Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →How to update XML from Excel
This article explains how to transfer data from Excel to XML using the Excel Add-In for XML.
The CData Excel Add-In for XML enables you to edit and save XML data directly from Excel. This article explains how to transfer data from Excel to XML. This technique is useful if you want to work on XML data in Excel and update changes, or if you have a whole spreadsheet you want to import into XML. In this example, you will use the people table; however, the same process will work for any table that can be retrieved by the CData Excel Add-In.
Establish a Connection
If you have not already done so, create a new XML connection by clicking From XML on the ribbon.
See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation to authenticate to your data source: The data provider models XML APIs as bidirectional database tables and XML files as read-only views (local files, files stored on popular cloud services, and FTP servers). The major authentication schemes are supported, including HTTP Basic, Digest, NTLM, OAuth, and FTP. See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation for authentication guides.
After setting the URI and providing any authentication values, set DataModel to more closely match the data representation to the structure of your data.
The DataModel property is the controlling property over how your data is represented into tables and toggles the following basic configurations.
- Document (default): Model a top-level, document view of your XML data. The data provider returns nested elements as aggregates of data.
- FlattenedDocuments: Implicitly join nested documents and their parents into a single table.
- Relational: Return individual, related tables from hierarchical data. The tables contain a primary key and a foreign key that links to the parent document.
See the Modeling XML Data chapter for more information on configuring the relational representation. You will also find the sample data used in the following examples. The data includes entries for people, the cars they own, and various maintenance services performed on those cars.
Retrieve Data from XML
To insert data into XML, you will first need to retrieve data from the XML table you want to add to. This links the Excel spreadsheet to the XML table selected: After you retrieve data, any changes you make to the data are highlighted in red.
- Click the From XML button on the CData ribbon. The Data Selection wizard is displayed.
- In the Table or View menu, select the people table.
- In the Maximum Rows menu, select the number of rows you want to retrieve. If you want to insert rows, you need to retrieve only one row. The Query box will then display the SQL query that corresponds to your request.
- In the Sheet Name box, enter the name for the sheet that will be populated. By default the add-in will create a new sheet with the name of the table.
Insert Rows to XML
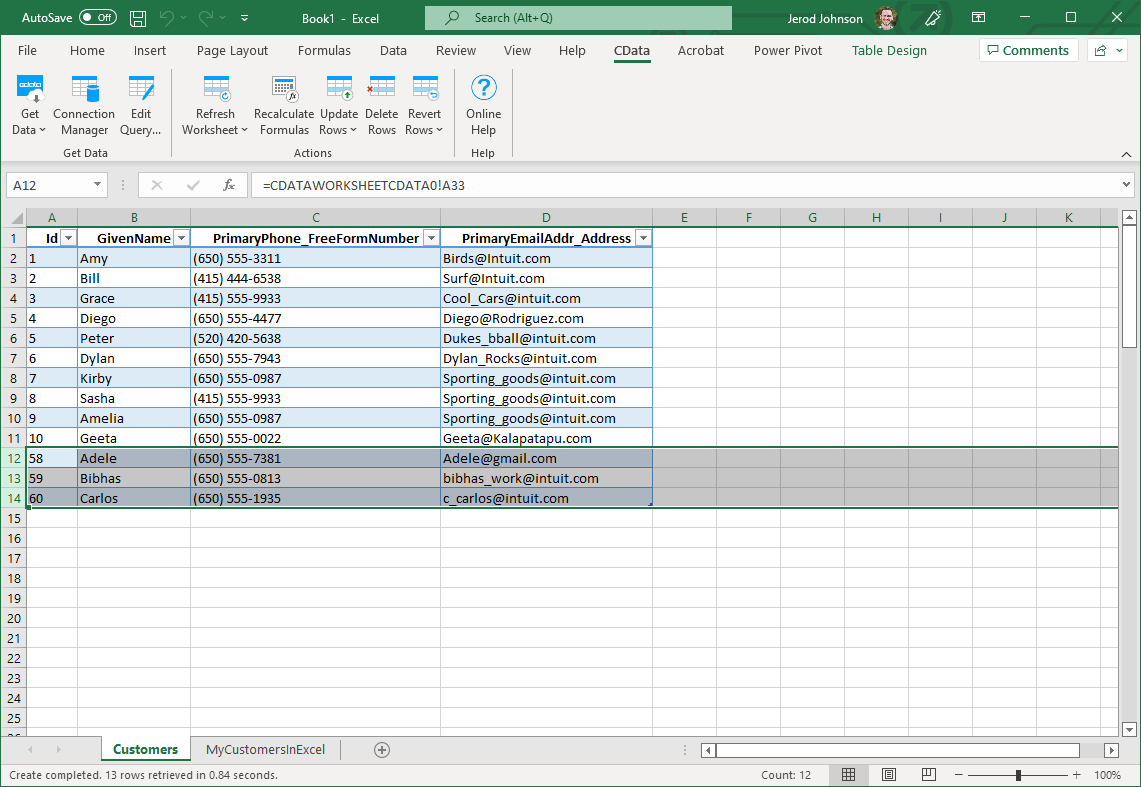
After retrieving data, you can add data from an existing spreadsheet in Excel.
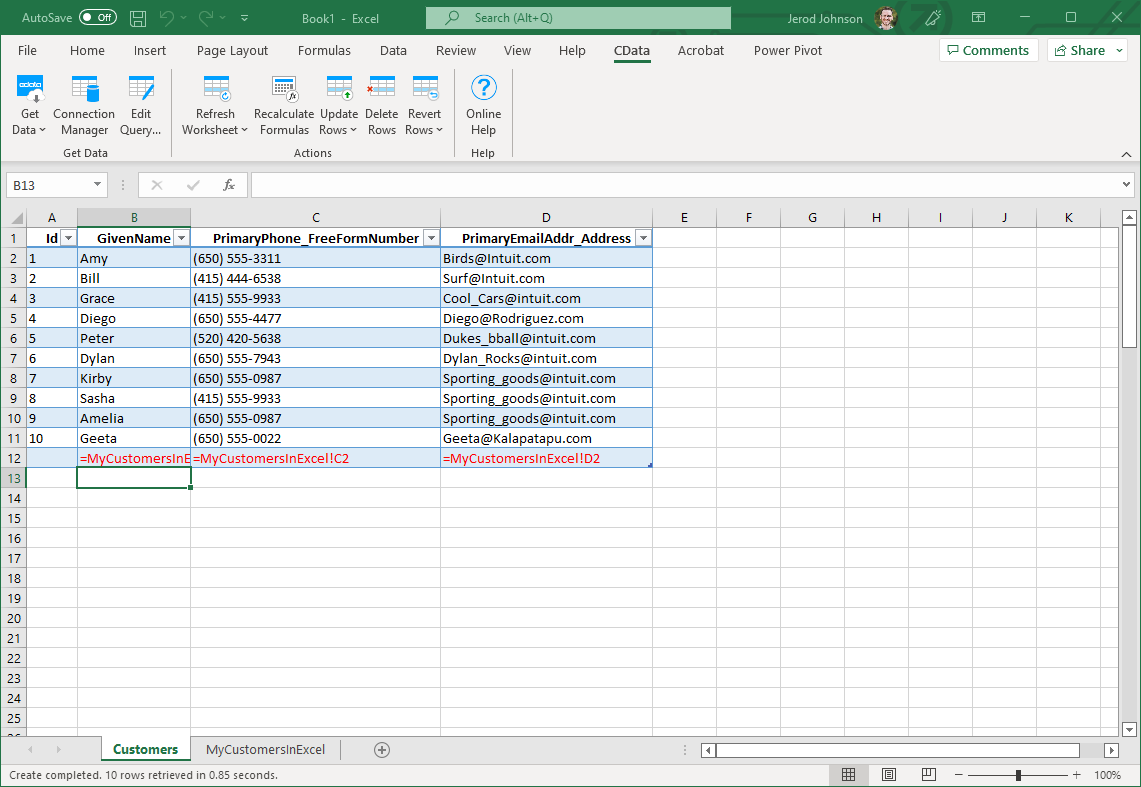
- In a cell after the last row, enter a formula referencing the corresponding cell from the other spreadsheet; for example, =MypeopleSheetInExcel!A1.
