Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Perform Batch Operations with Workday Data in Apache NiFi
Connect to Workday data and perform batch operations in Apache NiFi using the CData JDBC Driver.
Apache NiFi supports powerful and scalable directed graphs of data routing, transformation, and system mediation logic. When paired with the CData JDBC Driver for Workday, NiFi can work with live Workday data. This article shows how to read data from a CSV file and perform batch operations (INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE) using the CData JDBC Driver for Workday data in Apache NiFi (version 1.9.0 or later).
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live Workday data. When you issue complex SQL queries to Workday, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Workday and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). Its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze Workday data using native data types.
About Workday Data Integration
CData provides the easiest way to access and integrate live data from Workday. Customers use CData connectivity to:
- Access the tables and datasets you create in Prism Analytics Data Catalog, working with the native Workday data hub without compromising the fidelity of your Workday system.
- Access Workday Reports-as-a-Service to surface data from departmental datasets not available from Prism and datasets larger than Prism allows.
- Access base data objects with WQL, REST, or SOAP, getting more granular, detailed access but with the potential need for Workday admins or IT to help craft queries.
Users frequently integrate Workday with analytics tools such as Tableau, Power BI, and Excel, and leverage our tools to replicate Workday data to databases or data warehouses. Access is secured at the user level, based on the authenticated user's identity and role.
For more information on configuring Workday to work with CData, refer to our Knowledge Base articles: Comprehensive Workday Connectivity through Workday WQL and Reports-as-a-Service & Workday + CData: Connection & Integration Best Practices.
Getting Started
Generate a JDBC URL
We need a JDBC URL to connect to Workday data from Apachi NiFi.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Workday JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.workday.jar
Fill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
To connect to Workday, users need to find the Tenant and BaseURL and then select their API type.
Obtaining the BaseURL and Tenant
To obtain the BaseURL and Tenant properties, log into Workday and search for "View API Clients." On this screen, you'll find the Workday REST API Endpoint, a URL that includes both the BaseURL and Tenant.
The format of the REST API Endpoint is: https://domain.com/subdirectories/mycompany, where:
- https://domain.com/subdirectories/ is the BaseURL.
- mycompany (the portion of the url after the very last slash) is the Tenant.
Using ConnectionType to Select the API
The value you use for the ConnectionType property determines which Workday API you use. See our Community Article for more information on Workday connectivity options and best practices.
| API | ConnectionType Value |
|---|---|
| WQL | WQL |
| Reports as a Service | Reports |
| REST | REST |
| SOAP | SOAP |
Authentication
Your method of authentication depends on which API you are using.
- WQL, Reports as a Service, REST: Use OAuth authentication.
- SOAP: Use Basic or OAuth authentication.
See the Help documentation for more information on configuring OAuth with Workday.
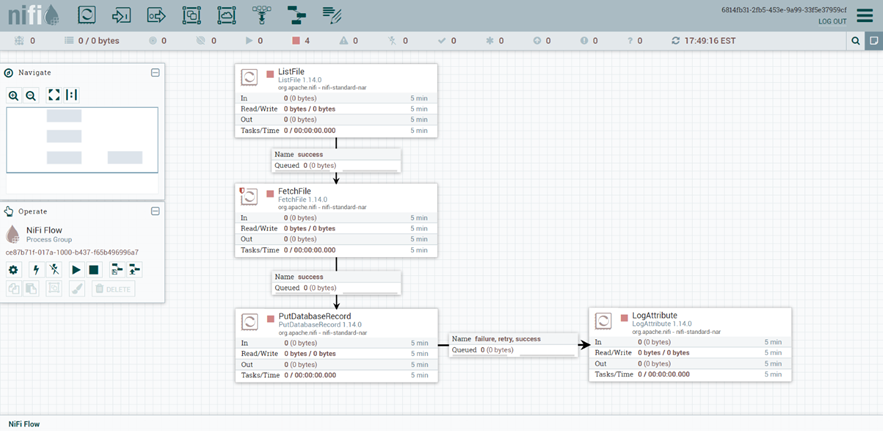
Batch Operations (INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE) in Apache NiFi
The sample flow presented below is based on the following NiFi Processors:
- ListFile - Retrieves a listing of files from the local filesystem and creates a FlowFile for each retrieved file.
- FetchFile - Reads the content of the FlowFile received from the ListFile processor.
- PutDatabaseRecord - Uses a specified RecordReader to input records from a flow file coming from the FetchFile processor. These records are translated to SQL statements and executed as a single transaction.
