Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Create Data Visualizations in Cognos BI with SharePoint Data
Access SharePoint data as an ODBC data source in Cognos Business Intelligence and create data visualizations in Cognos Report Studio.
You can use the CData ODBC driver for SharePoint to integrate SharePoint data with the drag-and-drop style of Cognos Report Studio. This article describes both a graphical approach to create data visualizations, with no SQL required, as well as how to execute any SQL query supported by SharePoint.
About SharePoint Data Integration
Accessing and integrating live data from SharePoint has never been easier with CData. Customers rely on CData connectivity to:
- Access data from a wide range of SharePoint versions, including Windows SharePoint Services 3.0, Microsoft Office SharePoint Server 2007 and above, and SharePoint Online.
- Access all of SharePoint thanks to support for Hidden and Lookup columns.
- Recursively scan folders to create a relational model of all SharePoint data.
- Use SQL stored procedures to upload and download documents and attachments.
Most customers rely on CData solutions to integrate SharePoint data into their database or data warehouse, while others integrate their SharePoint data with preferred data tools, like Power BI, Tableau, or Excel.
For more information on how customers are solving problems with CData's SharePoint solutions, refer to our blog: Drivers in Focus: Collaboration Tools.
Getting Started
Configure and Publish the Data Source
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
Set the URL property to the base SharePoint site or to a sub-site. This allows you to query any lists and other SharePoint entities defined for the site or sub-site.
The User and Password properties, under the Authentication section, must be set to valid SharePoint user credentials when using SharePoint On-Premise.
If you are connecting to SharePoint Online, set the SharePointEdition to SHAREPOINTONLINE along with the User and Password connection string properties. For more details on connecting to SharePoint Online, see the "Getting Started" chapter of the help documentation
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
If you are running Cognos from a 64-bit machine and want to modify the DSN or create other SharePoint DSNs, you must use a system DSN. You will also need to open the 32-bit ODBC Data Source Administrator. You can open it with the following command:
C:\Windows\sysWOW64\odbcad32.exe
After creating a DSN, you can then publish the data source:
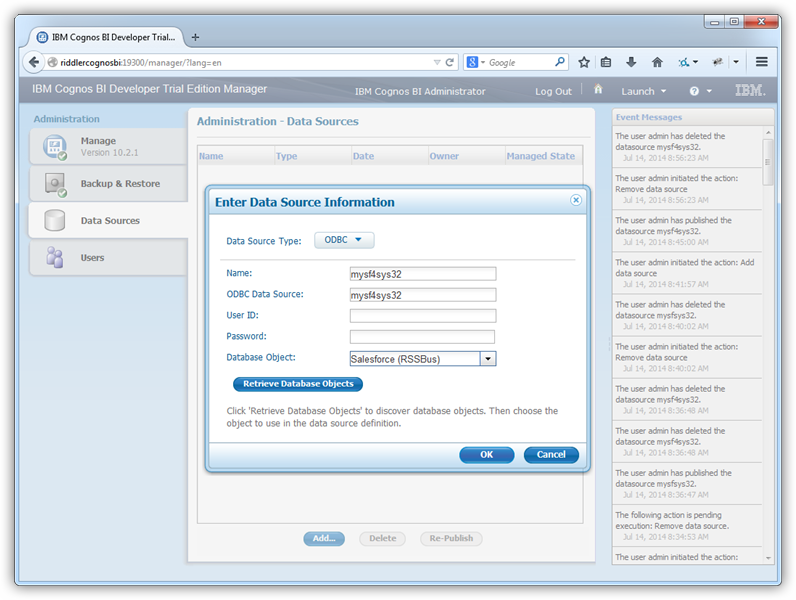
- Open Cognos Administration and click Data Source Connections to add a new data source:
-
Select the ODBC option and enter the DSN, CData SharePoint Sys, and a user-friendly name.
- Click Retrieve Objects and choose the CData SharePoint database object.
![The DSN used to add the data source. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
Add Data Visualizations to a Report
You can now create reports on SharePoint data in Cognos Report Studio by dragging and dropping table columns from the Source Explorer onto report objects. The sections below show how to create a simple report with a chart that shows up-to-date data.
As you build the report, Cognos Report Studio will generate SQL queries and rely on the driver to execute them. The driver will convert queries into requests to the SharePoint API. To execute queries to the live SharePoint data, the driver depends on the capabilities of the underlying API.
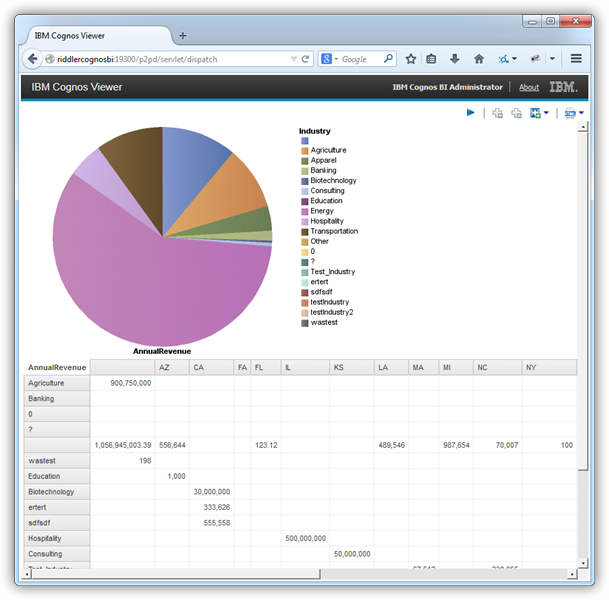
Create a Chart Based on an Aggregate
You can populate almost any report object in Cognos with SharePoint data by simply dragging and dropping columns from the Source Explorer onto the dimensions of the object. The column in the Series dimension of the chart is automatically grouped.
