Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Connect to MongoDB Data in Aqua Data Studio
Access MongoDB data from tools in Aqua Data Studio such as the Visual Query Builder and the Table Data Editor.
The CData JDBC Driver for MongoDB integrates MongoDB data with wizards and analytics in IDEs like Aqua Data Studio. This article shows how to connect to MongoDB data through the connection manager and execute queries.
About MongoDB Data Integration
Accessing and integrating live data from MongoDB has never been easier with CData. Customers rely on CData connectivity to:
- Access data from MongoDB 2.6 and above, ensuring broad usability across various MongoDB versions.
- Easily manage unstructured data thanks to flexible NoSQL (learn more here: Leading-Edge Drivers for NoSQL Integration).
- Leverage feature advantages over other NoSQL drivers and realize functional benefits when working with MongoDB data (learn more here: A Feature Comparison of Drivers for NoSQL).
MongoDB's flexibility means that it can be used as a transactional, operational, or analytical database. That means CData customers use our solutions to integrate their business data with MongoDB or integrate their MongoDB data with their data warehouse (or both). Customers also leverage our live connectivity options to analyze and report on MongoDB directly from their preferred tools, like Power BI and Tableau.
For more details on MongoDB use case and how CData enhances your MongoDB experience, check out our blog post: The Top 10 Real-World MongoDB Use Cases You Should Know in 2024.
Getting Started
Create a JDBC Data Source
You can use the connection manager to define connection properties and save them in a new JDBC data source. The MongoDB data source can then be accessed from Aqua Data Studio tools.
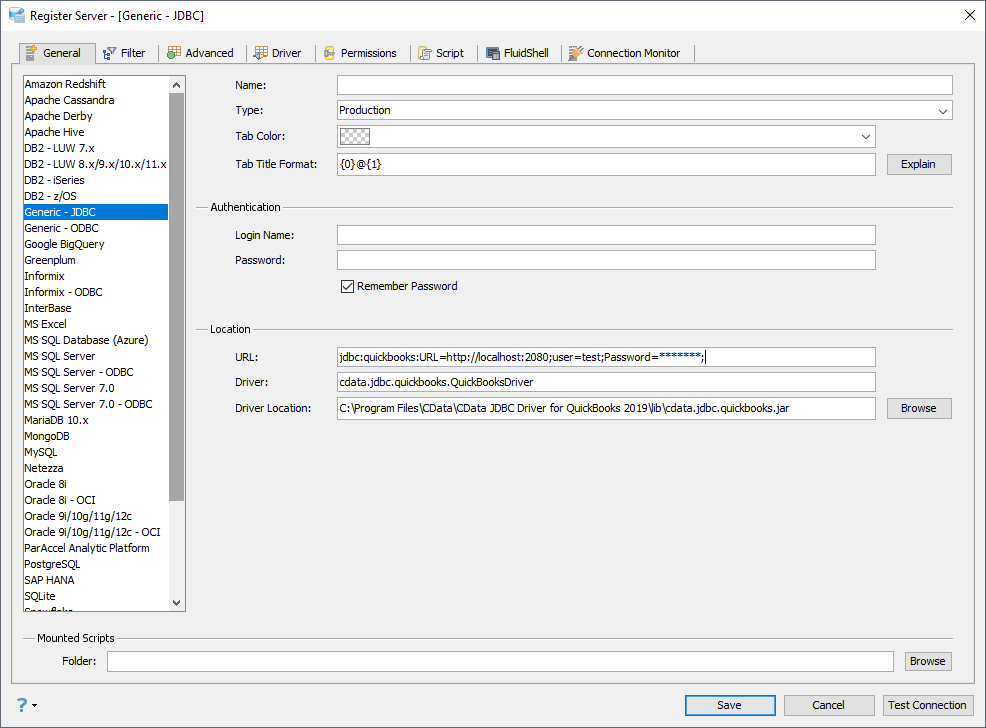
- In Aqua Data Studio, select Register Server from the Servers menu.
