Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Access Live WooCommerce Data in AWS Lambda
Connect to live WooCommerce data in AWS Lambda using the CData JDBC Driver.
AWS Lambda is a compute service that lets you build applications that respond quickly to new information and events. AWS Lambda functions can work with live WooCommerce data when paired with the CData JDBC Driver for WooCommerce. This article describes how to connect to and query WooCommerce data from an AWS Lambda function built in Eclipse.
At the time this article was written (June 2022), Eclipse version 2019-12 and Java 8 were the highest versions supported by the AWS Toolkit for Eclipse.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live WooCommerce data. When you issue complex SQL queries to WooCommerce, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to WooCommerce and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). In addition, its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze WooCommerce data using native data types.
Gather Connection Properties and Build a Connection String
WooCommerce supports the following authentication methods: one-legged OAuth1.0 Authentication and standard OAuth2.0 Authentication.
Connecting using one-legged OAuth 1.0 Authentication
Specify the following properties (NOTE: the below credentials are generated from WooCommerce settings page and should not be confused with the credentials generated by using WordPress OAuth2.0 plugin):
- ConsumerKey
- ConsumerSecret
Connecting using WordPress OAuth 2.0 Authentication
After having configured the plugin, you may connect to WooCommerce by providing the following connection properties:
In either case, you will need to set the Url property to the URL of the WooCommerce instance.
NOTE: To use the JDBC driver in an AWS Lambda function, you will need a license (full or trial) and a Runtime Key (RTK). For more information on obtaining this license (or a trial), contact our sales team.
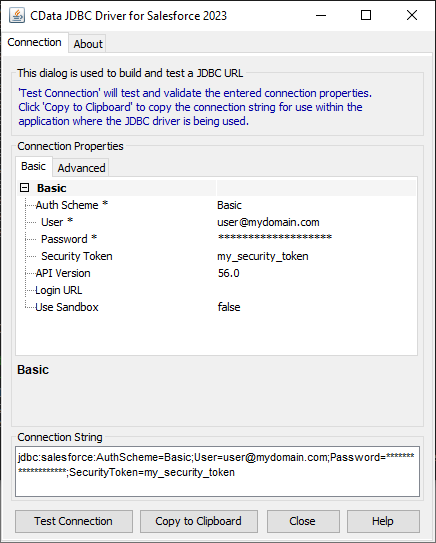
For assistance constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the WooCommerce JDBC Driver. Double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command line.
Fill in the connection properties (including the RTK) and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
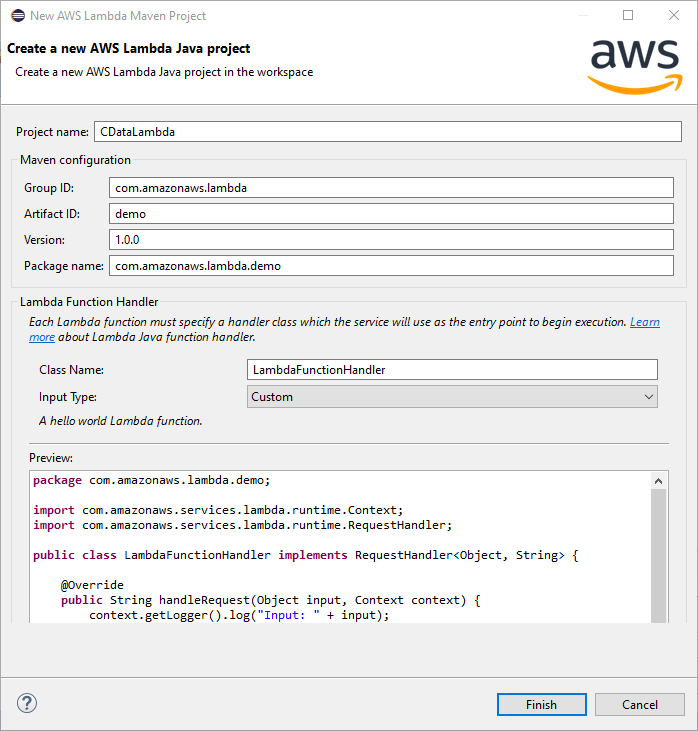
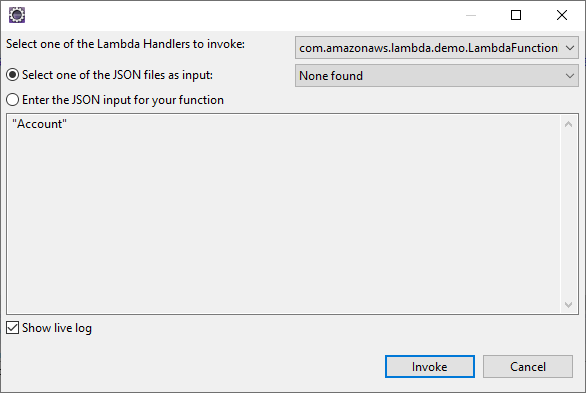
Create a new AWS Lambda Java Project in Eclipse using the AWS Toolkit for Eclipse. You can follow the tutorial from AWS (amazon.com). For this article, set the Input Type for the project to "Custom" so we can enter a table name as the input. Replace the body of the handleRequest method with the code below. Be sure to fill in the connection string in the DriverManager.getConnection method call. Once you build the function in Eclipse, you are ready to upload and run the function. In this article, the output is written to the AWS logs, but you can use this is a template to implement you own custom business logic to work with WooCommerce data in AWS Lambda functions.