Additionally, Cognos sets a logical default aggregate function for the measure dimension based on the data type. For this example, override the default by clicking the Revenue column in the Data Items tab and set the Aggregate Function property to Not Applicable. The Rollup Aggregate Function property must be set to Automatic.
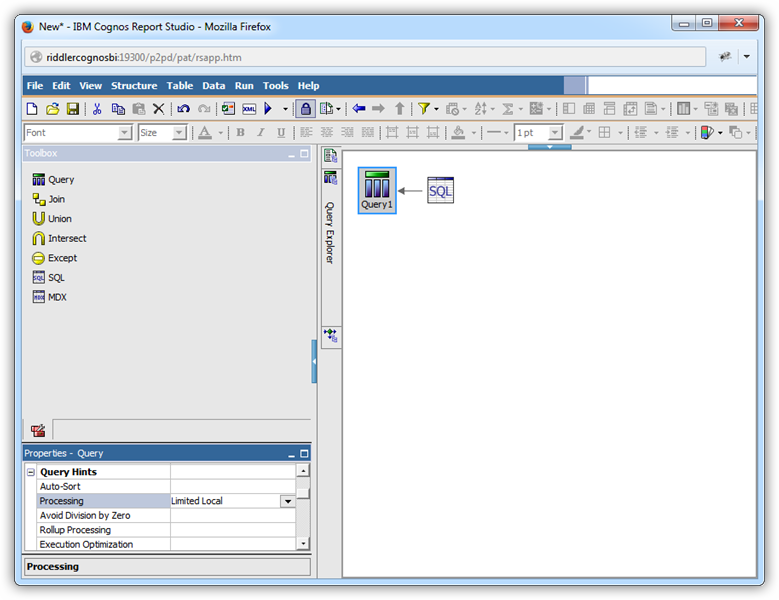
Convert a Query Object to SQL
When you know the query you need, or if you want to adjust the generated query, convert a query object into an SQL statement. After a query has been converted to SQL, the UI controls are not available for the query object. Follow the procedure below to populate a chart with user-defined SQL.
Cognos will rely on the driver to execute the user-defined query. Using the driver's SQL engine ensures that queries will always return up-to-date results, as there is no cached copy of the data.
- Hover over the Query Explorer and click the Queries folder to display the query objects in your report.
-
If you want to edit the autogenerated query, click the button in the Generated SQL property for the query object. In the resulting dialog, click Convert.
If you want to enter a new SQL statement, drop an SQL object in-line with the query object.
- Modify the properties for the SQL object: Select the SharePoint data source in the SQL properties and set the SQL Syntax property to Native.
Click the button in the SQL property and enter the SQL query in the resulting dialog. This example uses the query below:
SELECT Name, Revenue FROM MyCustomListModify the properties for the query object: Set the Processing property to "Limited Local". This value is required to convert a query object to SQL.
![A query object created from an SQL statement.]()
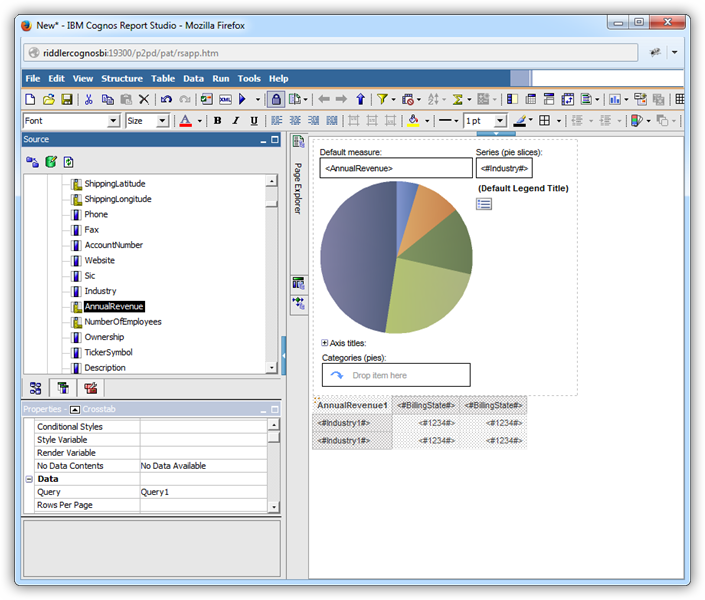
Fill a Chart with the Results of a Query
You can now access the results of the SQL query as objects in the Data Items tab. Follow the procedure below to create a chart with the results; for example, the Revenue for each Name from the MyCustomList table.
- Return to the page by hovering over the Page Explorer and then clicking the page object.
- Drag a pie chart from the toolbox onto the workspace.
- In the properties for the chart, set the Query property to the name of the query you created above.
- Click the Data Items tab and drag columns onto the x- and y-axes. In this example, drag the Name column to the Series (pie slices) box and the Revenue column to the Default Measure box.
-
Modify the default properties for the Default Measure (the Revenue values): In the Aggregate Function box, select the Total option.
Run the report to add the results of the query.