- LogAttribute - Emits attributes of the FlowFile at the specified log level.
This is what our finished product looks like:
Disclaimers
1. The column names of the CSV file must match the column names of the data source table records to be inserted/updated/deleted.
2. Apache NiFi versions earlier than 1.9.0 do not support the Maximum Batch Size property in the PutDatabaseRecord processor.
Configurations
In order to perform batch INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE, the NiFi Processors should be configured similar to the following:
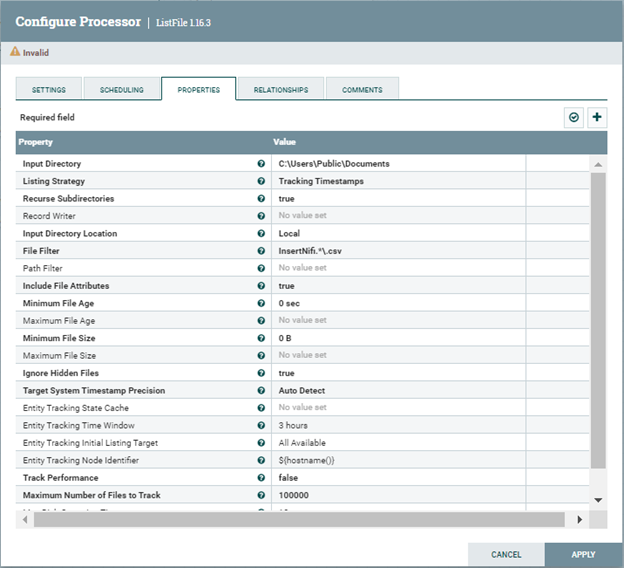
- Configure the ListFile processor: Set the Input Directory property to the local folder path from where to pull the CSV files. Set the File Filter property to a regular expression to pick up only the files whose names match the expression. i.e., if the CSV file's full path is C:\Users\Public\Documents\InsertNiFi.csv, the properties should be configured like in the following image:
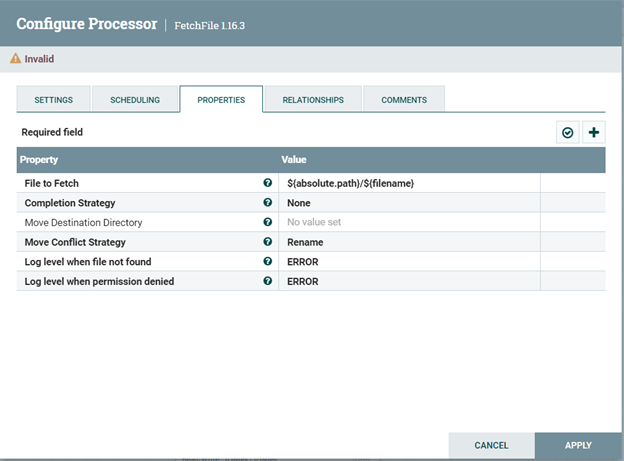
- Configure the FetchFile processor Leave the FetchFile processor's property configurations to their default values:
- Configure the PutDatabaseRecord processor
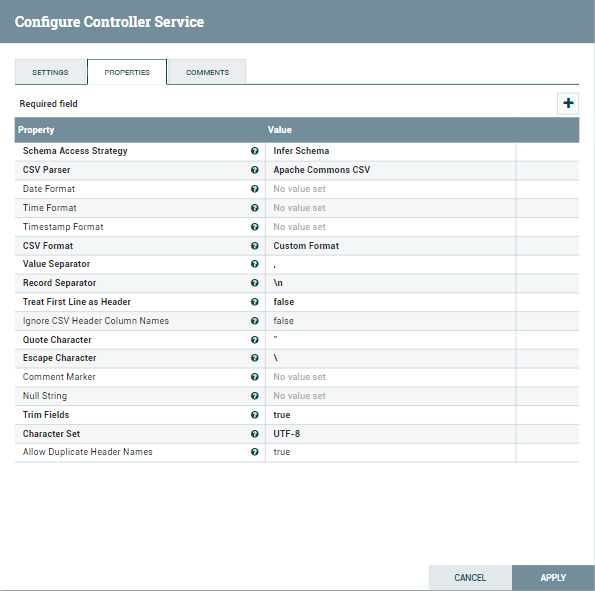
- Set the Record Reader property to a CSV Reader Controller Service. Configure the CSV Reader Controller Service to match the format of your CSV file.
- Set the Statement Type property to INSERT.