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for WooCommerce and start working with your live WooCommerce data in AWS Lambda. Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.
Built-in Connection String Designer
java -jar cdata.jdbc.woocommerce.jar
Create an AWS Lambda Function
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
String query = "SELECT * FROM " + input;
try {
Class.forName("cdata.jdbc.woocommerce.WooCommerceDriver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
context.getLogger().log("Error: class not found");
}
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:cdata:woocommerce:RTK=52465...;Url=https://example.com/; ConsumerKey=ck_ec52c76185c088ecaa3145287c8acba55a6f59ad; ConsumerSecret=cs_9fde14bf57126156701a7563fc87575713c355e5; InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH");
} catch (SQLException ex) {
context.getLogger().log("Error getting connection: " + ex.getMessage());
} catch (Exception ex) {
context.getLogger().log("Error: " + ex.getMessage());
}
if(connection != null)
{
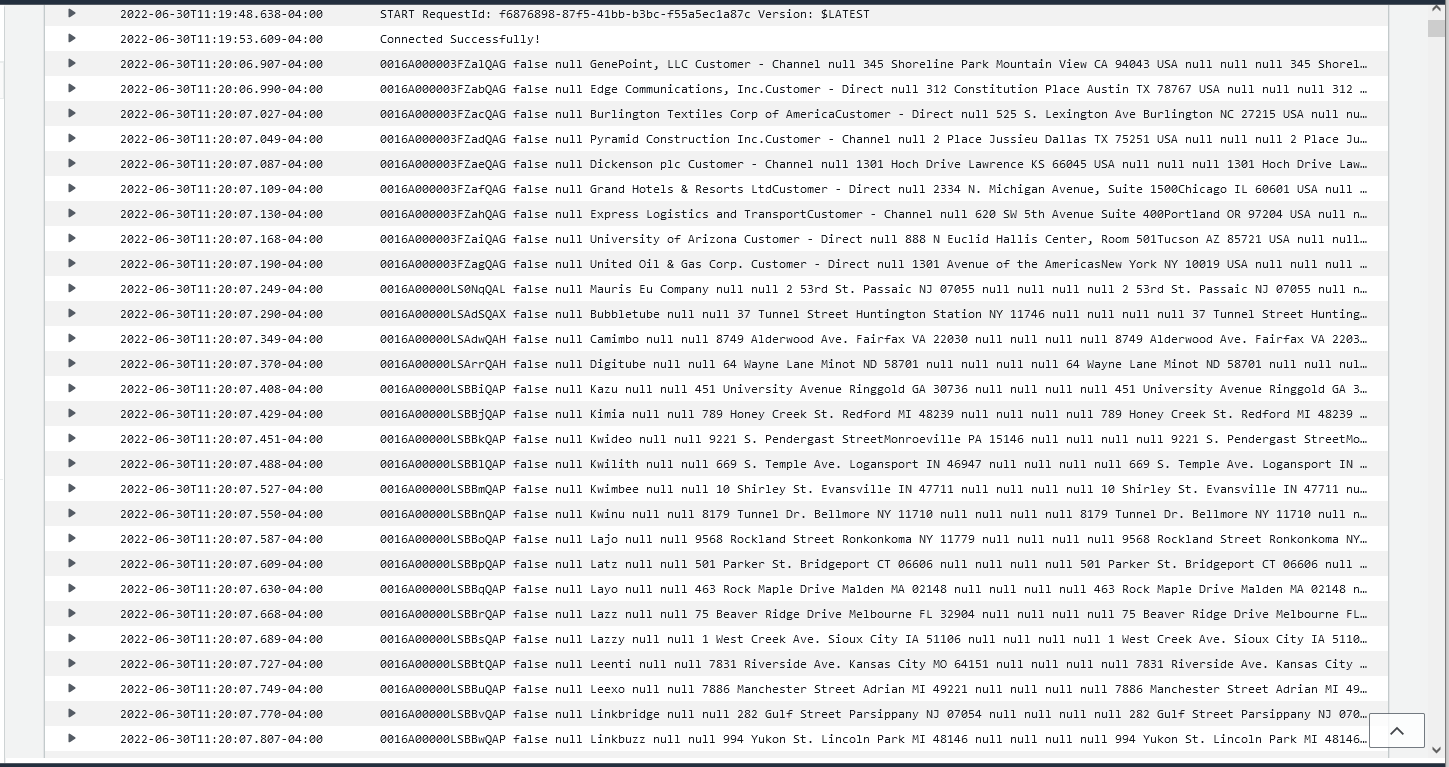
context.getLogger().log("Connected Successfully!\n");
}
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try
{
//executing query
Statement stmt = connection.createStatement();
resultSet = stmt.executeQuery(query);
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int numCols = metaData.getColumnCount();
//printing the results
while(resultSet.next())
{
for(int i = 1; i <= numCols; i++)
{
System.out.printf("%-25s", (resultSet.getObject(i) != null) ? resultSet.getObject(i).toString().replaceAll("\n", "") : null );
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
catch (SQLException ex)
{
System.out.println("SQL Exception: " + ex.getMessage());
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
System.out.println("General exception: " + ex.getMessage());
}
String output = "query: " + query + " complete";
return output;
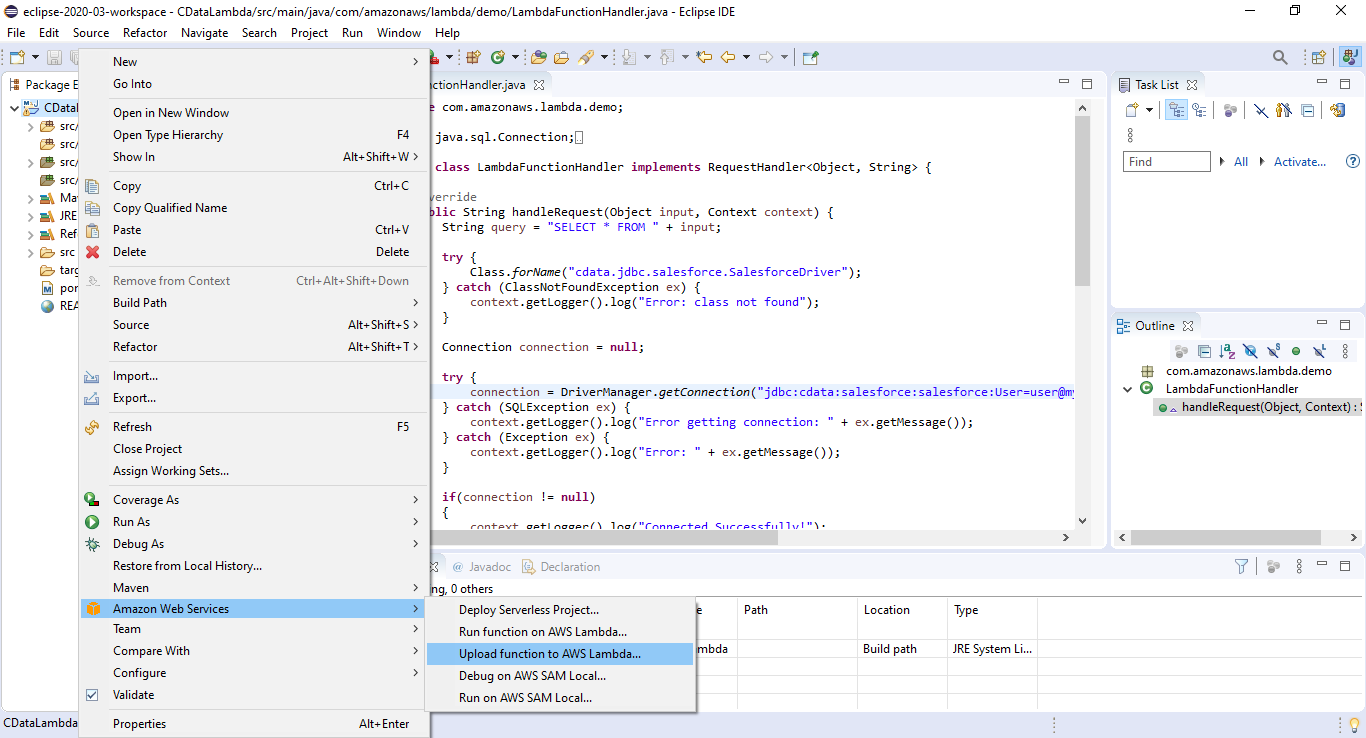
Deploy and Run the Lambda Function
Free Trial & More Information