- In the Register Server form, select the 'Generic - JDBC' connection.
- Enter the following JDBC connection properties:
- Name: Enter a name for the data source; for example, MongoDB.
- Driver Location: Click the Browse button and select the cdata.jdbc.mongodb.jar file, located in the lib subfolder of the installation directory.
- Driver: Enter the Driver's class name, cdata.jdbc.mongodb.MongoDBDriver.
URL: Enter the JDBC URL, which starts with jdbc:mongodb: and is followed by a semicolon-separated list of connection properties.
Set the Server, Database, User, and Password connection properties to connect to MongoDB. To access MongoDB collections as tables you can use automatic schema discovery or write your own schema definitions. Schemas are defined in .rsd files, which have a simple format. You can also execute free-form queries that are not tied to the schema.
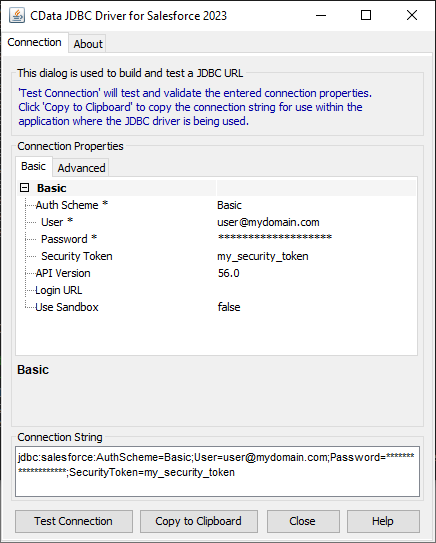
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the MongoDB JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.mongodb.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]() A typical JDBC URL is below:
A typical JDBC URL is below:jdbc:mongodb:Server=MyServer;Port=27017;Database=test;User=test;Password=Password;
![The JDBC data source, defined by the JAR path, driver class, and JDBC URL. (QuickBooks is shown.)]()
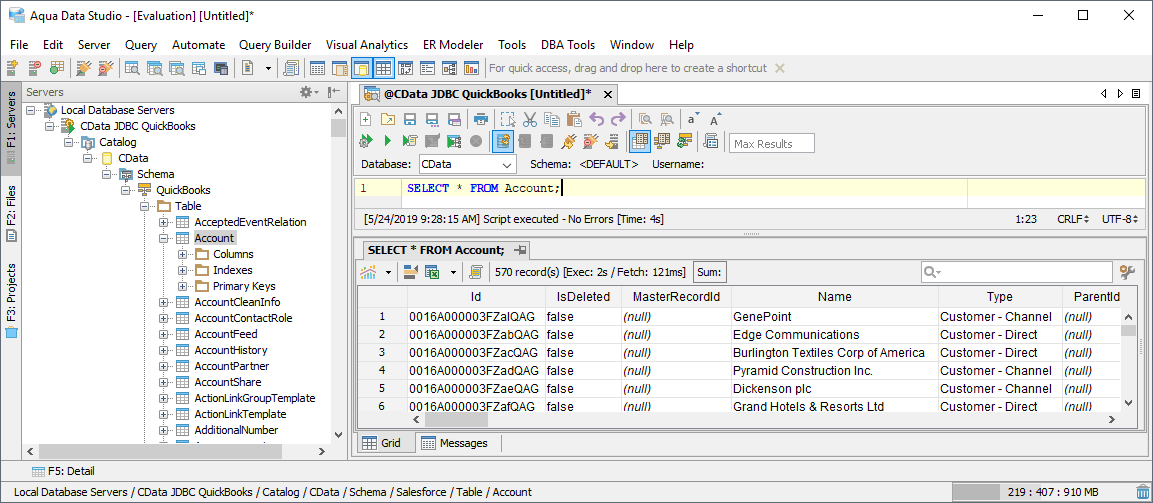
Query MongoDB Data
You can now query the tables exposed.

 A typical JDBC URL is below:
A typical JDBC URL is below: