Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →How to work with SQL Server Data in Apache Spark using SQL
Access and process SQL Server Data in Apache Spark using the CData JDBC Driver.
Apache Spark is a fast and general engine for large-scale data processing. When paired with the CData JDBC Driver for SQL Server, Spark can work with live SQL Server data. This article describes how to connect to and query SQL Server data from a Spark shell.
The CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live SQL Server data due to optimized data processing built into the driver. When you issue complex SQL queries to SQL Server, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to SQL Server and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations (often SQL functions and JOIN operations) client-side. With built-in dynamic metadata querying, you can work with and analyze SQL Server data using native data types.
Install the CData JDBC Driver for SQL Server
Download the CData JDBC Driver for SQL Server installer, unzip the package, and run the JAR file to install the driver.
Start a Spark Shell and Connect to SQL Server Data
- Open a terminal and start the Spark shell with the CData JDBC Driver for SQL Server JAR file as the jars parameter:
$ spark-shell --jars /CData/CData JDBC Driver for SQL Server/lib/cdata.jdbc.sql.jar - With the shell running, you can connect to SQL Server with a JDBC URL and use the SQL Context load() function to read a table.
Connecting to Microsoft SQL Server
Connect to Microsoft SQL Server using the following properties:
- Server: The name of the server running SQL Server.
- User: The username provided for authentication with SQL Server.
- Password: The password associated with the authenticating user.
- Database: The name of the SQL Server database.
Connecting to Azure SQL Server and Azure Data Warehouse
You can authenticate to Azure SQL Server or Azure Data Warehouse by setting the following connection properties:
- Server: The server running Azure. You can find this by logging into the Azure portal and navigating to "SQL databases" (or "SQL data warehouses") -> "Select your database" -> "Overview" -> "Server name."
- User: The name of the user authenticating to Azure.
- Password: The password associated with the authenticating user.
- Database: The name of the database, as seen in the Azure portal on the SQL databases (or SQL warehouses) page.
Built-in Connection String Designer
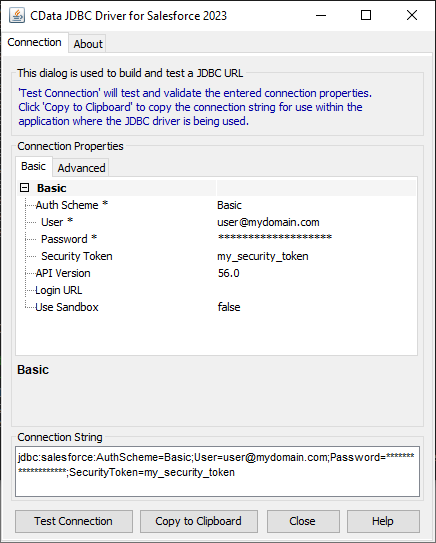
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the SQL Server JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.sql.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
Configure the connection to SQL Server, using the connection string generated above.
scala> val sql_df = spark.sqlContext.read.format("jdbc").option("url", "jdbc:sql:User=myUser;Password=myPassword;Database=NorthWind;Server=myServer;Port=1433;").option("dbtable","Orders").option("driver","cdata.jdbc.sql.SQLDriver").load() - Once you connect and the data is loaded you will see the table schema displayed.