![A local copy of a table. One row will be inserted. (QuickBooks is shown.)]()
- After using a formula to reference the cells you want to add to XML, select the cells that you are inserting data into and drag the formula down as far as needed. The referenced values you want to add will be displayed on
the people sheet.
![The range of changes to update. (QuickBooks is shown.)]()
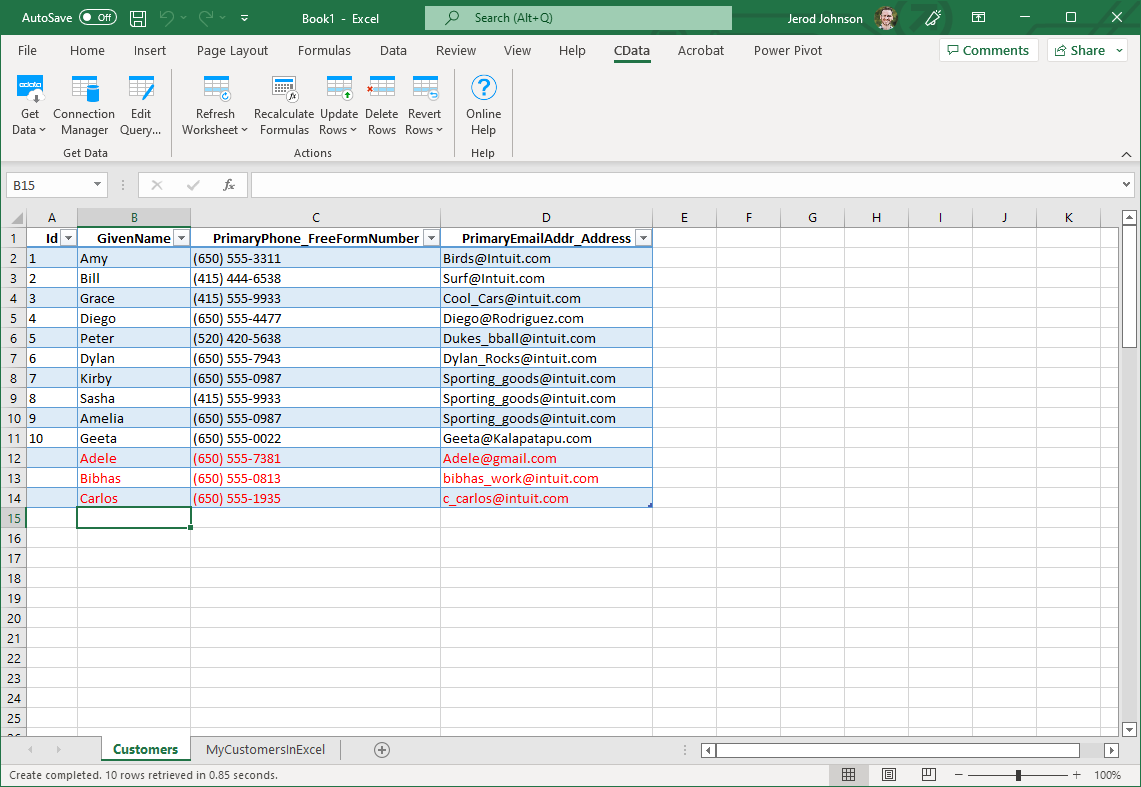
- Highlight the rows you want to insert and click the Update Rows button.
As each row is inserted, the Id value will appear in the Id column and the row's text will change to black, indicating that the record has been inserted.