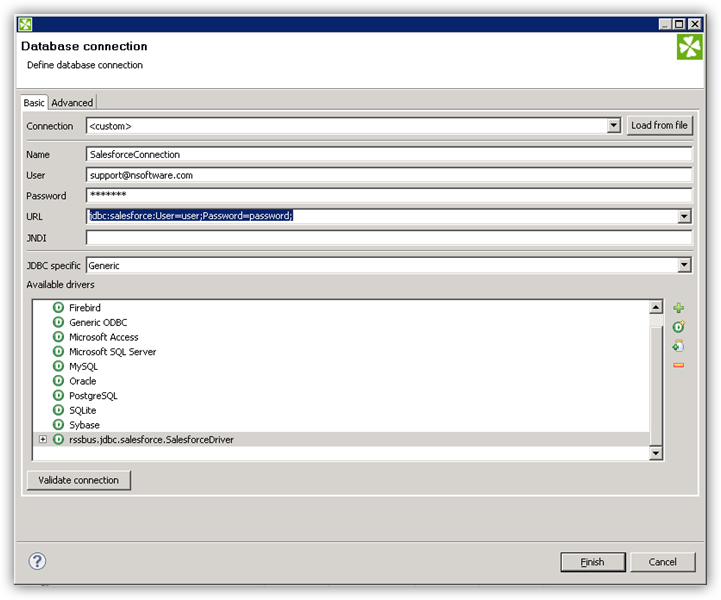
- Create the connection to ServiceNow data. In a new CloverDX graph, right-click the Connections node in the Outline pane and click Connections -> Create Connection. The Database Connection wizard is displayed.
- Click the plus icon to load a driver from a JAR. Browse to the lib subfolder of the installation directory and select the cdata.jdbc.servicenow.jar file.
- Enter the JDBC URL.
ServiceNow uses the OAuth 2.0 authentication standard. To authenticate using OAuth, you will need to register an OAuth app with ServiceNow to obtain the OAuthClientId and OAuthClientSecret connection properties. In addition to the OAuth values, you will need to specify the Instance, Username, and Password connection properties.
See the "Getting Started" chapter in the help documentation for a guide on connecting to ServiceNow.
Built-in Connection String Designer
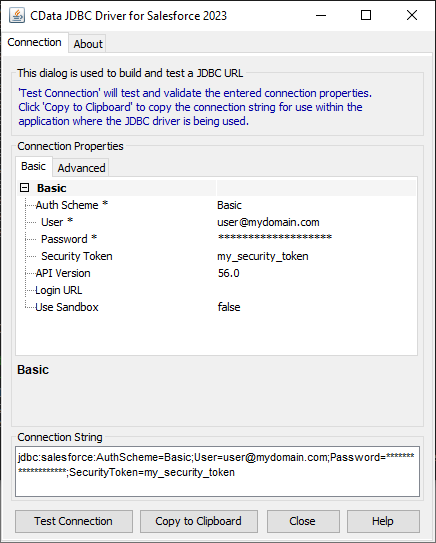
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the ServiceNow JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.servicenow.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
A typical JDBC URL is below:
jdbc:servicenow:OAuthClientId=MyOAuthClientId;OAuthClientSecret=MyOAuthClientSecret;Username=MyUsername;Password=MyPassword;Instance=MyInstance;InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH
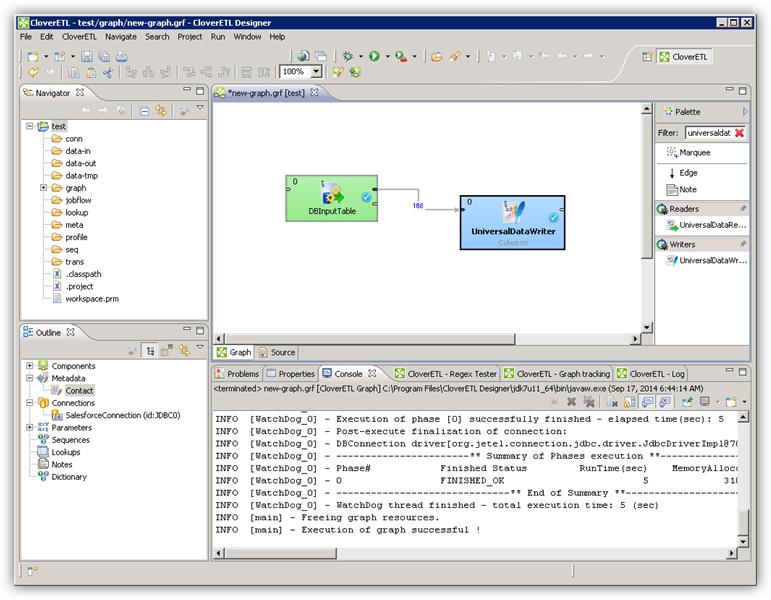
Query ServiceNow Data with the DBInputTable Component
- Drag a DBInputTable from the Readers selection of the Palette onto the job flow and double-click it to open the configuration editor.
- In the DB connection property, select the ServiceNow JDBC data source from the drop-down menu.
- Enter the SQL query. For example:
SELECT sys_id, priority FROM incident
Write the Output of the Query to a UniversalDataWriter
- Drag a UniversalDataWriter from the Writers selection onto the jobflow.
- Double-click the UniversalDataWriter to open the configuration editor and add a file URL.
- Right-click the DBInputTable and then click Extract Metadata.
- Connect the output port of the DBInputTable to the UniversalDataWriter.
- In the resulting Select Metadata menu for the UniversalDataWriter, choose the incident table. (You can also open this menu by right-clicking the input port for the UniversalDataWriter.)
- Click Run to write to the file.