Register the SQL Server data as a temporary table:
scala> sql_df.registerTable("orders")-
Perform custom SQL queries against the Data using commands like the one below:
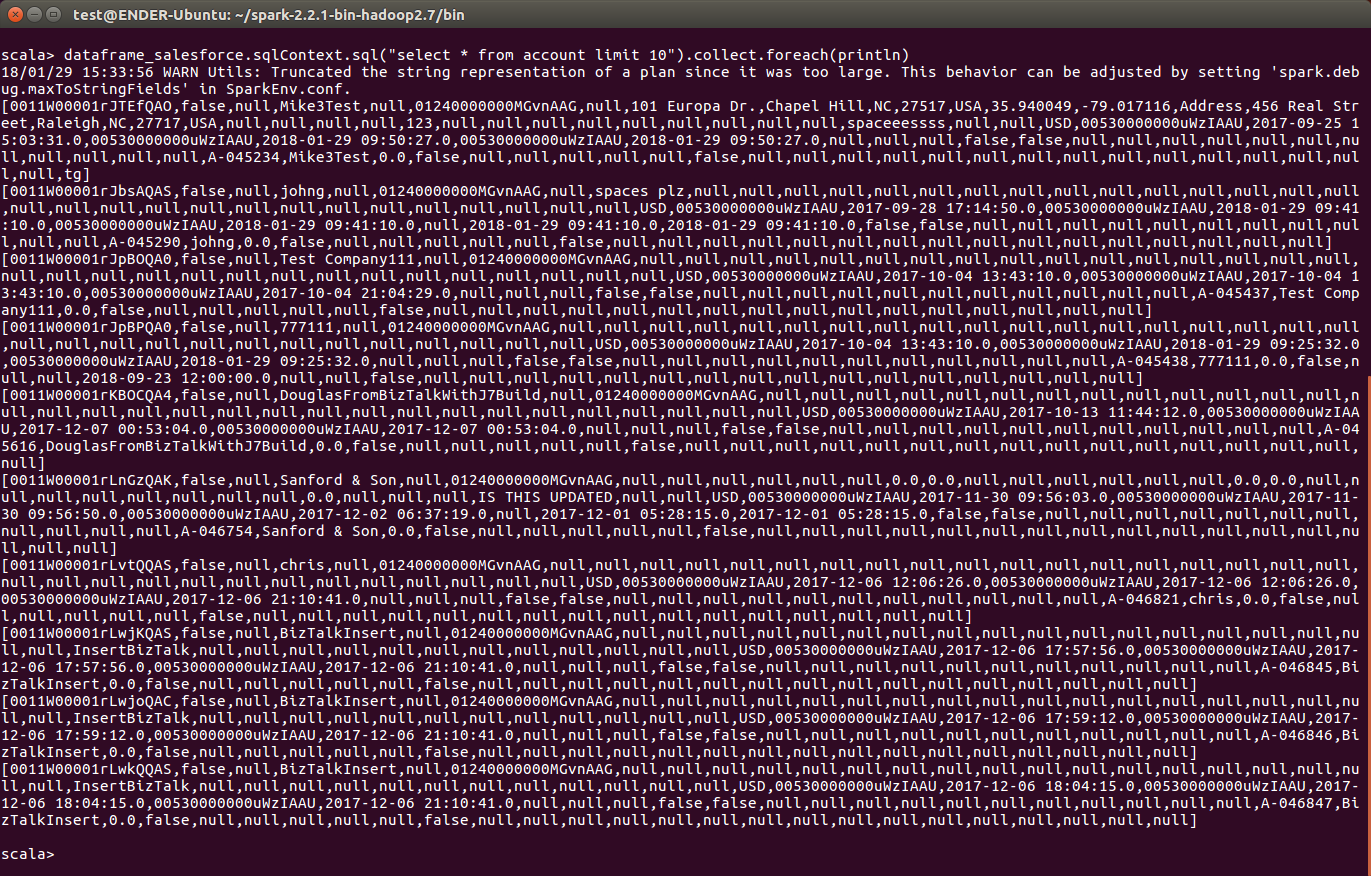
scala> sql_df.sqlContext.sql("SELECT ShipName, Freight FROM Orders WHERE ShipCountry = USA").collect.foreach(println)You will see the results displayed in the console, similar to the following:
![Data in Apache Spark (Salesforce is shown)]()
Using the CData JDBC Driver for SQL Server in Apache Spark, you are able to perform fast and complex analytics on SQL Server data, combining the power and utility of Spark with your data. Download a free, 30 day trial of any of the 200+ CData JDBC Drivers and get started today.