-
Set the Database Connection Pooling Service to the DBCPConnection Pool that
holds the driver configuration. Please note that the driver should be configured
to use Bulk API.
Property Value Database Connection URL jdbc:workday:User=myuser;Password=mypassword;Tenant=mycompany_gm1;BaseURL=https://wd3-impl-services1.workday.com;ConnectionType=WQL;InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH Database Driver Class Name cdata.jdbc.workday.WorkdayDriver - Set the Catalog Name property to the name of the catalog that your table is part of.
- Set the Schema Name property to the name of the schema that your table is part of.
- Set the Table Name property to the name of the table that you want to INSERT into.
-
Set the Maximum Batch Size property to the maximum number of records that you want to be included in a single batch.
![config for PutDatabaseRecord-INSERT]()
-
Set the Record Reader property to a CSV Reader Controller Service. Configure the CSV Reader Controller Service to match the format of your CSV file.
![config for PutDatabaseRecord-INSERT]()
![config for PutDatabaseRecord-INSERT]()
- Set the Statement Type property to UPDATE.
- Set the Database Connection Pooling Service to the DBCPConnection Pool that holds the driver configuration. Please note that the driver should be configured to use Bulk API. Use the same Database Connection URL format as seen above.
- Set the Catalog Name property to the name of the catalog that your table is part of.
- Set the Schema Name property to the name of the schema that your table is part of.
- Set the Table Name property to the name of the table that you want to UPDATE.
- Set the Update Keys property to the name of the columns that are required for an UPDATE.
-
Set the Maximum Batch Size property to the maximum number of records that you want to be included in a single batch.
![config for PutDatabaseRecord-UPDATE]()
-
Set the Record Reader property to a CSV Reader Controller Service. Configure the CSV Reader Controller Service to match the format of your CSV file.
![config for PutDatabaseRecord-UPDATE]()
![config for PutDatabaseRecord-UPDATE]()
- Set the Statement Type property to DELETE.
- Set the Database Connection Pooling Service to the DBCPConnection Pool that holds the driver configuration. Please note that the driver should be configured to use Bulk API. Use the same Database Connection URL format as seen above.
- Set the Catalog Name property to the name of the catalog that your table is part of.
- Set the Schema Name property to the name of the schema that your table is part of.
- Set the Table Name property to the name of the table that you want to UPDATE.
- In comparison to INSERT and UPDATE statement types, the DELETE operation does not expose a Maximum Batch Size property. However, the operations are still processed in batches. If not changed, the maximum number of records per batch is 2000, adhering to the default value. In order to change the value of the Maximum Batch Size used for DELETE operations, change the statement type to INSERT or UPDATE, then change the value of the Maximum Batch Size property, and click Apply Changes. Finally, reopen the processor's configuration, change the Statement Type back to DELETE, and click Apply Changes.
-
Configure the LogAttribute processor
Finally, configure the LogAttribute processor by specifying the Attributes that you would like to log or ignore, as well as the log level, based on your use case.
INSERT operation
Configure the PutDatabaseRecord processor similar to the following in order to perform Batch INSERT Operations:

UPDATE Operation
Configure the PutDatabaseRecord processor similar to the following in order to perform Batch UPDATE Operations:
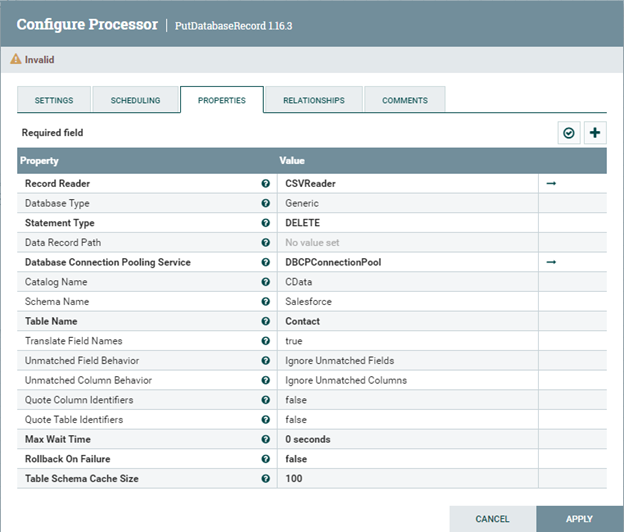
DELETE Operation
Configure the PutDatabaseRecord processor similar to the following in order to perform Batch DELETE Operations:
Free Trial & More Information
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for Workday and start working with your live Workday data in Apache NiFi. Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.







